1) This document discusses the names and formulas of ionic compounds. It defines key terms like monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, and oxyanions.
2) Ionic compounds are made up of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. Monatomic ions contain a single atom while polyatomic ions contain multiple atoms.
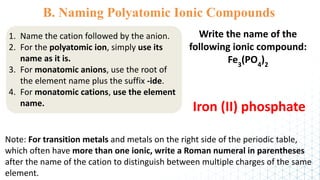
3) The document provides rules for writing formulas and naming ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions. The cation is written first followed by the anion and charges are balanced to give the overall formula unit a net neutral charge.