This document discusses various leadership theories including:
- Great Man Theories which propose that leaders are born, not made.
- Trait Theories which examine physical and mental traits of leaders.
- Behavioral Theories which analyze what leaders do such as directing, supporting, and coaching.
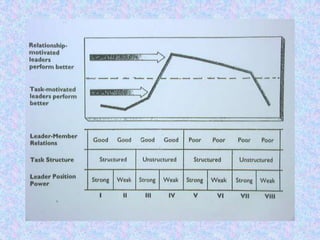
- Contingency Theories which propose there is no single best leadership style and that the effectiveness depends on the situation, including Fiedler's Contingency Theory and the Ohio State, Michigan, and Hersey-Blanchard theories.
- Transformational and Charismatic theories of modern leadership.