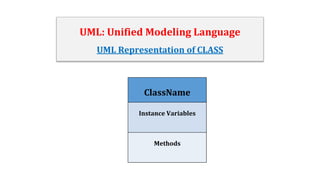
This document discusses classes and objects in Java. It defines a class as a blueprint for creating objects, with classes containing variables, methods, constructors and other elements. An object is an instance of a class. The document provides examples of creating Box and Person classes, with objects of each class being instantiated and their variable values displayed. It also shows how to represent a class in UML notation and provides an example of writing Java code based on a UML class diagram.








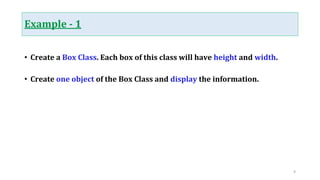
![Solution of Example - 1:
public class Box {
int height;
int width;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box box1 = new Box();
box1.height = 10;
box1.width = 20;
System.out.println("nHeight of box1 = " + box1.height);
System.out.println("Width of box1 = " + box1.width);
}
}
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-classandobject-230517165318-9dcca9b9/85/Lecture_4-Class-and-Object-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![UML representation of Class from Example - 1
Box
height: int
width: int
+ main(String[]) : void
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-classandobject-230517165318-9dcca9b9/85/Lecture_4-Class-and-Object-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![Example – 3: Write a Java code from this UML
Student
- name: String
- id: int
+ main(String[]) : void
14
• Create two objects of the Student Class, Set the values and display the information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-classandobject-230517165318-9dcca9b9/85/Lecture_4-Class-and-Object-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Solution of Example - 3:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int id;
private double cgpa;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student std1 = new Student();
std1.name = "Abdullah";
std1.id = 100;
std1.cgpa = 3.5;
System.out.println("Name of Student -1 : "+std1.name);
System.out.println("ID of Student - 1 : "+std1.id);
System.out.println("CGPA of Student - 1: "+std1.cgpa); 15
Student std2 = new Student();
std2.name = "Kabir";
std2.id = 200;
std2.cgpa = 3.8;
System.out.println("nnName of Student -1 : "+std2.name);
System.out.println("ID of Student - 1 : "+std2.id);
System.out.println("CGPA of Student - 1: "+std2.cgpa);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-classandobject-230517165318-9dcca9b9/85/Lecture_4-Class-and-Object-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Example – 4: Write a Java code from this UML
Department
- deptName: String
- deptCode: int
- faculty: String
+ main(String[]) : void
16
• Create two objects of the Department Class, Set the values and display the information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-classandobject-230517165318-9dcca9b9/85/Lecture_4-Class-and-Object-pptx-16-320.jpg)
