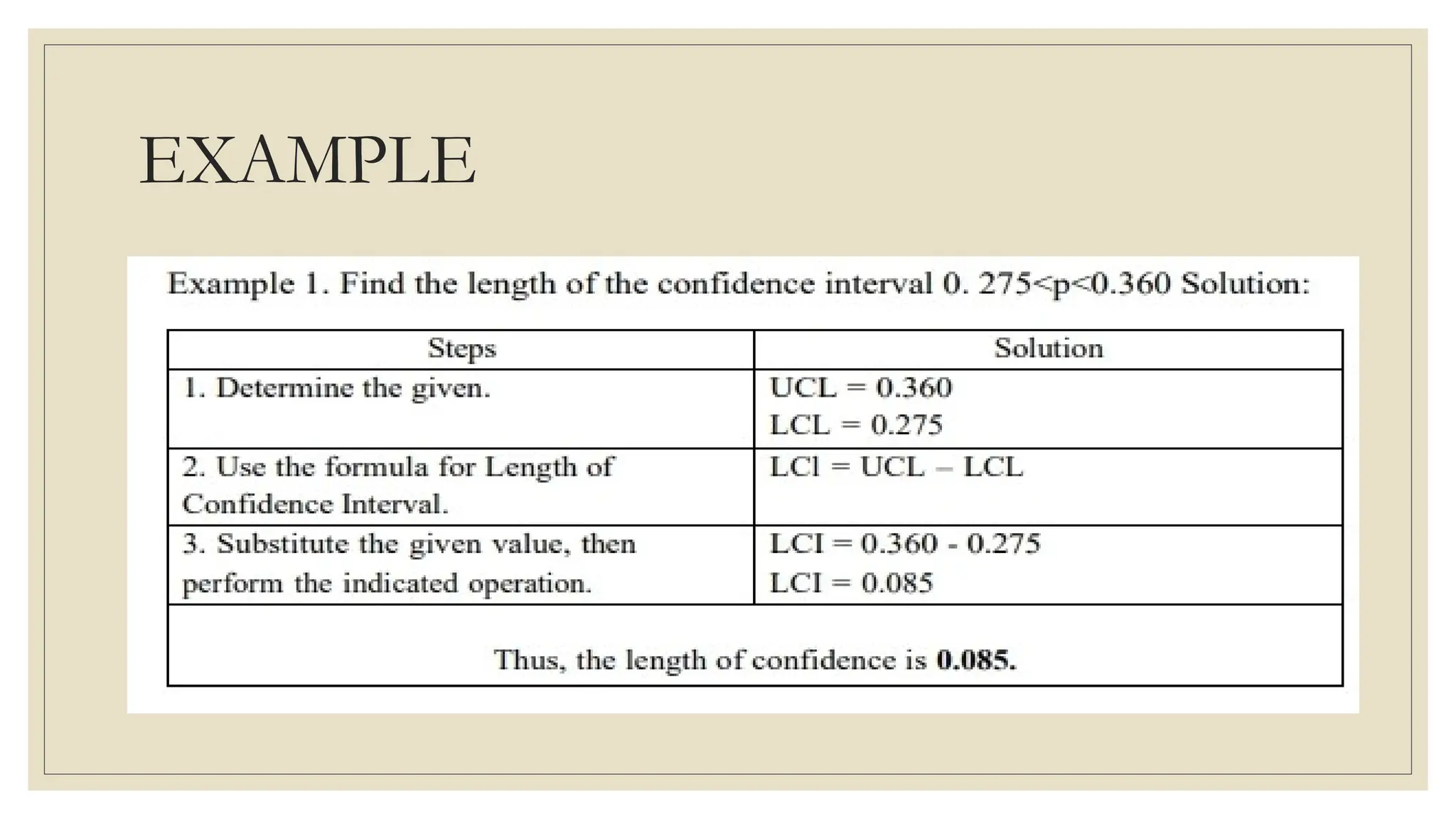
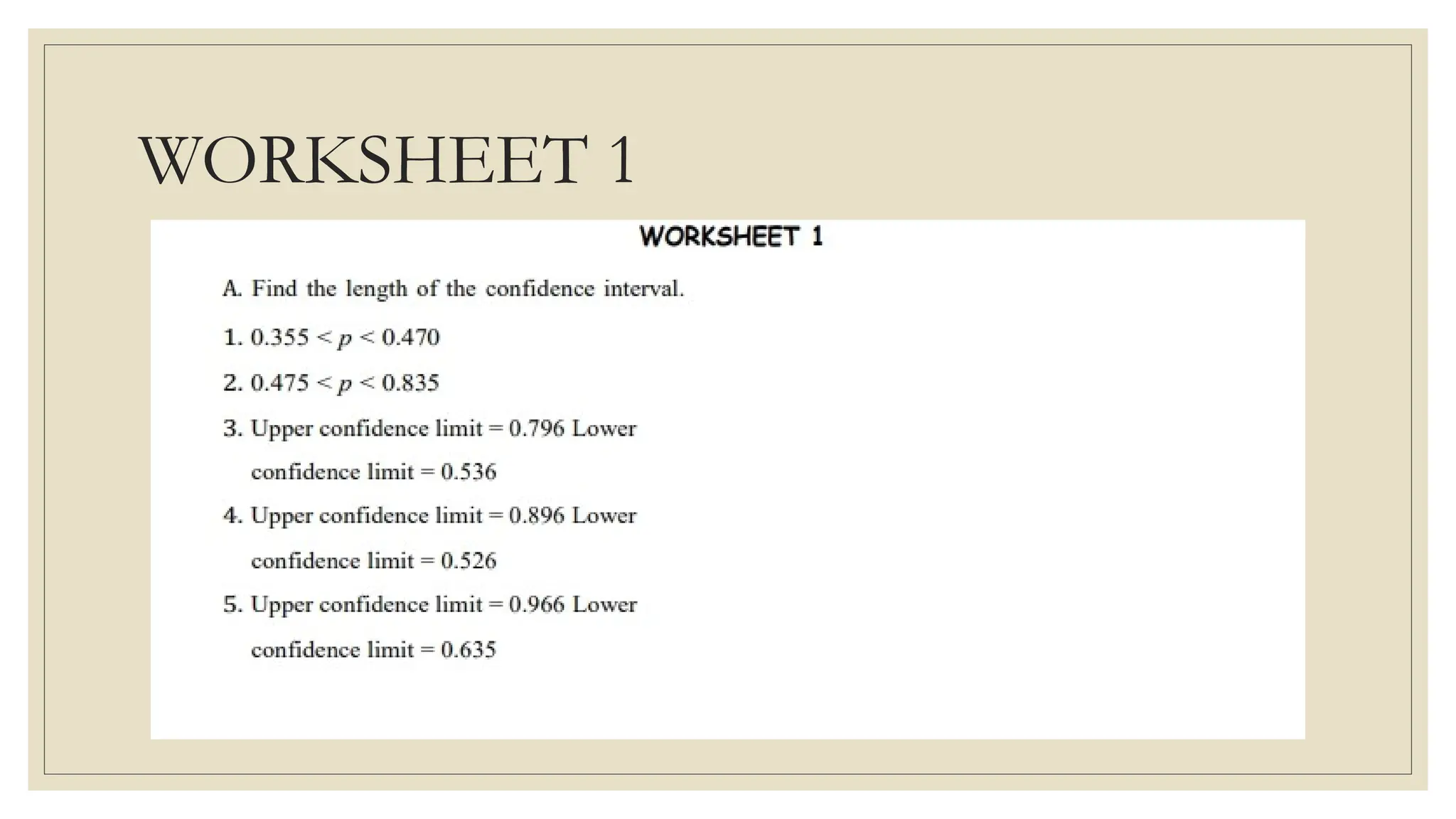
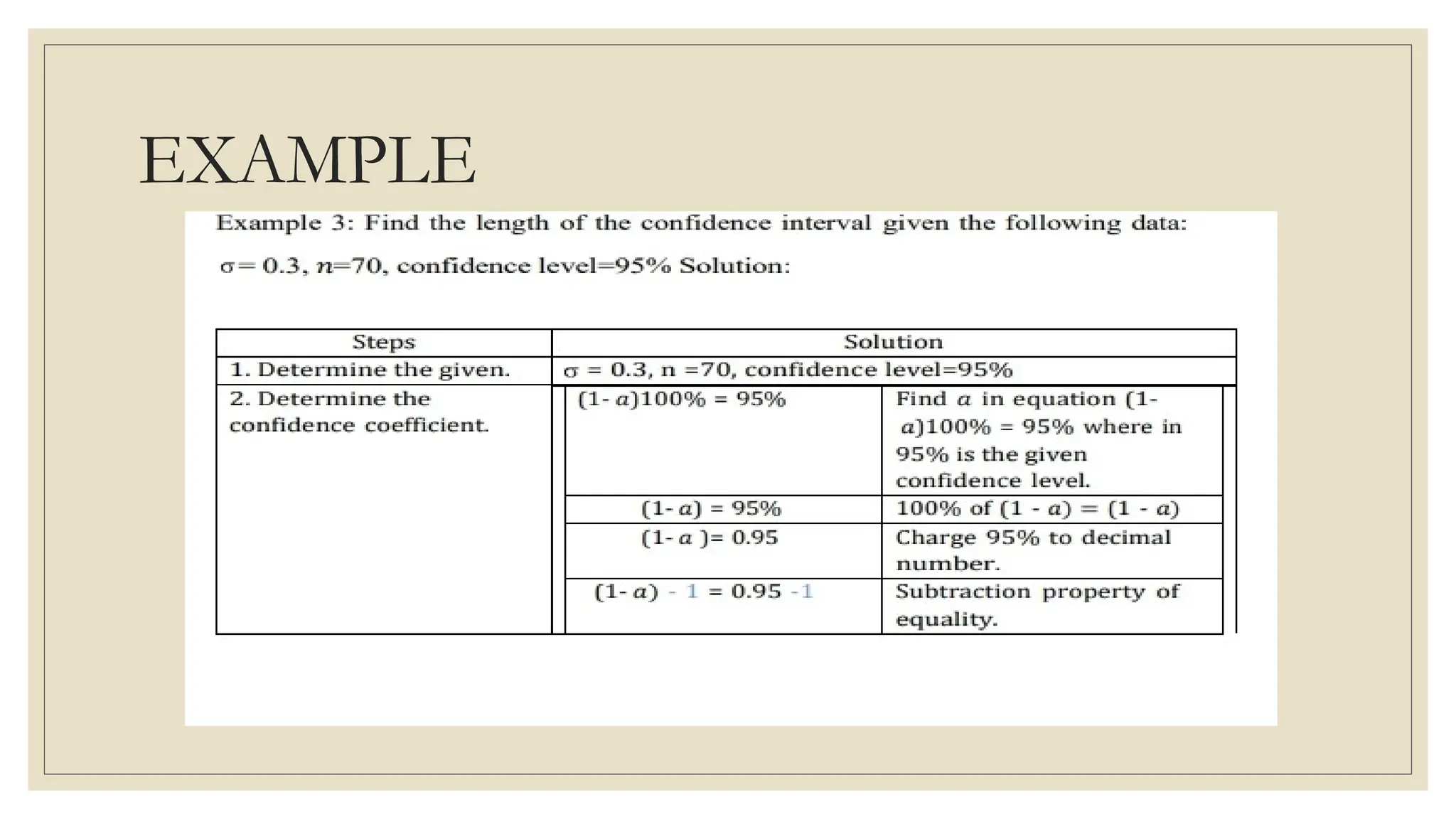
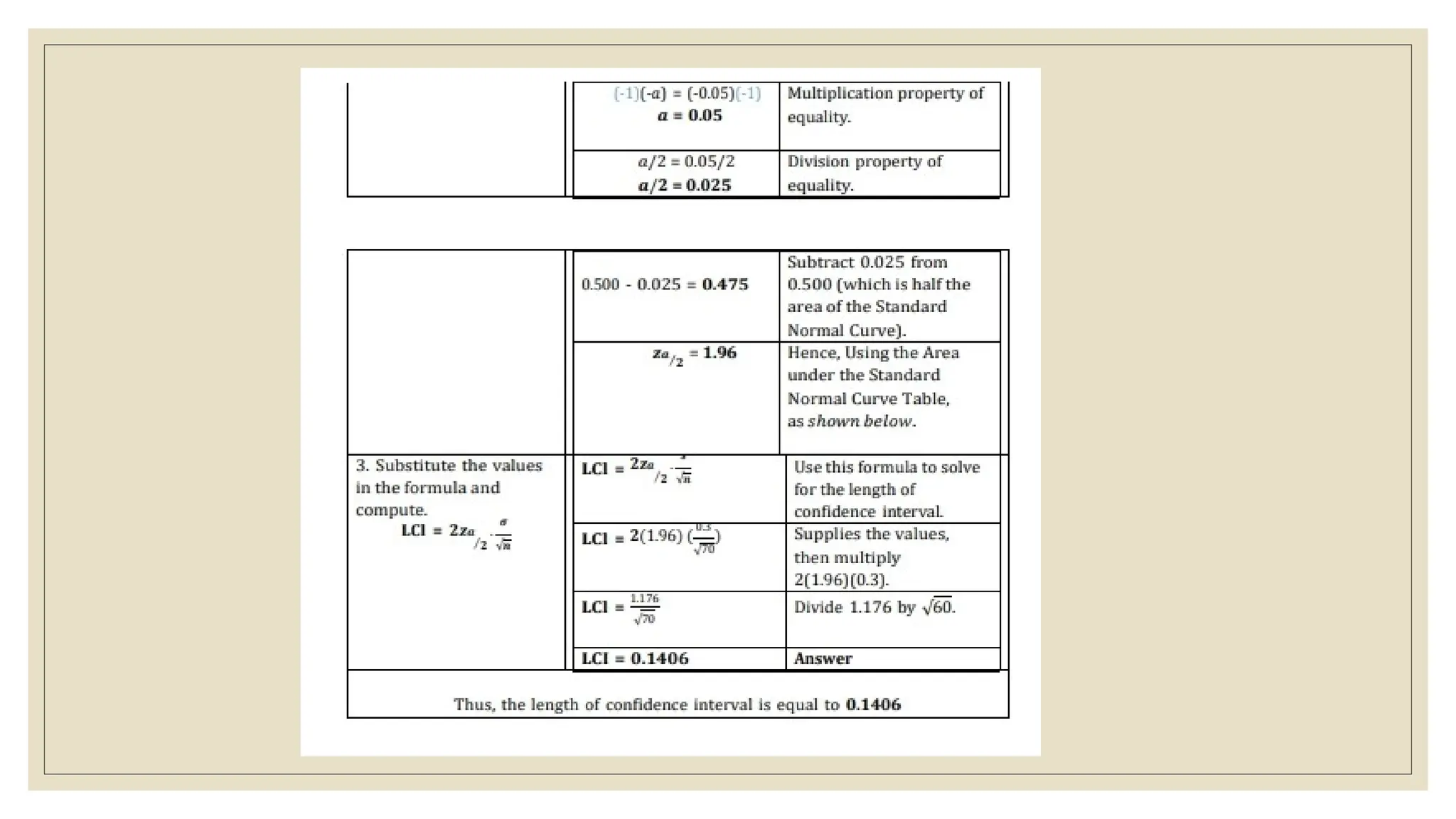
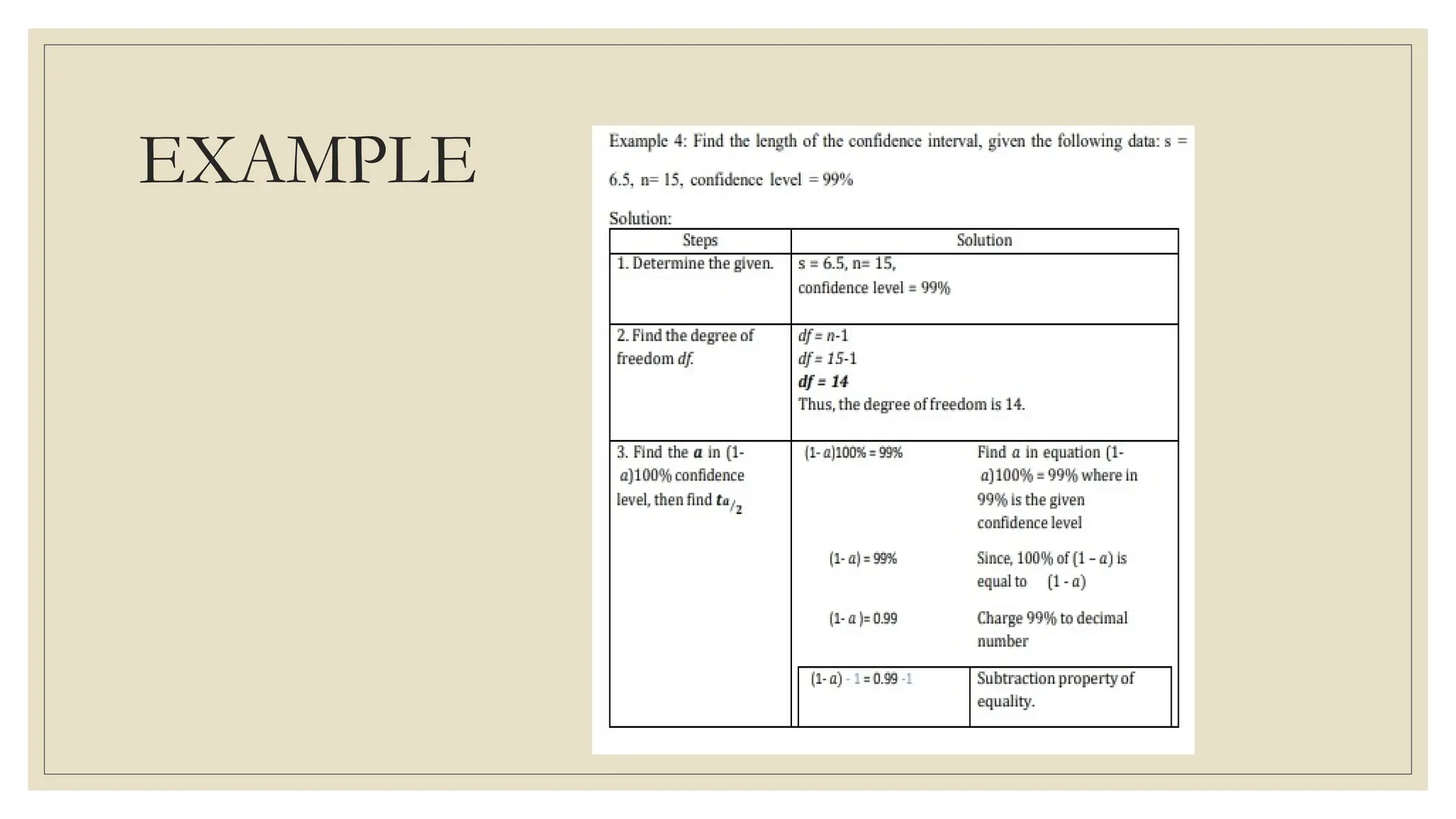
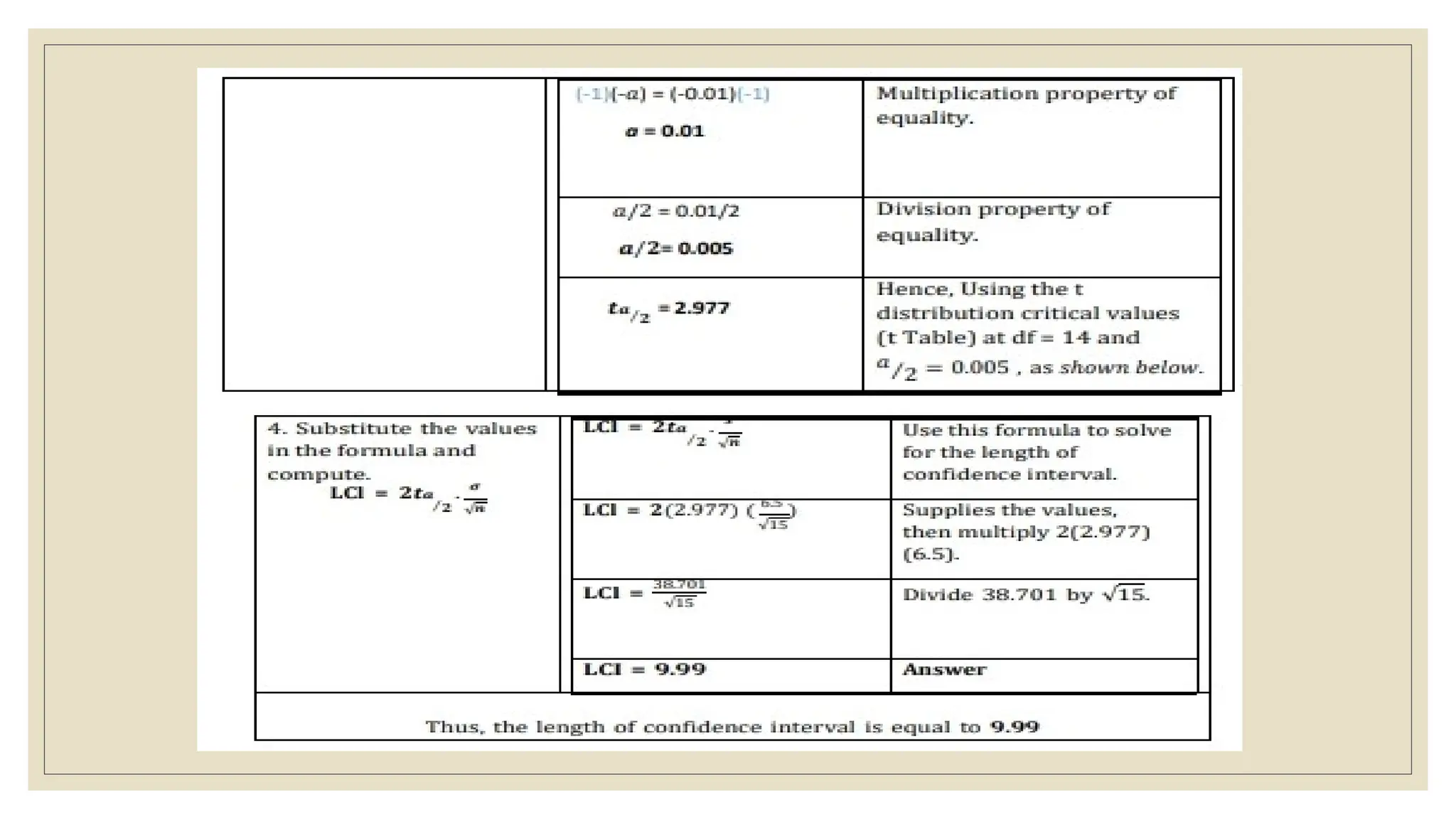
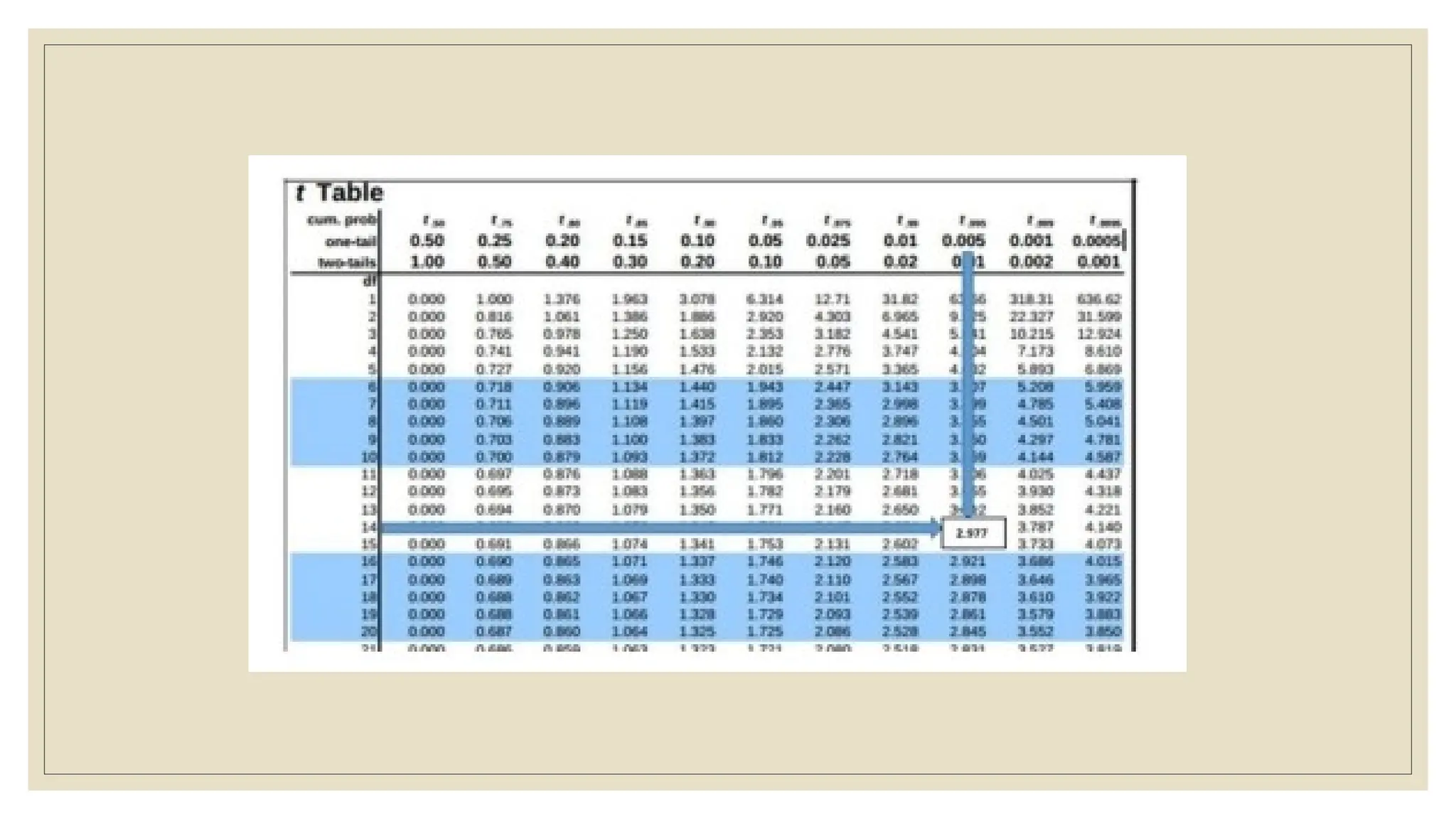
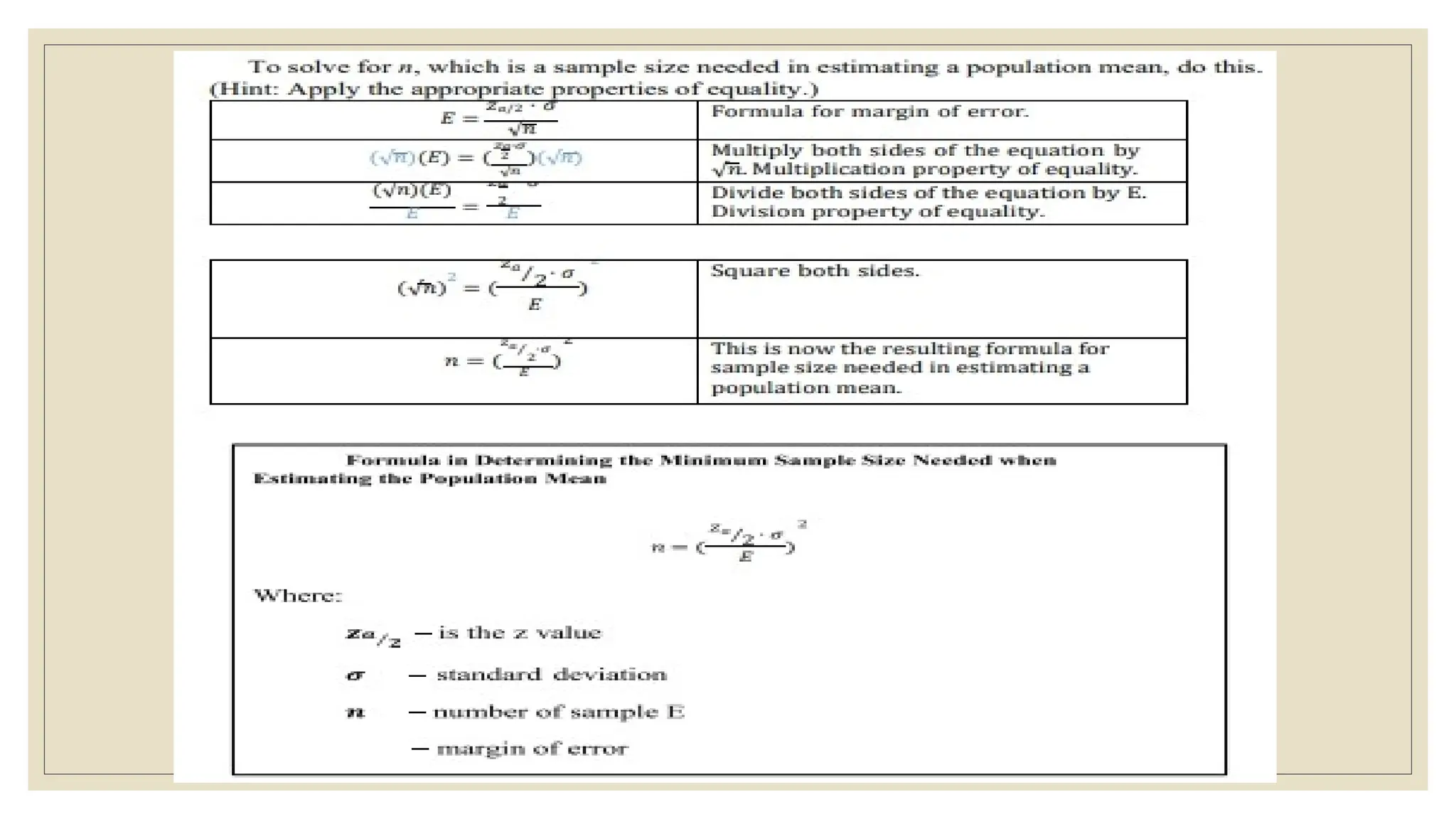
The document discusses the concepts of statistics and probability, emphasizing the importance of estimates and confidence intervals in data analysis. It explains that a confidence interval helps to quantify uncertainty about population parameters, with larger sample sizes yielding smaller intervals. Additionally, it provides formulas and examples for calculating the length of confidence intervals.