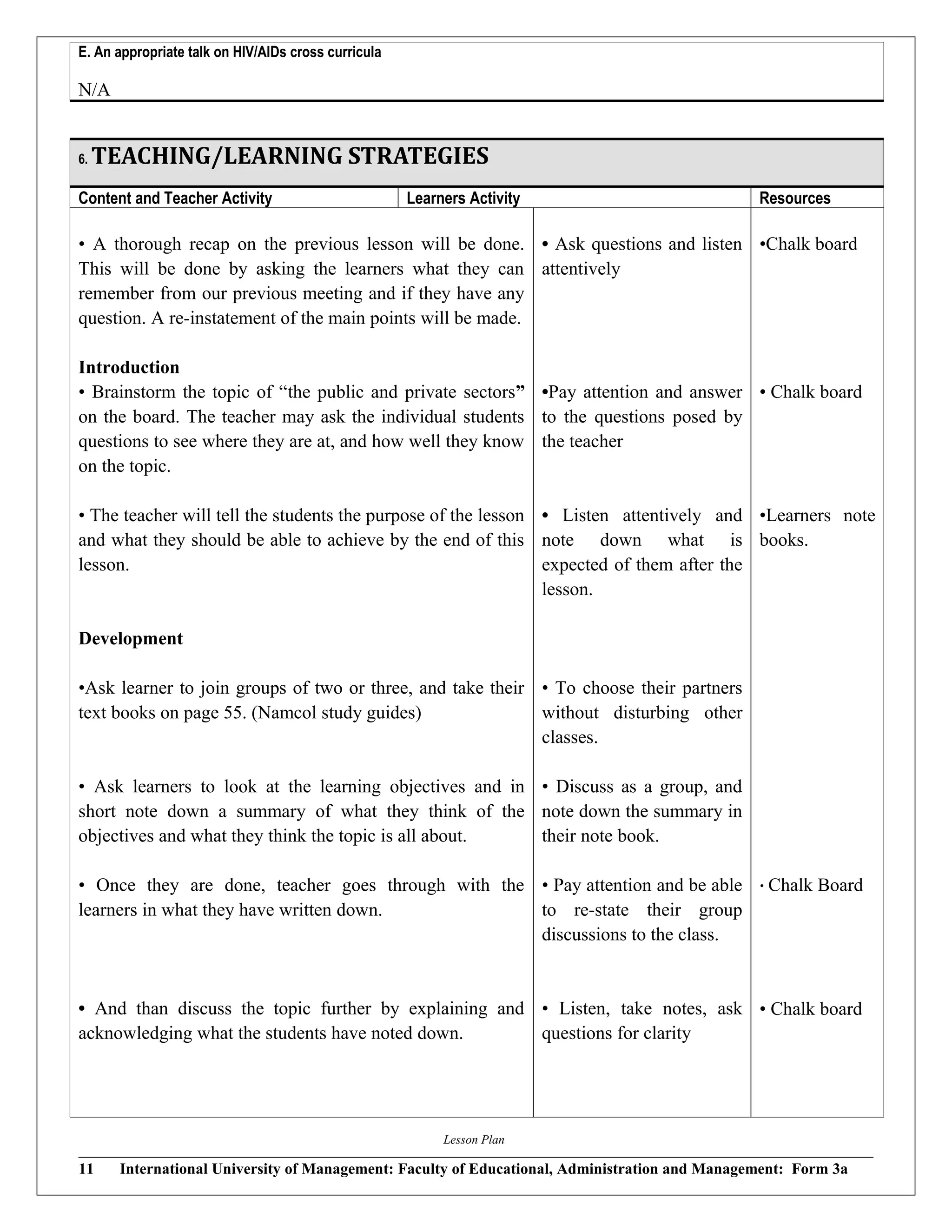
The document contains lesson plans and teaching materials for economics and business studies. For economics, the lesson plan covers trade unions, defining what they are, their aims, and the types of trade unions in Namibia. The teaching materials provide notes on trade unions, defining them as workers' organizations that represent workers in dealings with management. It also lists the aims of trade unions such as protecting members against unfair dismissal, representing members in wage negotiations, and ensuring compensation for work injuries. For business studies, the lesson plan covers the public and private sectors, and nationalization vs. privatization. The teaching materials provide summaries of the public and private sectors and their differences, along with reasons for and advantages/disadvantages of nationalization and







![Assesment Task for Economics
Name: _________________________ Grade 12_
Class Activity Date: _________________
1. What is a trade union?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________[2]
2. Write a summary of not longer than five sentences identifying the aims of trade unions.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________[6]
3. Name by describing at least three different types of trade unions in Namibia, also give an example
to each.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________[12]
4. List any four advantages of joining a trade union.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________[4]
[Total 24]
Lesson Plan
8 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-8-2048.jpg)
![Marking Rubric for Economics
Name:_________________________ Grade 12_
Class Activity Date:_________________
1. What is a trade union?
Is a worker’s organisation which represents workers in their dealings with the management and owners of
a firm. [2marks]
2. Write a summary of not longer than five sentences identifying the aims of trade unions.
To protect their members against unfair dismissals at work.
To represent their members at wage negotiations.
To ensure that members get compensated for injuries at work
To ensure that members receive market related salaries and fringe benefits
To advise and encourage government to strive towards democracy, freedom and justice for all
To provide members with legal and financial advice. [1 mark for each]
3. Name by describing at least three different types of trade unions in Namibia; also give an
example to each.
Craft Union [1 mark]
This type of unions restrict their membership to skilled workers who have undergone lengthy, specialised
technical training and who possess technical skills such as plumbers, electricians, carpenters, boilermaker
etc. traditionally, this trade unions are joined by members that have undergone a recognised
apprenticeship. [2 marks]
E.g. Namibia Building Workers Union (NABWU). [1 mark]
General Union [1 mark]
This is a union that represent unskilled and semi-skilled workers from trade and industries. [2 marks]
E.g. Namibian Domestic and Allied Workers Union (NDAWU). [1 mark]
Industrial Union [1 mark]
These are trade unions that represent all workers in many different trades and industries regardless of their
skill or type of work. E.g. all workers who form a trade union in the clothing industry, mining, railways,
motor car manufacturing, etc. will form an industrial union. [2 marks]
E.g. Mineworkers Union of Namibia (MUN). [1 mark]
White Collar Unions [1 mark]
These unions include general office workers, working in banking and insurance sectors as well as those in
management and professional occupations such as lawyers, teachers, etc. [2 marks]
E.g. Namibian Public Workers Unions (NAPWU), Namibian National Teachers Union (NANTU), etc. [1
mark]
[any three makes 12 marks]
4. List any four advantages of joining a trade union.
The rights of members are protected
Additional benefits, such as counselling
Some unions give loans to members at reasonable interest rates.
Negotiate better working conditions, like more holidays or improved health and safety
Some provide training for new skills
Trade unions give general advice and support. [1 mark for any four]
Lesson Plan
9 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-9-2048.jpg)




![Assessment Task for Business Studies
Name: _________________________ Grade 12__
Class Test 01 Date: _________________
1. Distinguish between Nationalisation and privatization. [4]
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
2. Why is business activities like broadcasting corporations owned and run by the state? [4]
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3. What are the advantages of privatization? [4]
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
4. Explain with examples what is meant by a private and public sector business. [6]
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Lesson Plan
15 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-15-2048.jpg)
![_________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
[Total 18]
Lesson Plan
16 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-16-2048.jpg)
![Marking Rubric for Business Studies
1. Distinguish between Nationalisation and privatization. [4]
Nationalisation, is the process by which the state or government takes over the ownership and control of
businesses from the private sector. [2 marks]
Privatisation is the process of transferring ownership of businesses from the state to the private sector. [2
marks]
2. Why is business activities like broadcasting corporations owned and run by the state? [4]
• To provide services to the public in all areas of the country.
• To keep people in jobs so that unemployment does not rise.
• To keep prices low so that everybody can afford the services.
•To break even, the point of sales where there is no profit neither a loss. [1 mark for each]
3. What are the advantages of privatization? [4]
• New owners who have a profit as a main aim in mind might run the business more efficiently
• It raises money for the government because it has to pay tax
• Competition increases, which will keep prices low and encourage efficiency
• New owners may have more capital to invest, and it may improve the service they offer.
• There is no politics involved as in the case where the government owns it and decisions are only for business
[1 mark for each]
4. Explain with examples what is meant by a private and public sector business. [6]
• The Public Sector business are usually organizations that are owned and operated by the government and exist
Lesson Plan
17 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-17-2048.jpg)
![to provide services for its citizens, organizations in the public sector do not seek to generate a profit. [2 marks]
• Example is Nampower, Namcor and Transnamib. The Katutura state hospital, as well as Jan Mor SSS. [1
mark]
• The private sector business are businesses that are not state controlled and are run by individuals and
companies for profit. [2 marks] • E.g. Shoprite, Pupkewitz Holdings; Game; Pep stores [1 mark]
Lesson Plan
18 International University of Management: Faculty of Educational, Administration and Management: Form 3a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lessonplantemplatetem80py-180523111537/75/Lesson-plan-template-Economics-grade-12-18-2048.jpg)

