Embed presentation
Download to read offline




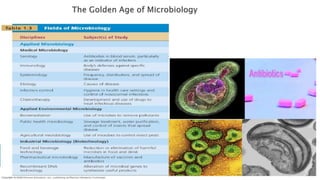

This document discusses the history and fields of microbiology. It describes Koch's early experiments that helped establish microbiology as a scientific discipline, including his use of staining techniques to visualize bacteria and development of methods to culture and study bacteria. The document also outlines key areas of microbiology including biochemistry, genetics, molecular biology, recombinant DNA technology, and gene therapy. It notes applications such as using microbes to study biochemical reactions, manipulating genes for practical uses like producing human blood clotting factors, and inserting genes to treat genetic diseases.







