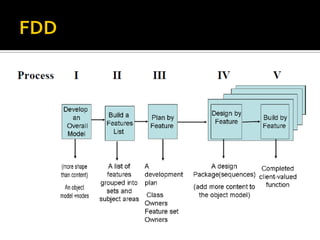
The document discusses principles of lean development and feature driven development (FDD). It outlines five principles of lean development: decide as late as possible, deliver as fast as possible, empower the team, build integrity in, and see the whole. It then provides examples to illustrate each principle. The document also provides an overview of FDD, outlining its activities of developing an overall model, building a feature list, planning by feature, designing by feature, and building by feature. It describes the develop overall model activity in more detail.