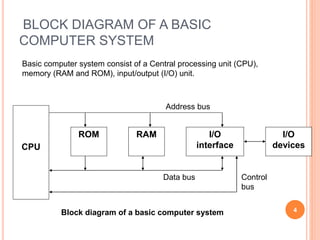
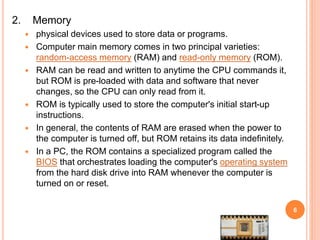
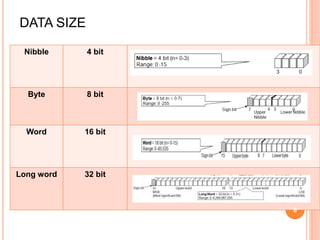
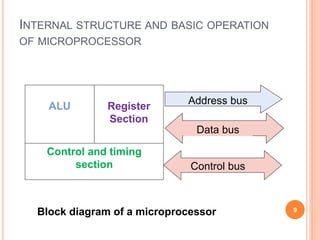
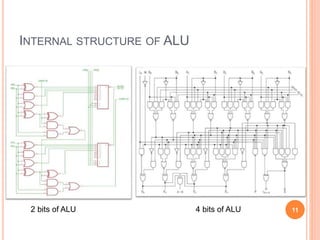
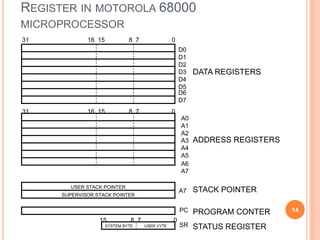
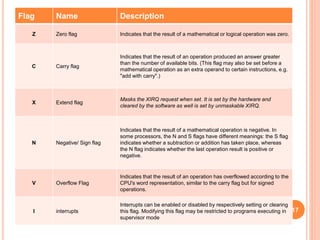
A computer system consists of a central processing unit (CPU), memory, and input/output devices connected via buses. The CPU contains an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) to perform calculations, registers to store data and instructions, a control unit to coordinate operations, and a program counter. The memory stores programs and data and comes in read-only (ROM) and random-access (RAM) varieties. Early microprocessors evolved from 4-bit to 64-bit designs and introduced features like accumulators, flags, and stack pointers. Common microprocessors include the Intel 8086 and Motorola 6800.