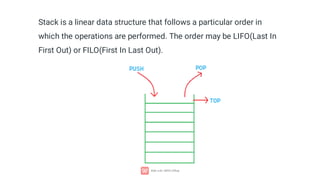
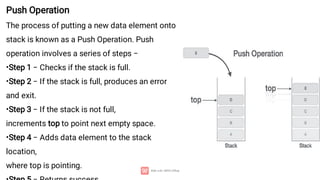
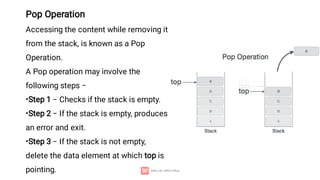
A stack is a linear data structure characterized by LIFO (Last In First Out) operation, supporting basic operations like push, pop, peek, isempty, and isfull, all with O(1) time complexity. Stacks are utilized in various applications such as undo-redo features, web navigation, algorithm implementations like backtracking, and memory management. They can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, with specific steps for push and pop operations to manage the data effectively.