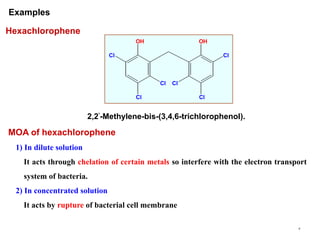
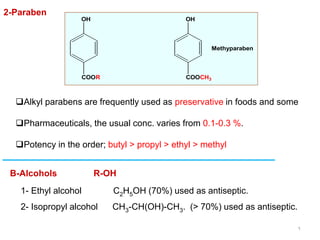
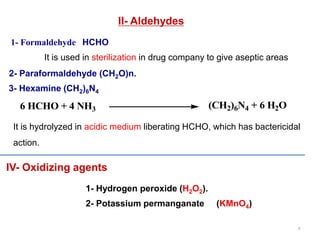
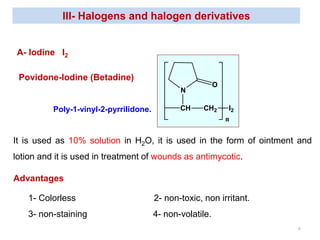
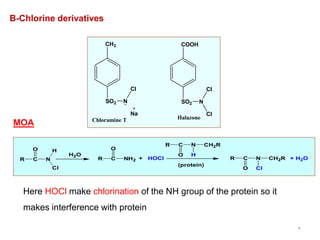
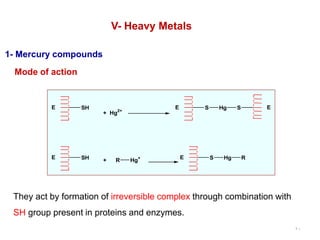
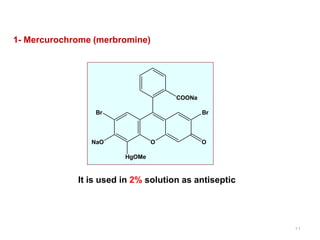
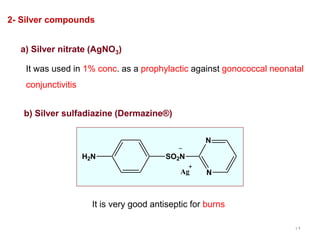
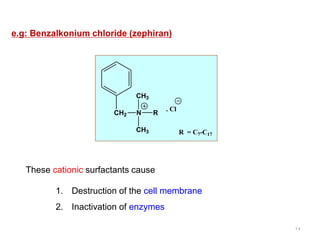
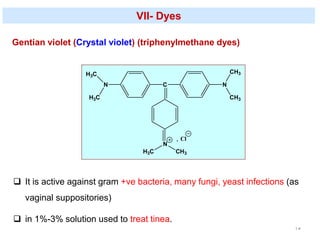
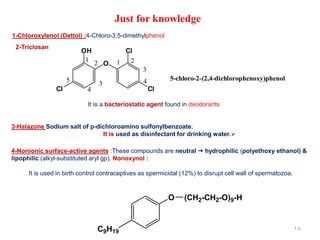
This document discusses various topical antimicrobial agents used for disinfection and antisepsis. It describes different classes of antimicrobials including alcohols, phenols, aldehydes, acids, heavy metals, halogens, quaternary ammonium compounds, dyes, and others. It provides examples such as iodine, chlorhexidine, hexachlorophene, and povidone-iodine. It also explains the mechanisms of action of these compounds, such as disrupting bacterial cell membranes and inhibiting enzymes through metal chelation.