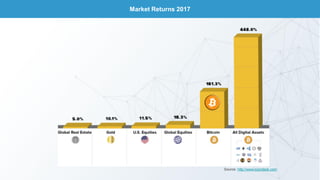
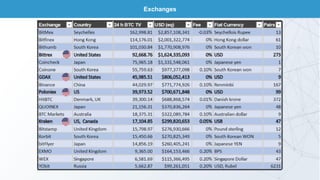
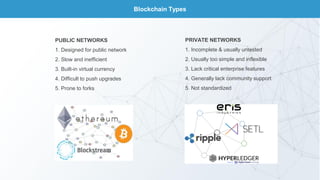
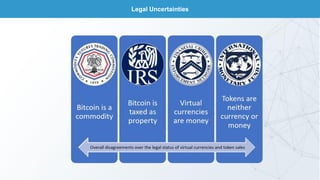
This document discusses blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. It provides an overview of investing in blockchain and crypto assets, as well as the current fintech landscape. It also examines the potential disruption of blockchain, popular initial coin offerings (ICOs) in 2017, cryptocurrency exchanges, basic blockchain economics, and legal uncertainties around blockchain. It explores concepts like decentralized autonomous organizations, and the potential end of fiat currency.