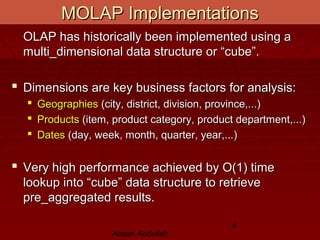
- MOLAP refers to multidimensional OLAP, which implements OLAP using a multi-dimensional data structure known as a cube. Dimensions typically include factors like time, geography, and products.
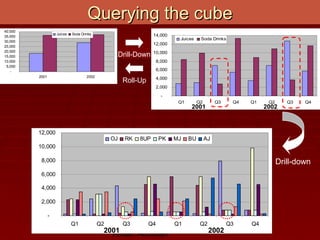
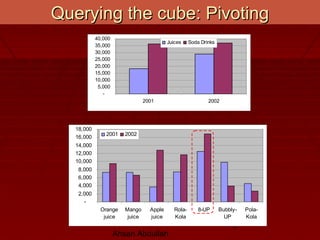
- Cubes allow for fast retrieval of pre-aggregated data in near-constant time. Vendors provide proprietary query languages for analyzing cubes through pivots, drills, rolls, and slices.
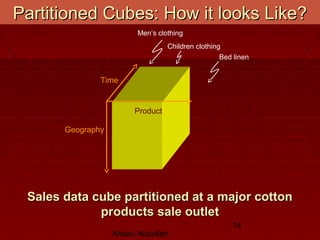
- While MOLAP provides fast response times, it faces challenges of long load times to pre-calculate aggregates, sparse cubes wasting storage, and significant maintenance to aggregate new data. Partitioning and virtual cubes help address some of these issues.