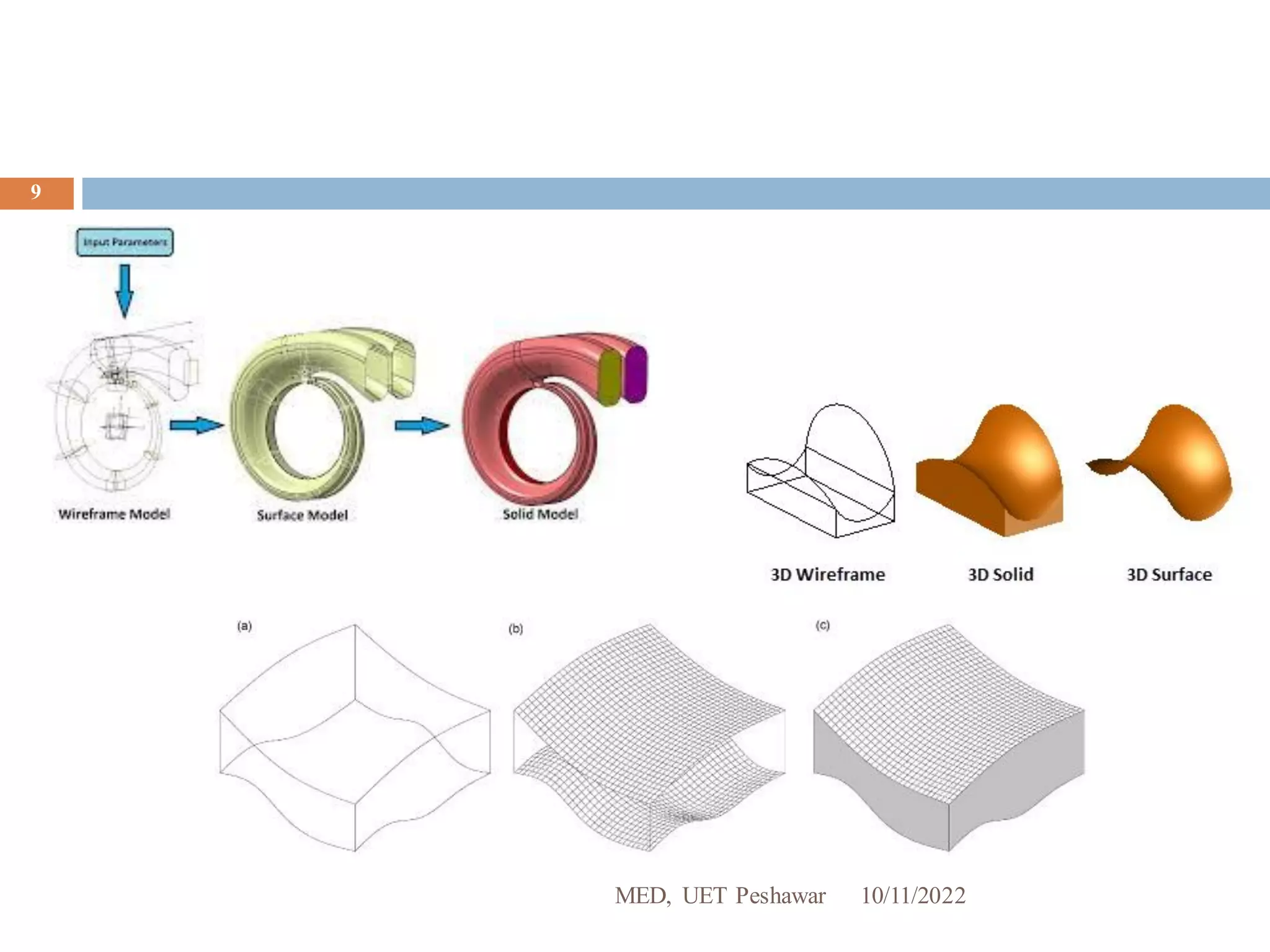
The document is a course outline for ME-213 CAD-I taught by Engr. Muhammad Arsalan Khan at UET Peshawar, detailing his academic background and role as a lecturer. It provides an overview of computer-aided design (CAD), including its history, types, and functionality, specifically highlighting AutoCAD's development and features. The document also covers the basic components, commands, and operations involved in using AutoCAD for design tasks.