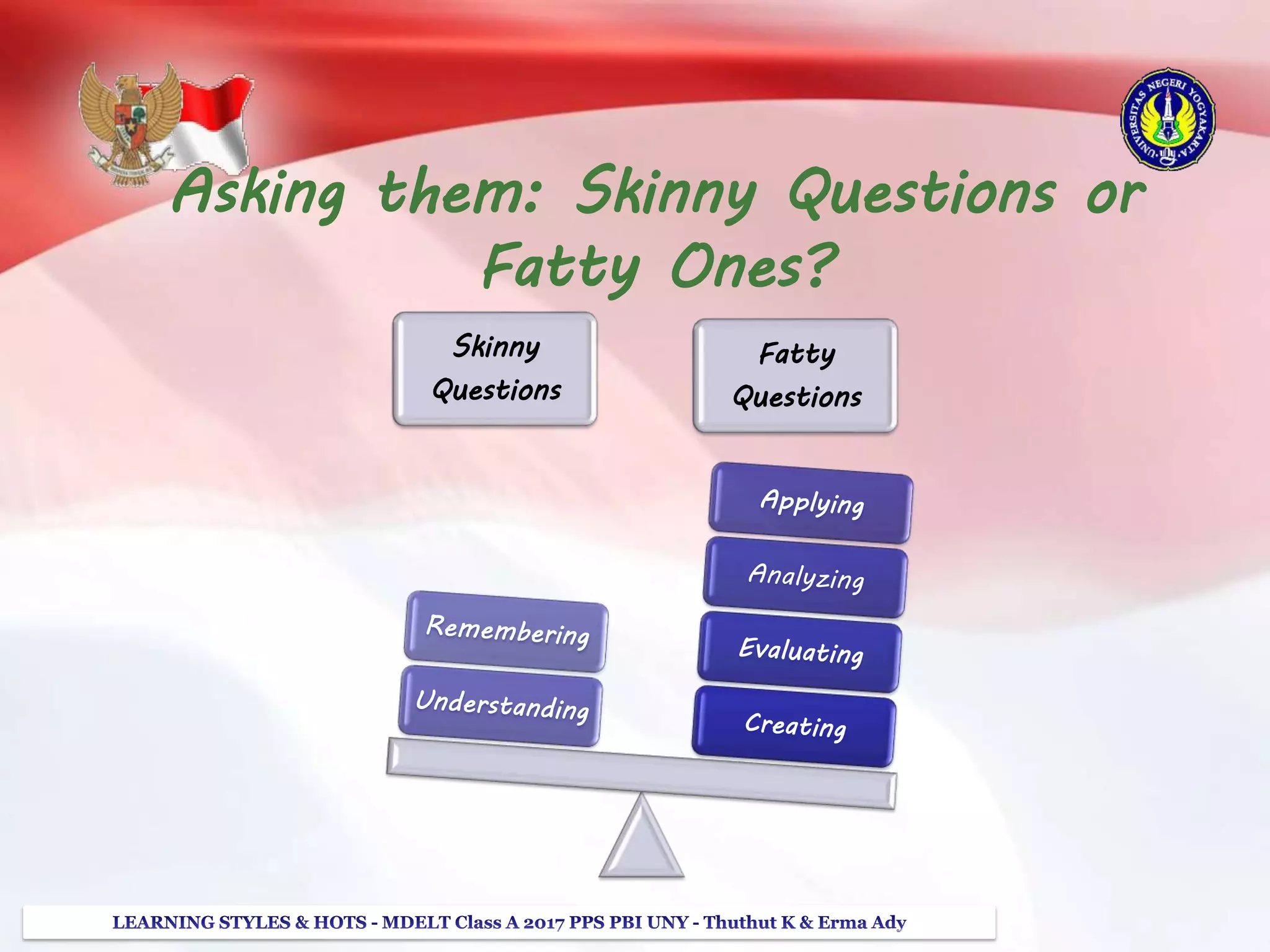
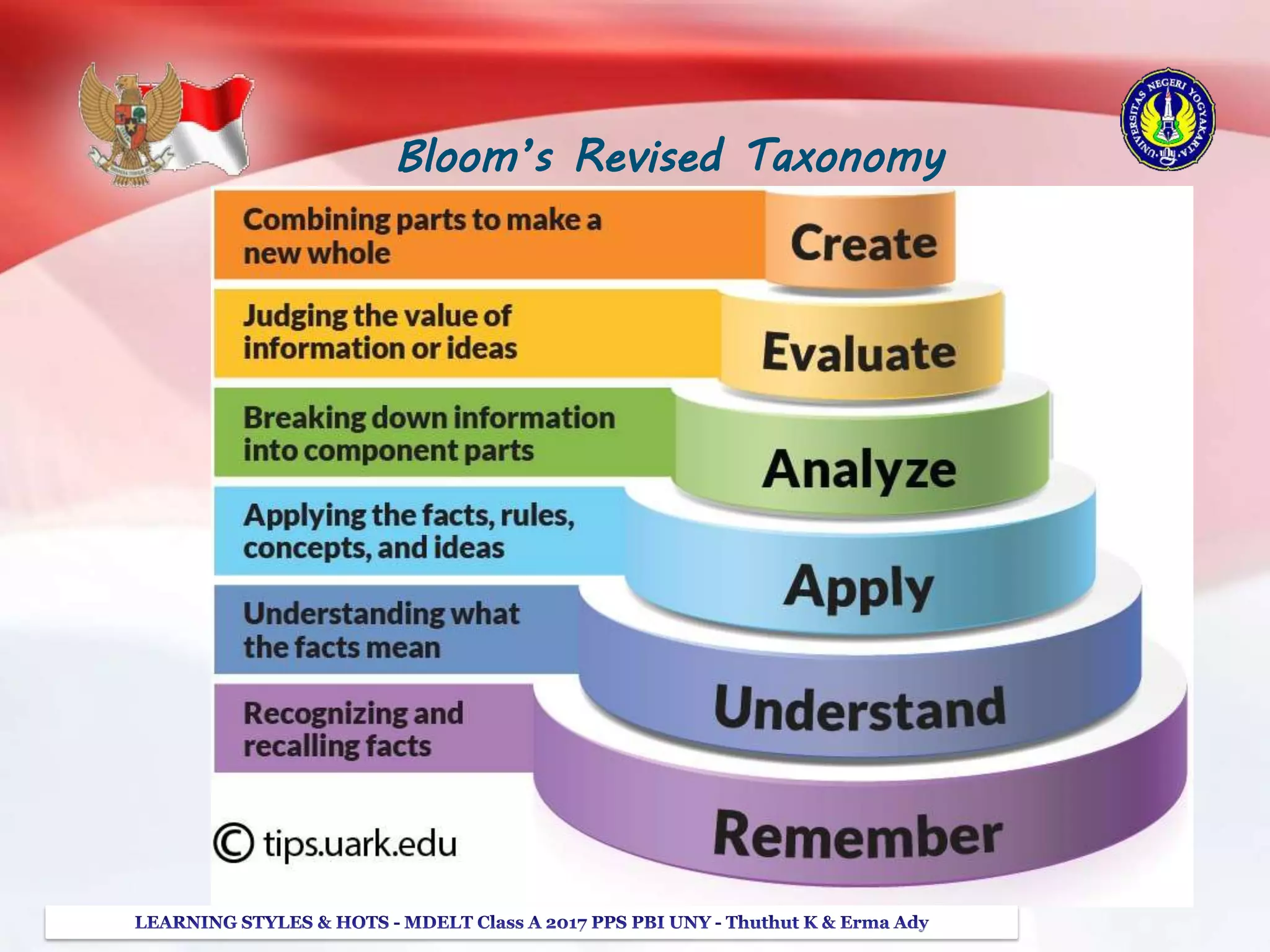
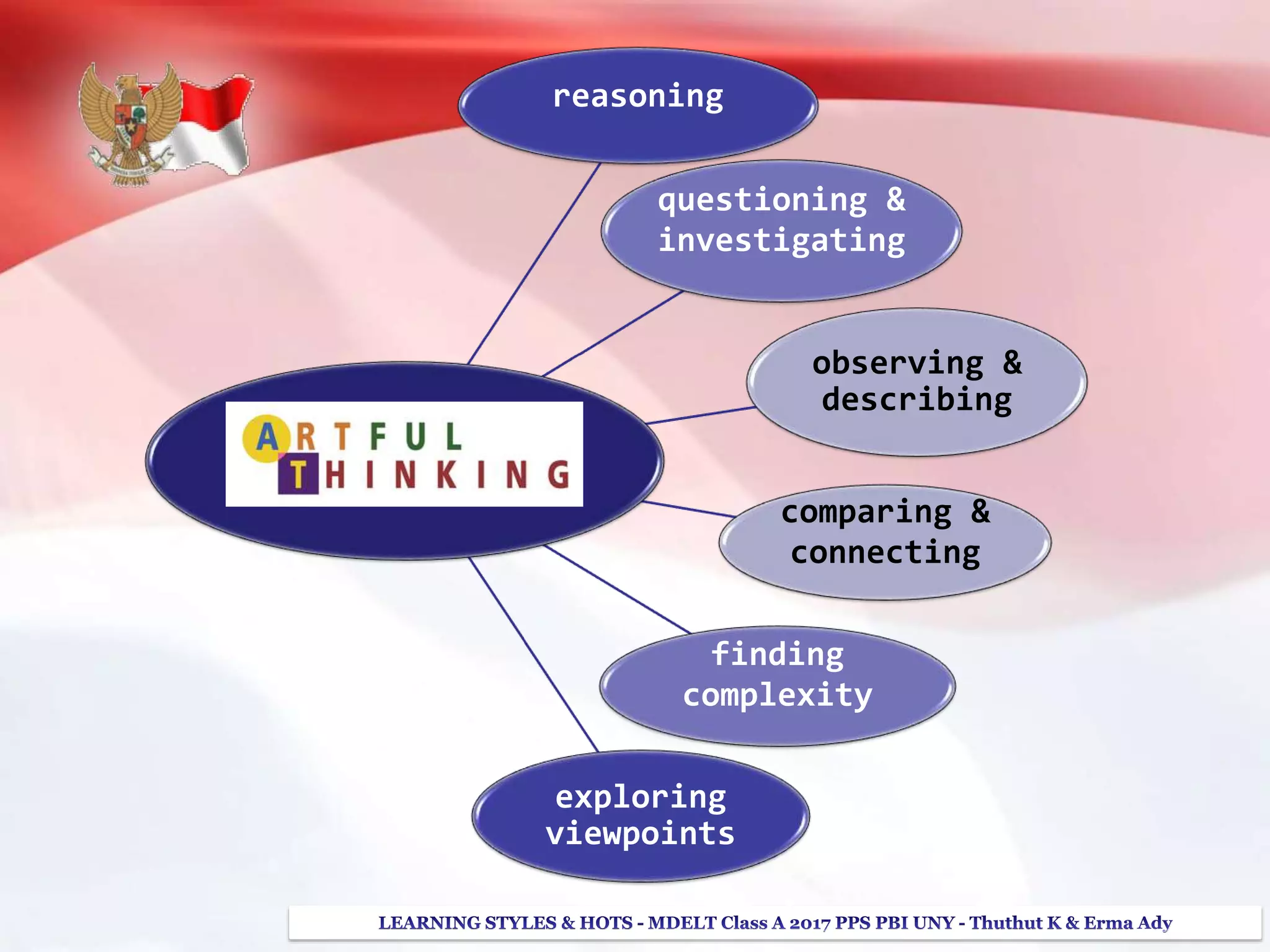
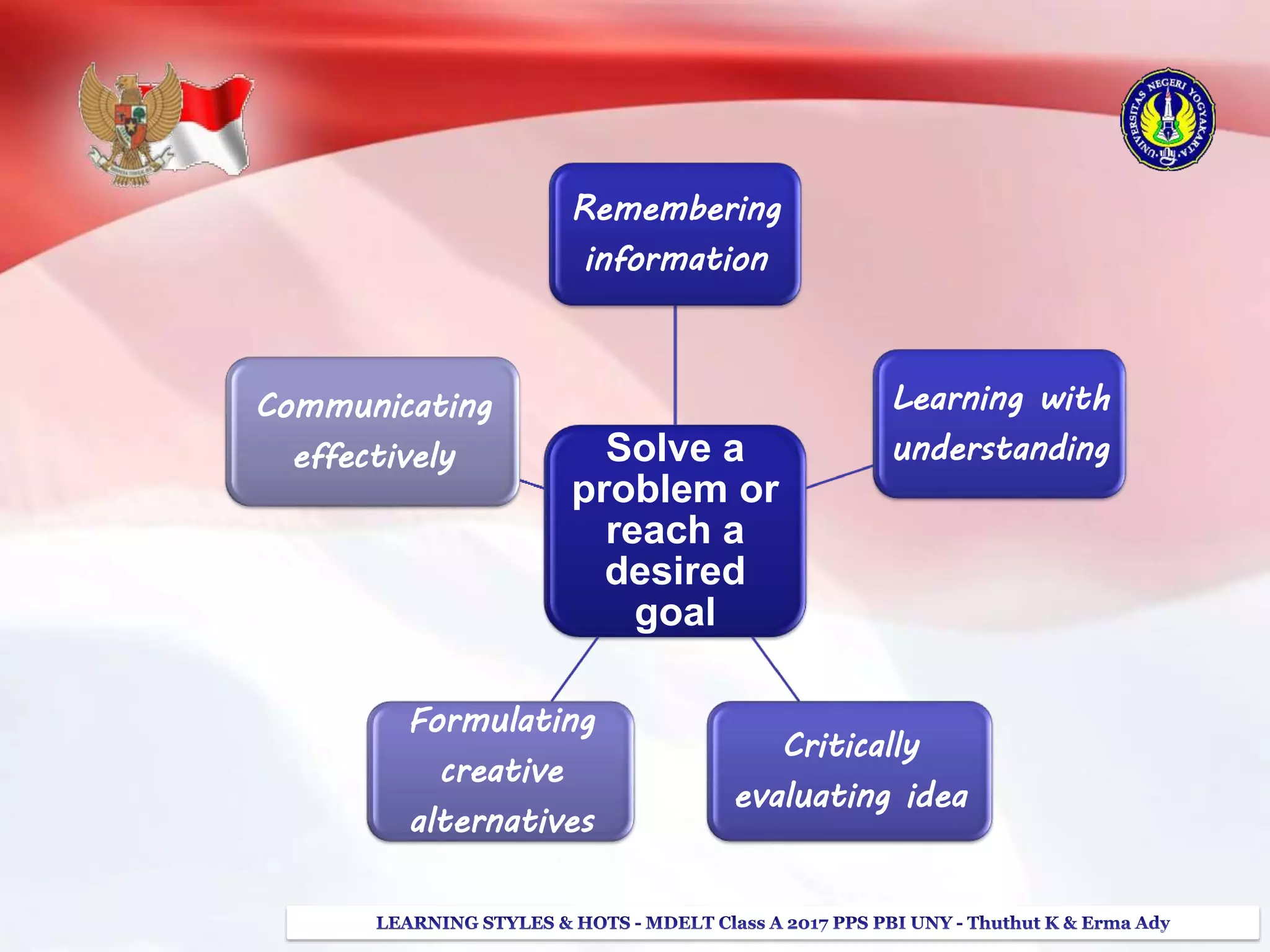
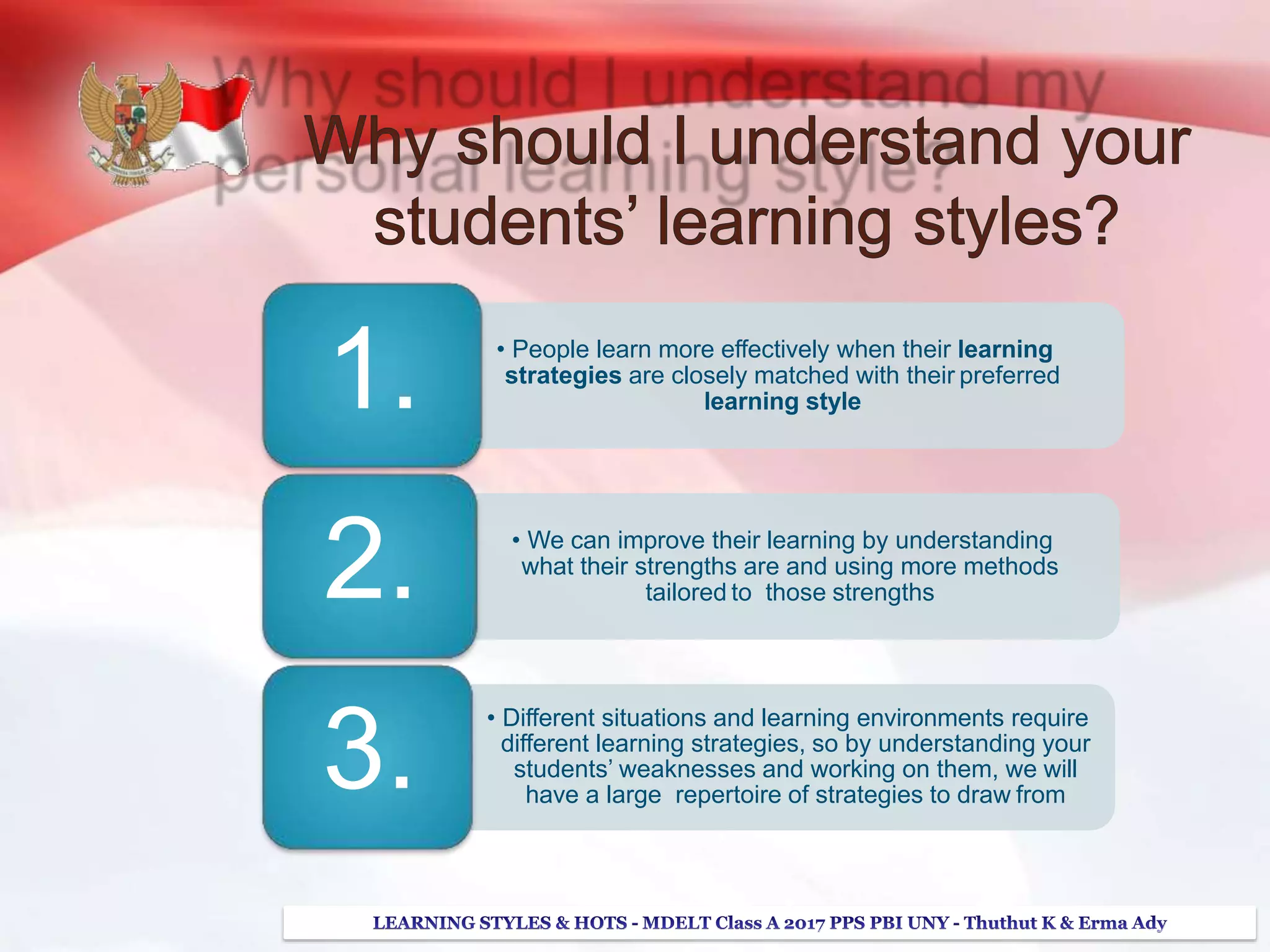
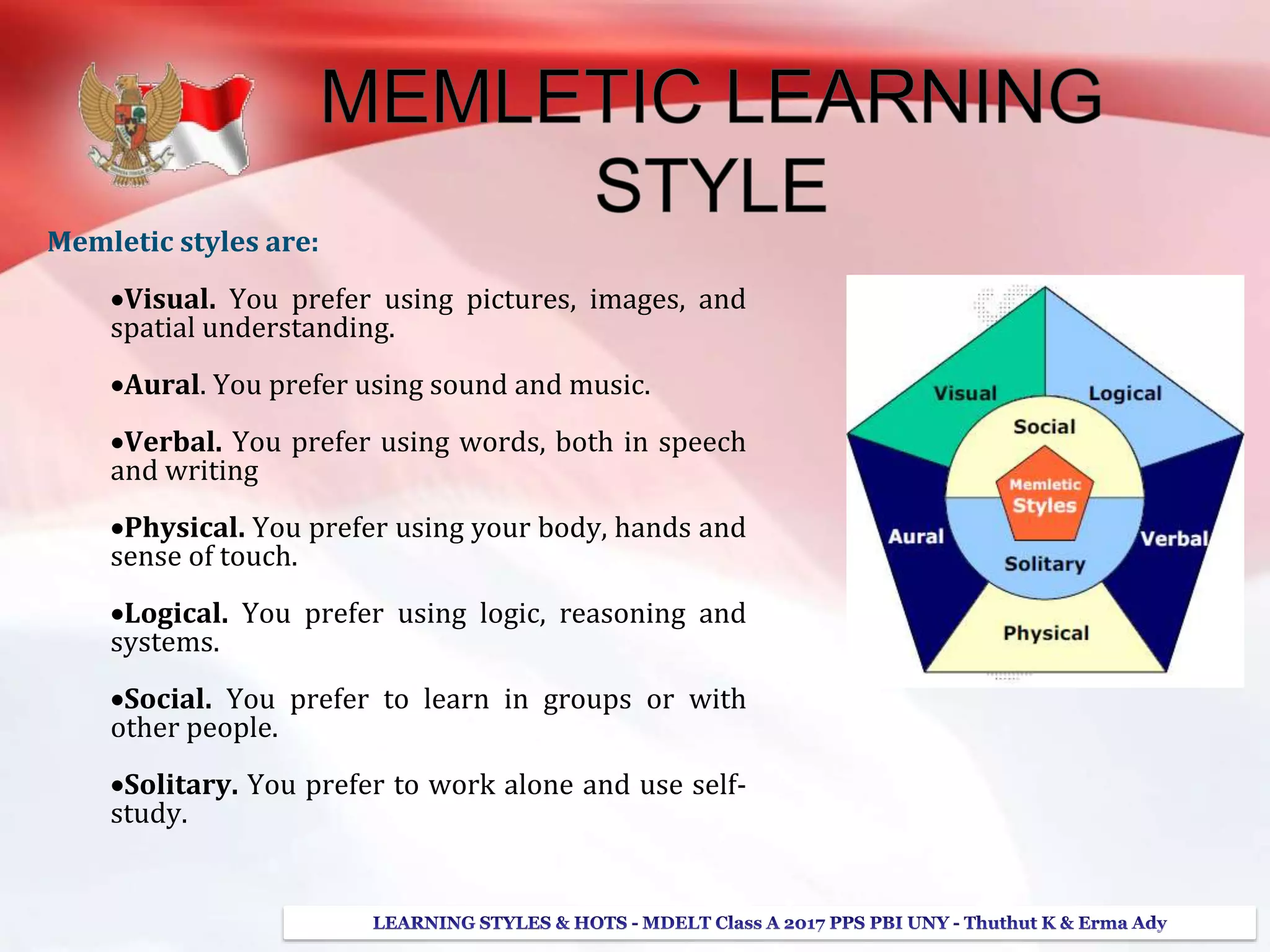
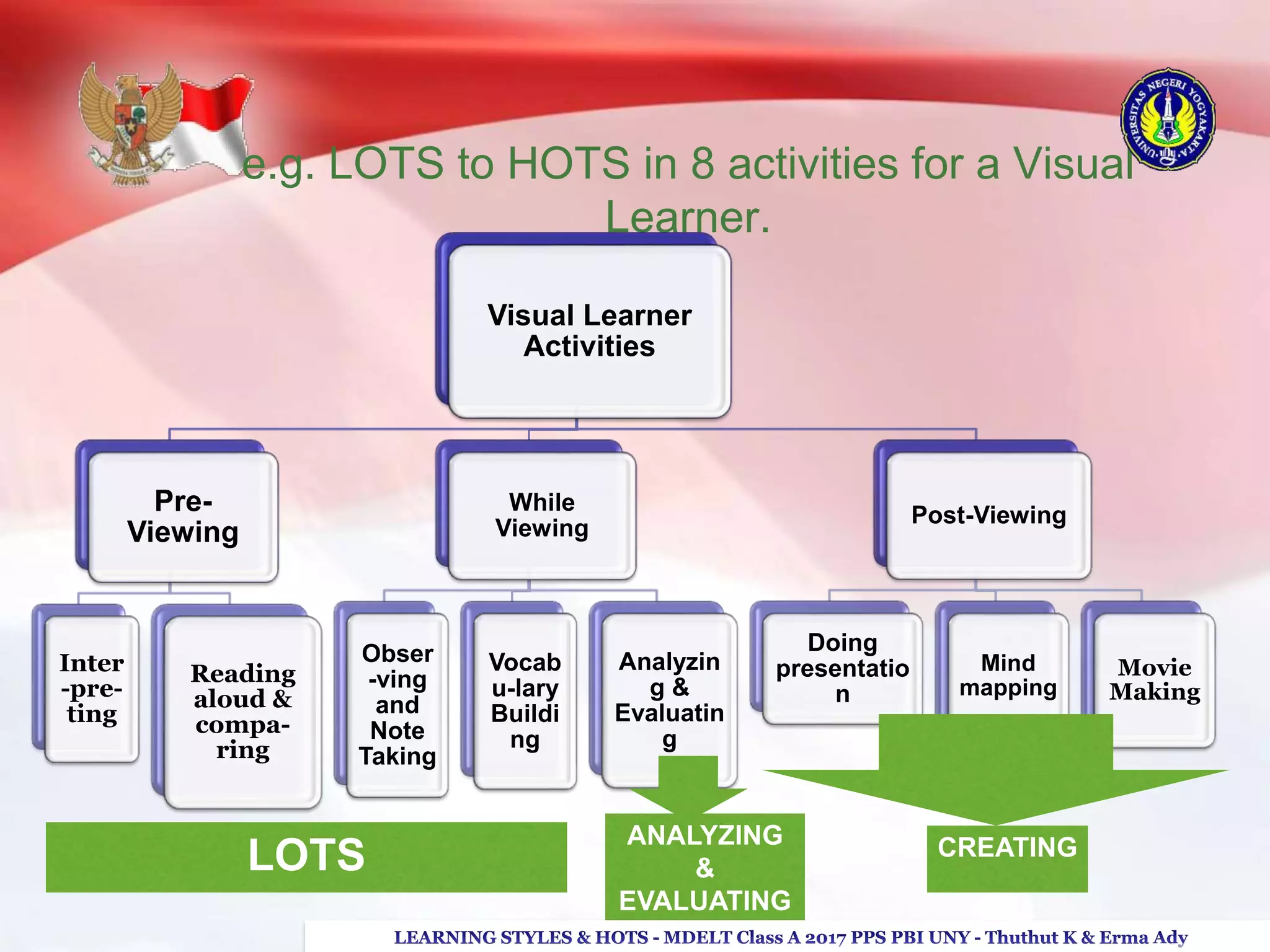
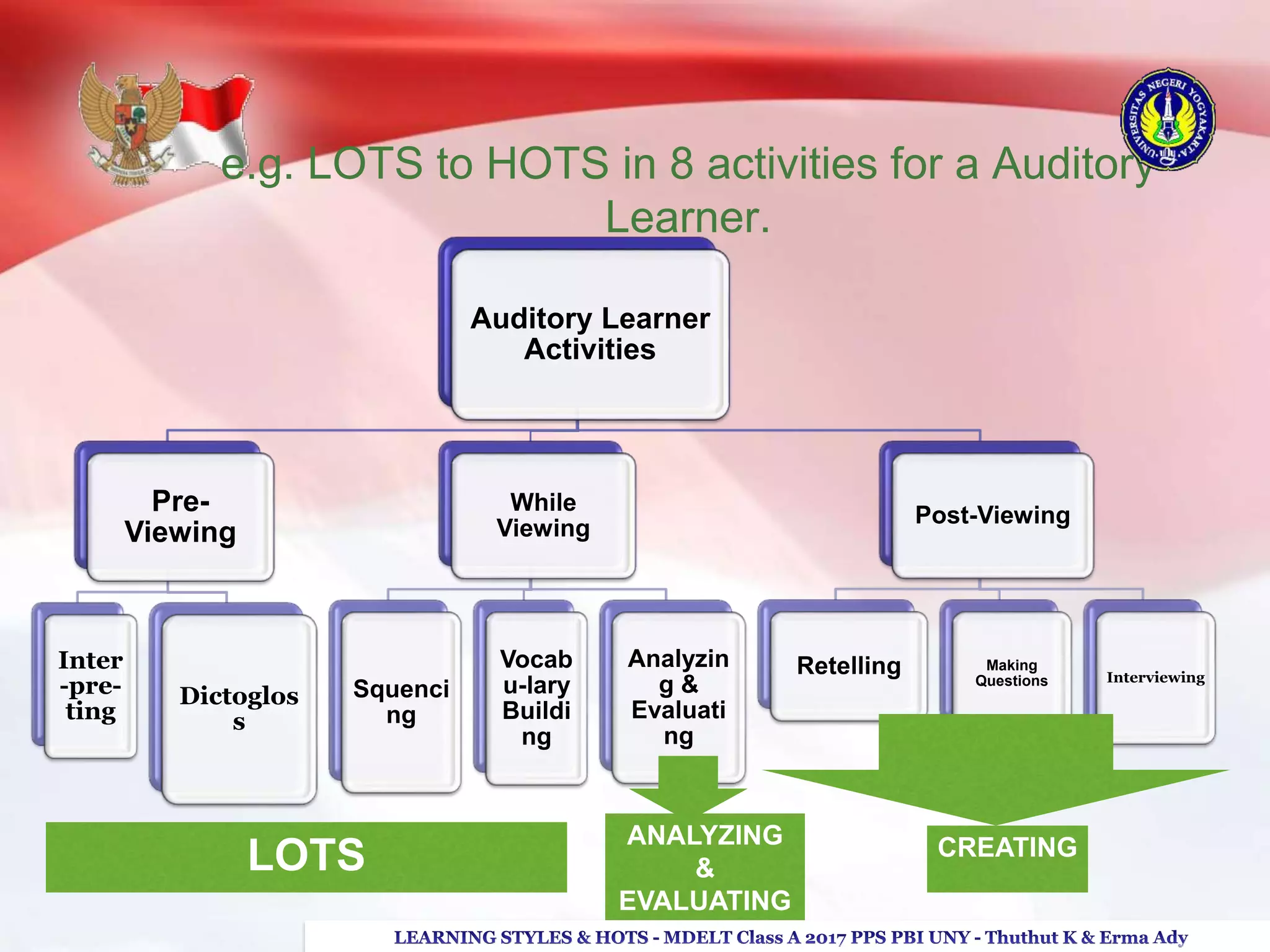
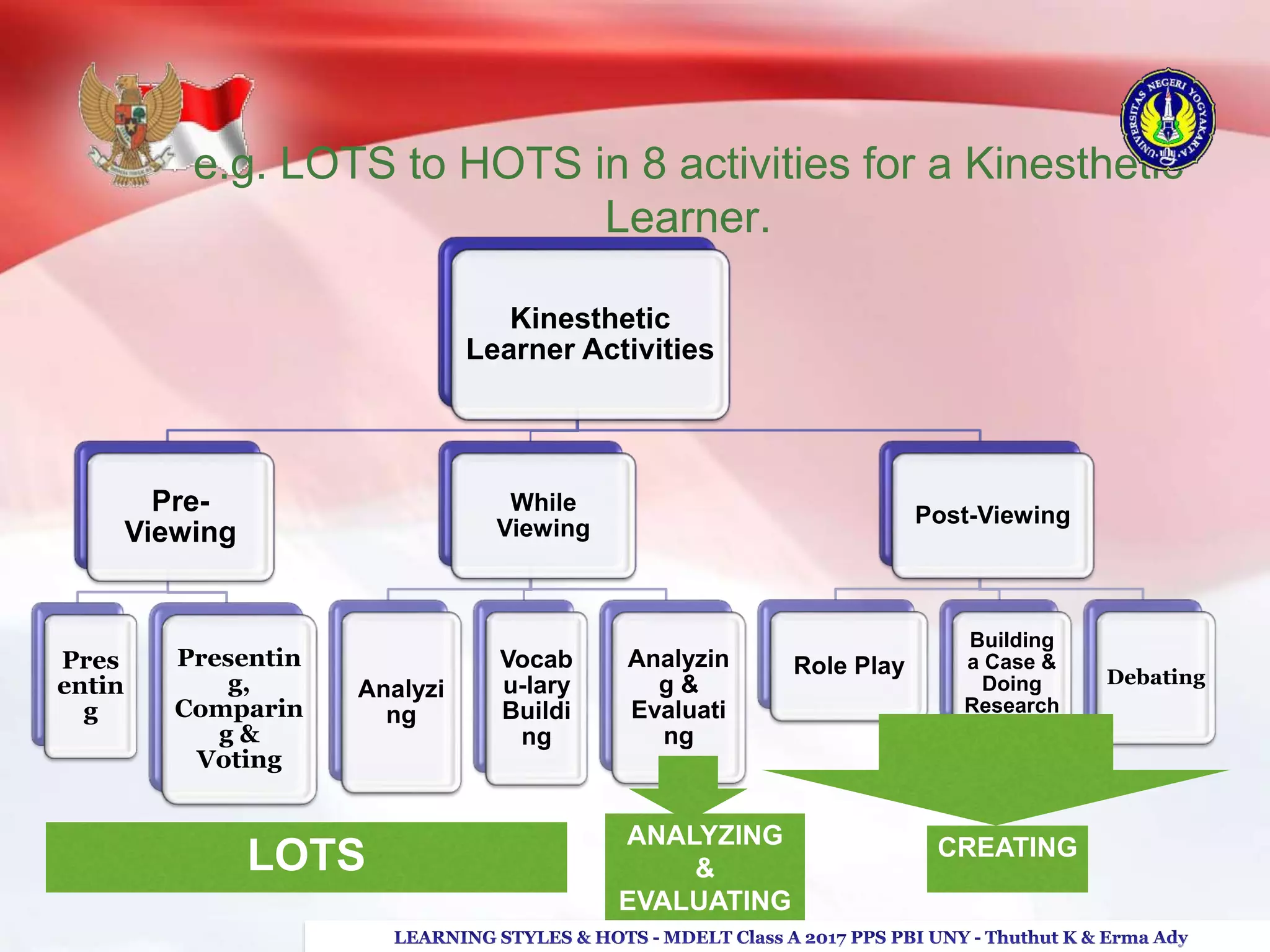
The document discusses higher order thinking skills (HOTS), emphasizing the types of questions educators should use to challenge students, categorizing them as 'skinny' or 'fatty' questions. It outlines strategies for enhancing HOTS, including question-answer relationships, teaching learning styles, and applying Bloom’s revised taxonomy. Additionally, it provides approaches tailored to different learning styles—visual, auditory, and kinesthetic—to help students apply knowledge effectively and engage in critical thinking.