Good language learners employ a variety of strategies from the six categories to maximize their learning. They:
- Use memorization strategies like imagery and recitation to remember vocabulary and concepts (direct strategies).
- Apply cognitive strategies like summarizing, guessing meaning from context, and drilling to understand and practice the language (direct strategies).
- Draw from compensation strategies such as circumlocution and gestures to communicate when gaps in knowledge exist (direct strategies).
- Employ metacognitive strategies like planning, monitoring, and evaluating their own learning process (indirect strategies).
- Regulate their emotions, attitudes and motivation through affective strategies (indirect strategies).
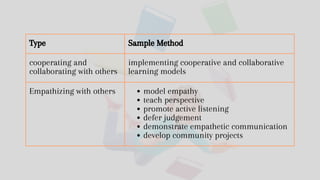
- Seek opportunities for practice and collaboration through social strategies (indirect