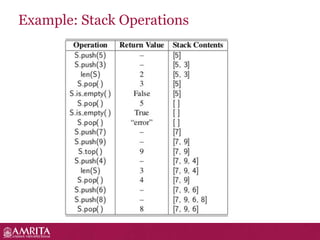
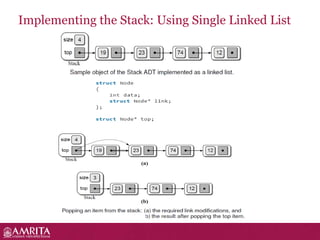
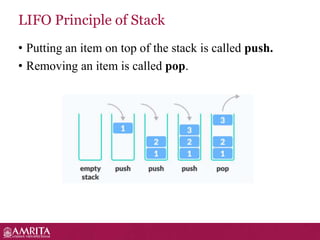
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (last-in, first-out) principle for adding and removing items. It allows push and pop operations at one end called the top. Common stack operations include push to add an item to the top, pop to remove the top item, peek to view the top item without removing it, and functions to check if the stack is empty or full. Stacks have applications in expression evaluation, backtracking, recursion, undo/redo operations, and graph searches like depth-first search. Recursive functions work by calling themselves during execution and are useful for implementing stacks.

![• Int stk[10], top=-1
Void Push( stk[10], int n)
Int pop(stk[10])
Int peep(stk[10])
Bool isFull() // overflow
If(top>=n-1) //overflow
Bool isEmpty() //underflow
If(top<=-1) //underflow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-stackadt-221020062335-e524a099/85/Lecture-5-Stack-ADT-pptx-4-320.jpg)