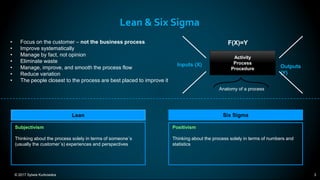
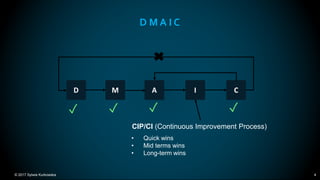
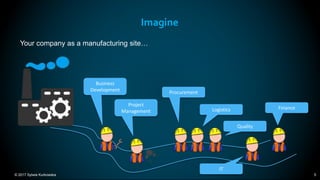
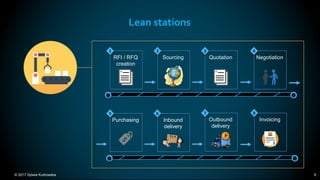
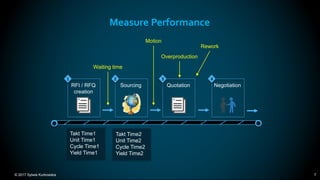
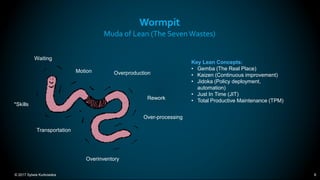
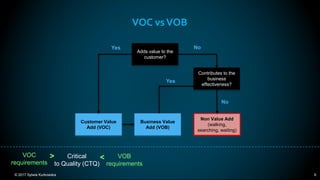
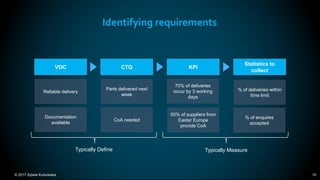
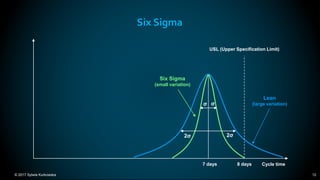
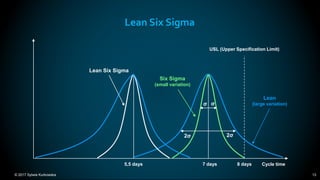
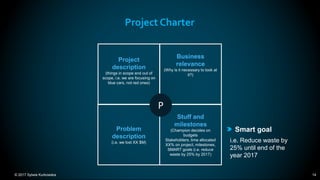
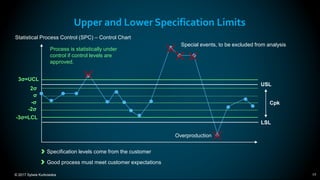
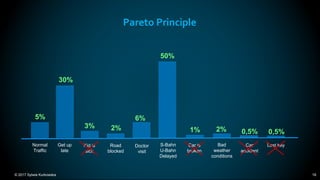
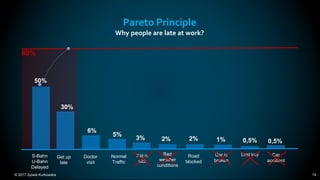
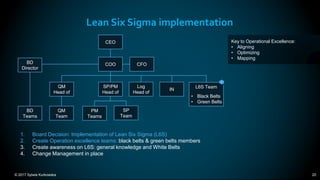
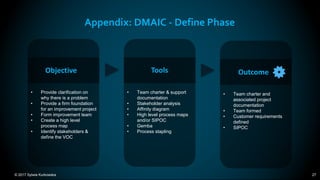
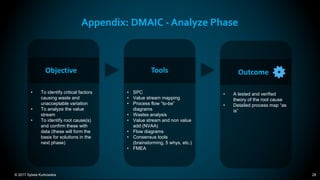
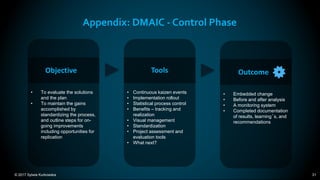
The document outlines the principles and methodologies of Lean Six Sigma, emphasizing customer focus, systematic improvement, and waste elimination. It details the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) for process improvement, including tools and strategies for identifying and addressing inefficiencies. Additionally, it discusses the importance of stakeholder involvement and continuous improvement in achieving operational excellence.