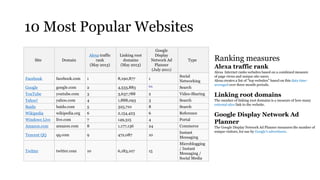
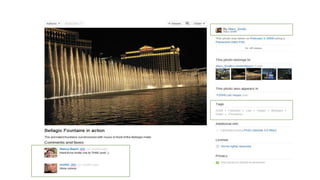
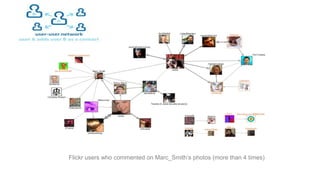
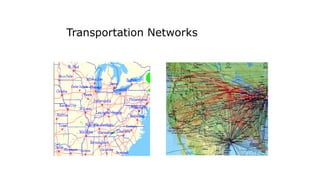
The document discusses 10 most popular websites based on traffic rankings from Alexa, linking domains, and Google Display Network Ad Planner from July 2011. Facebook is the most popular social networking site ranked #1 by Alexa traffic. Google is the #1 search engine and #2 most visited overall. YouTube is the #3 most visited site for video sharing. Social media encompasses activities that integrate technology, social interaction, and user-generated content like photos, videos and text. Social networking sites are very popular, with over 2/3 of internet users visiting them and 78% of people trusting recommendations from other consumers.