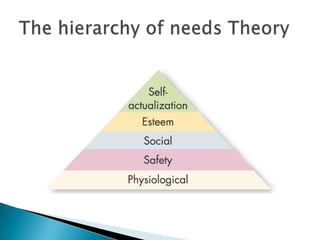
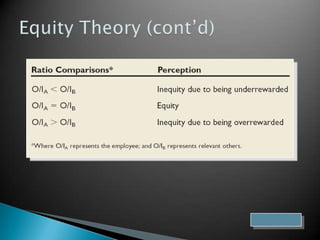
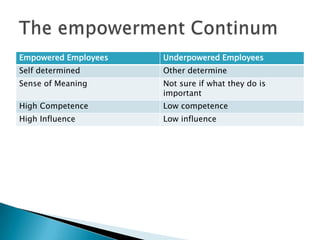
Leadership behavior influences follower satisfaction and organizational citizenship. Satisfied followers engage in behaviors that accomplish common goals. Motivation theories examine individual differences and cognitive processes that influence performance. Approaches like empowerment, operant conditioning, and situational factors also impact motivation. Leaders can increase follower satisfaction and motivation by giving meaningful work, treating people fairly, and ensuring just reward and disciplinary systems.