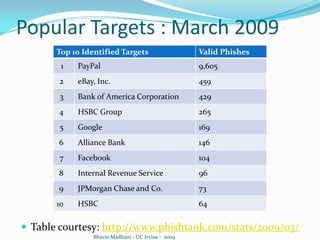
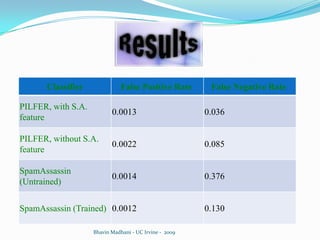
The document discusses a machine learning approach to detecting phishing emails. It presents the authors who developed a method called PILFER that uses email and webpage classification features to train a random forest classifier to detect phishing emails. The method is empirically evaluated on two datasets and achieves high accuracy in detecting phishing emails while minimizing false positives and negatives. The challenges of evolving phishing techniques and unavailable web domains are also discussed.