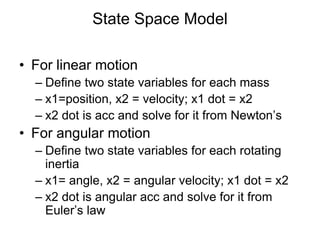
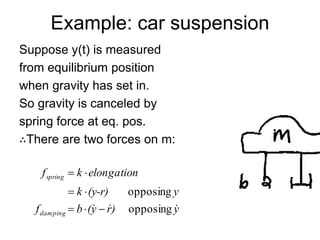
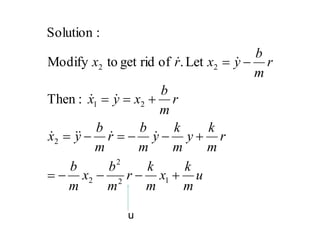
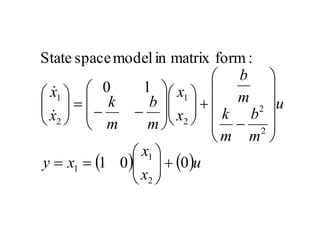
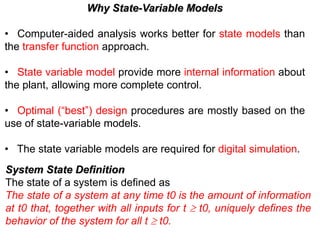
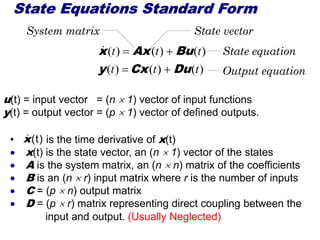
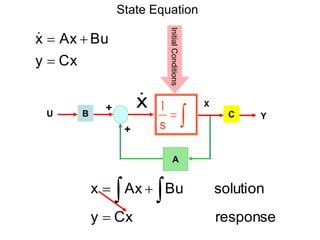
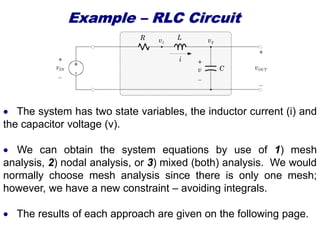
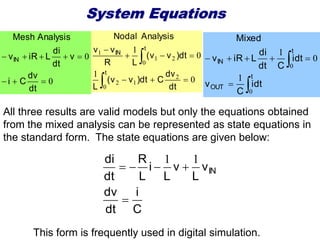
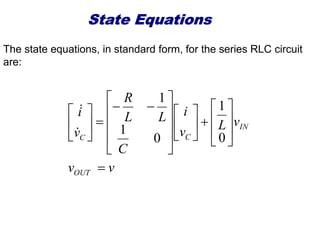
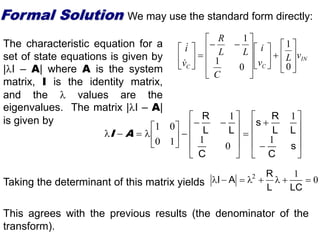
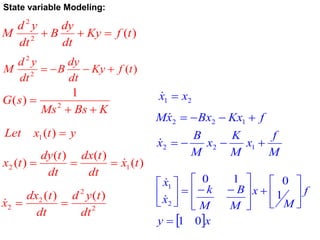
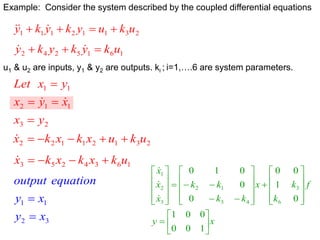
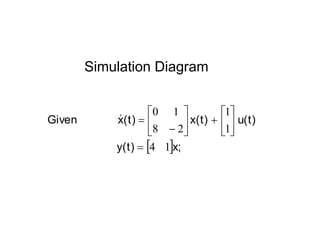
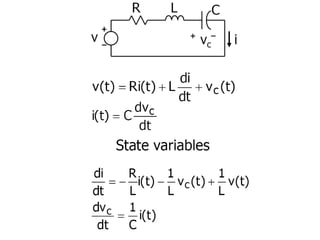
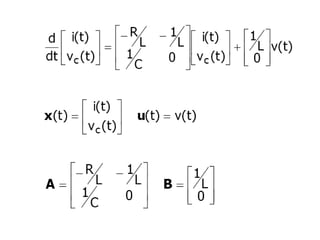
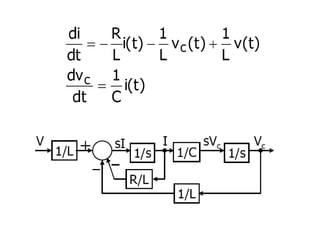
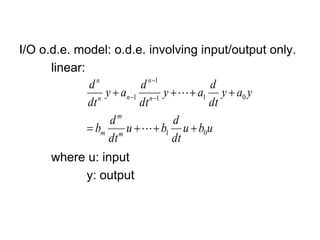
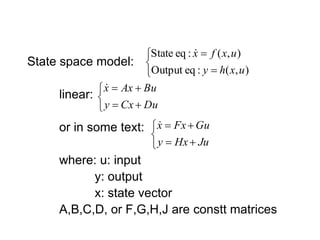
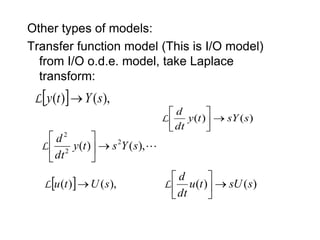
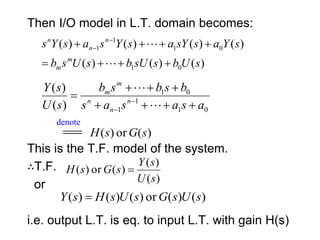
State variable models provide more internal information about a system compared to transfer function models, allowing for more complete control system design and analysis. The state of a system is defined as the minimum amount of information needed to uniquely determine the future behavior of the system given the inputs. State variable models are written in standard state space form with state, input, and output equations relating the state vector x, input vector u, and output vector y. An example RLC circuit is modeled using state space equations, and the solution is obtained using Laplace transforms.


![1
s 1
s
1
s
( )
u t
1
y
1
x
2
x
3
x
w w w w
0
a
1
a
2
a
0
b
1
b
2
b
1
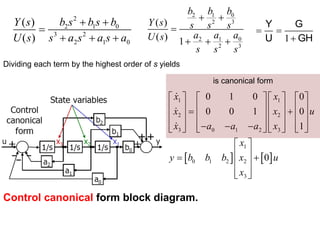
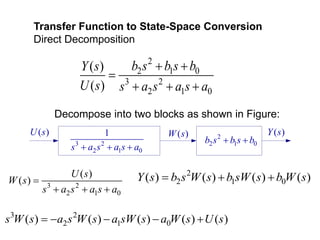
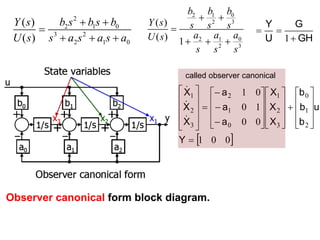
Signal flow graph similar to the Simulation diagram :
Control System Toolbox contains a set of functions for model
conversion:
G = tf(num, den)
[A, B, C, D] = tf2ss(num, den), [num, den] = ss2tf(A, B, C, D, 1)
Converts the system in transfer function form to state-space phase
variable control canonical form & vice versa
For list of all functions type help/control/control at MATLAB prompt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-21-320.jpg)
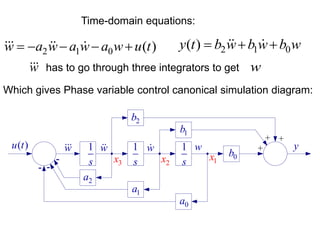
![Example:
For the following transfer function:
2
3 2
( ) 7 2
( )
( ) 9 26 24
Y s s s
G s
U s s s s
(a) Draw the simulation diagram and find the state-space
representation of the above transfer function.
(b) Use MATLAB Control System Toolbox
[A, B, C, D] = tf2ss(num, den) to find the state model.
Sol: a) Draw the transfer function block diagram in cascade form
3 2
1
9 26 24
s s s
2
7 2
s s
( )
Y s
( )
U s ( )
W s
From this we have:
3 2 2
( ) 9 ( ) 26 ( ) 24 ( ) ( ) & ( ) ( ) 7 ( ) 2 ( )
s W s s W s sW s W s U s Y s s W s sW s W s
or in time-domain 9 26 24 & y 7 2
w w w w u w w w
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-22-320.jpg)
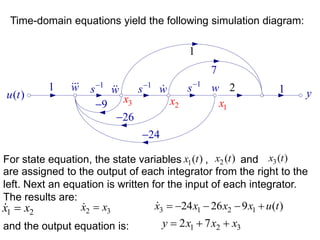
![Hence, in matrix form
1 1
2 2
3 3
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 ( )
24 26 9 1
x x
x x u t
x x
1
2
3
2 7 1
x
y x
x
(b) Re-write the following statements:
num = [1 7 2]; den = [1 9 26 24];
[A, B, C, D] = tf2ss(num, den)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-24-320.jpg)
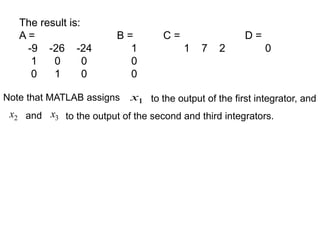
![2 1 0
2 2 3 2 3
3 2
2 1 0
2 3 2 3
2 8 6
( ) 2 8 6
8 26 6
( ) 8 26 6 1 1
b b b
C s s s s s s s s s
a a a
R s s s s
s s s s s s
The form is:
1 1
2 2
3 3
1
2
3
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0
6 26 8 1
6 8 2 [0] .
x x
x x r
x x
x
y x r
x
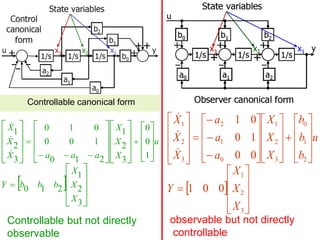
System controllable but not observable. Why?
Ans: State model is based on controllable canonical form, this
can be confirmed by another method later.
is controllable canonical form
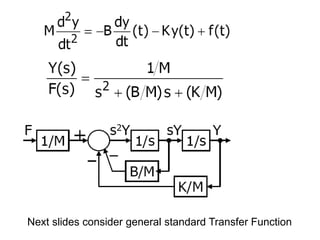
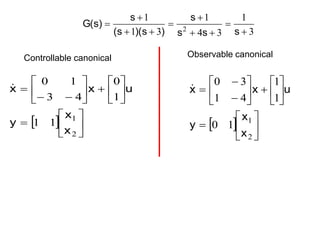
Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-26-320.jpg)
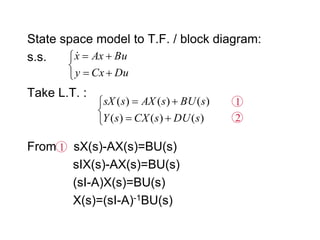
![into : Y(s)=C(sI-A)-1BU(s)+DU(s)
Y(s)=[C(sI-A)-1B+D] U(s)
G(s)= D+C(sI-A)-1B
is the T.F. from u to y
from
))
(
)
(
(
1
)
( s
BU
s
AX
s
s
X
2
1
1
s
u(s) +
+
x(s)
B C
A
+
+
D
y(s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-36-320.jpg)
![• In Matlab:
>> A=[0 1;-2 -3];
>> B=[0;1];
>> C=[1 3];
>> D=[0];
>> [n,d]=ss2tf(A,B,C,D)
n =
0 3.0000 1.0000
d =
1 3 2
>> n=[1 2 3];d=[1 4 5 6];
>> [A,B,C,D]=tf2ss(n,d)
A =
-4 -5 -6
1 0 0
0 1 0
B =
1
0
0
C =
1 2 3
D =
0
>> tf(n,d)
Transfer function:
s^2 + 2 s + 3
---------------------
s^3 + 4 s^2 + 5 s + 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec4statevariablemodels-240218064956-0a9352ef/85/Lec4-State-Variable-Models-are-used-for-modeing-39-320.jpg)