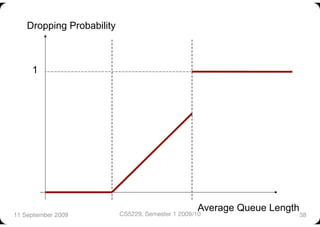
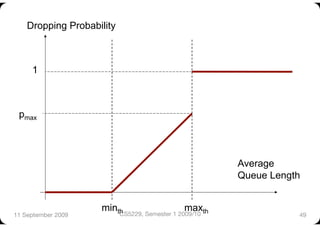
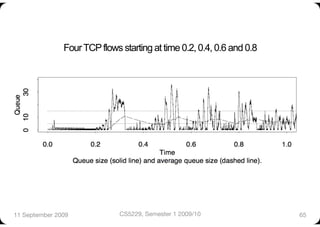
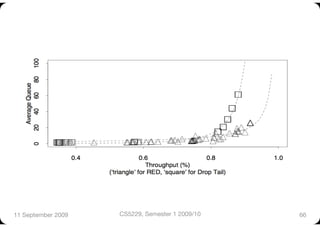
The document describes Random Early Detection (RED), a queue management algorithm used in routers. RED aims to avoid network congestion by randomly dropping some packets before the queue is full. This prevents synchronization between connections and biases less against bursty traffic. The key aspects of RED are calculating an exponentially weighted average queue size, determining a dropping probability based on the average, and dropping packets probabilistically when the average exceeds thresholds. Variations include Weighted RED which accounts for packet size. RED improves over Drop Tail by increasing throughput and controlling delays.