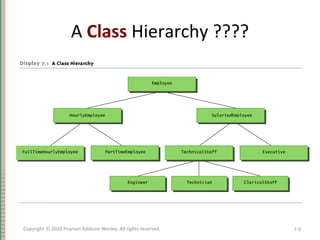
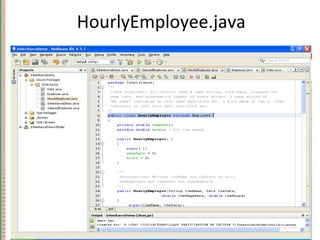
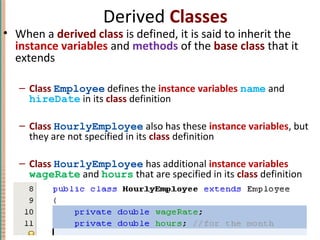
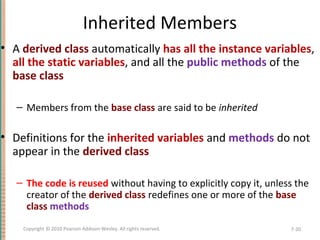
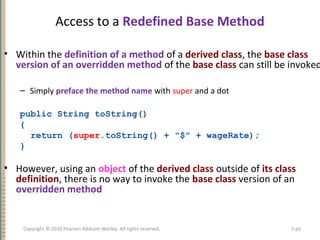
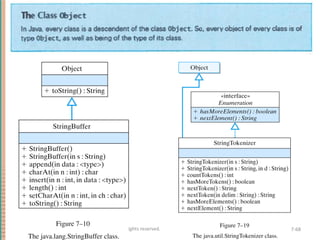
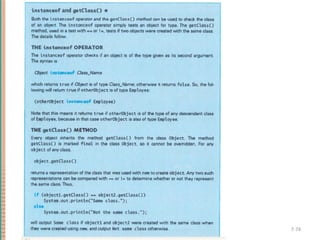
This document discusses inheritance in object-oriented programming and Java. It introduces inheritance as a technique where a derived class inherits attributes and behaviors from a base class. A derived class automatically has all instance variables and methods of the base class. The document provides examples of how to define derived classes in Java that extend and override methods from a base class. It also discusses concepts like final classes that cannot be inherited from, and using the super constructor to initialize inherited attributes.