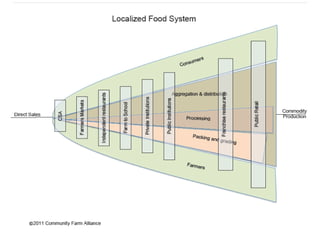
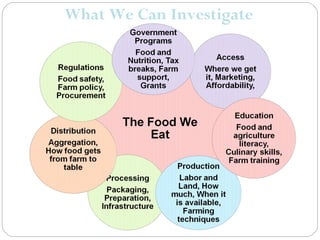
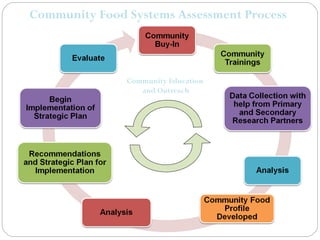
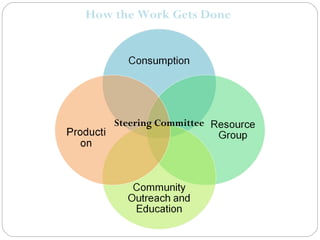
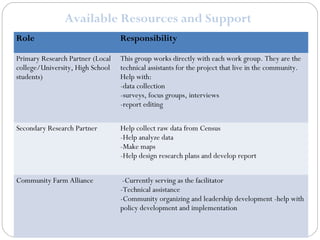
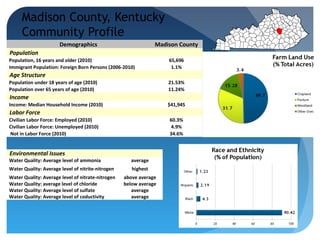
This document provides information about conducting a community food systems assessment. It defines a community food systems assessment as a collaborative process that examines local food issues and assets to inform actions to make the community more food secure. The document outlines the assessment process, including forming work groups to investigate elements of local food consumption, production, resources, and outreach. It also provides an example of a community profile report and contact information for assistance.