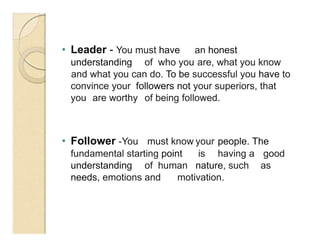
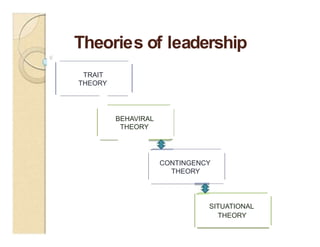
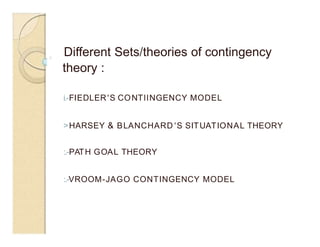
This document discusses different leadership theories including trait theory, behavioral theory, contingency theory, and situational theory. It defines leadership as a process of social influence where one person enlists the aid of others to accomplish a common task. Key factors of leadership discussed are the leader, follower, communication, and situational context. Theories covered in more depth include trait theory which focuses on identifying leadership traits, behavioral theory which says leadership can be learned, and contingency theory which emphasizes matching leadership style to situational factors.