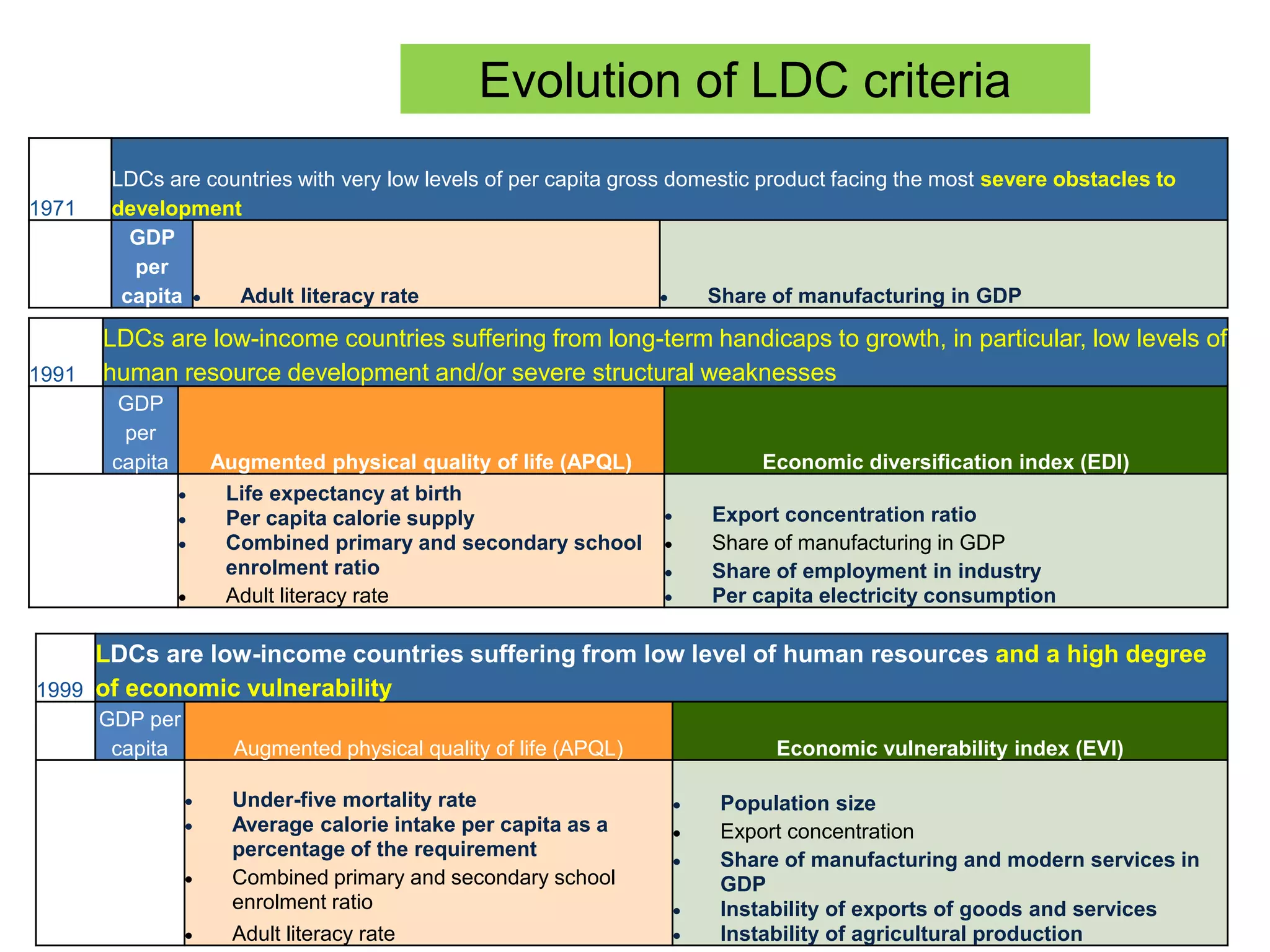
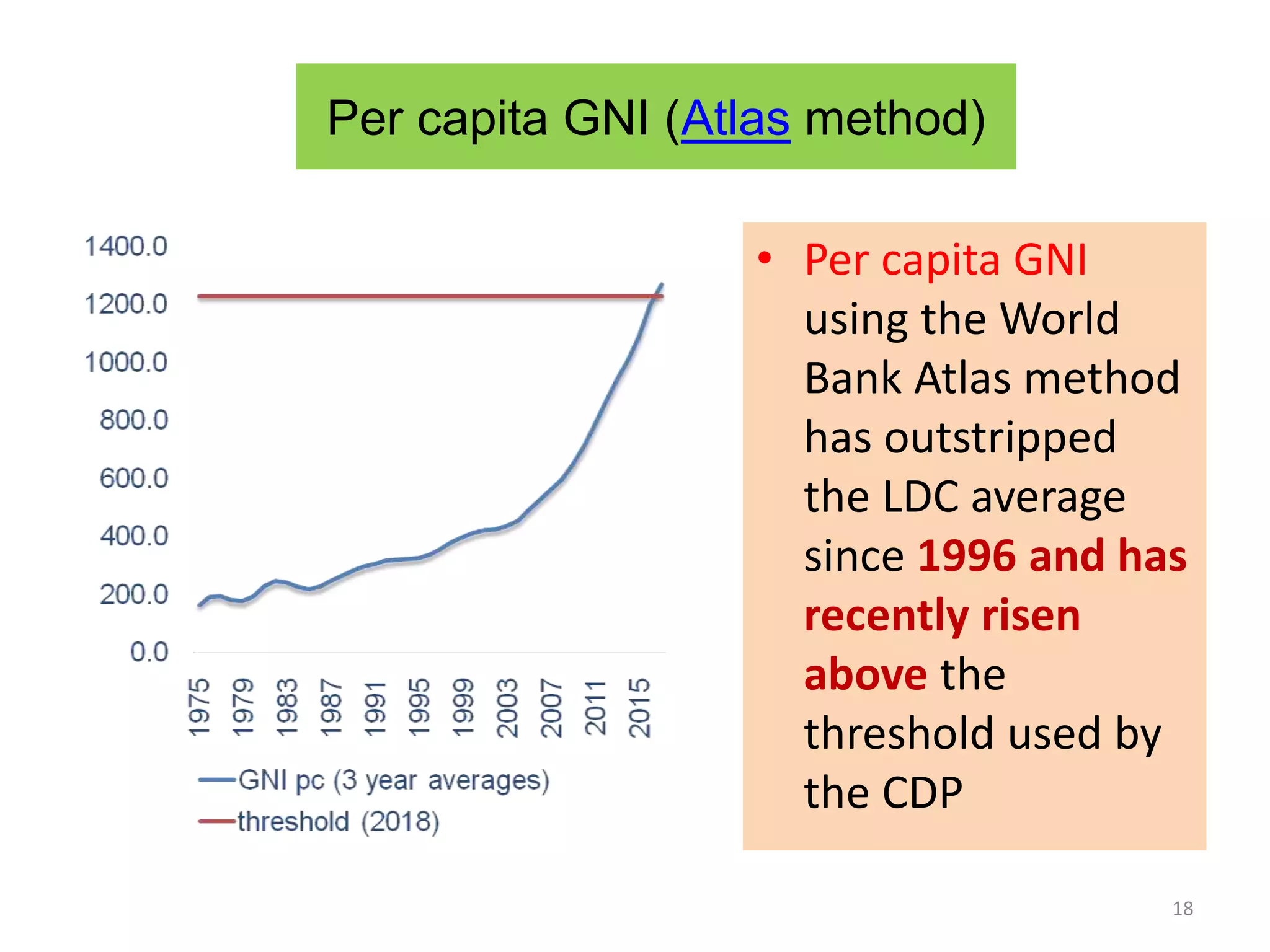
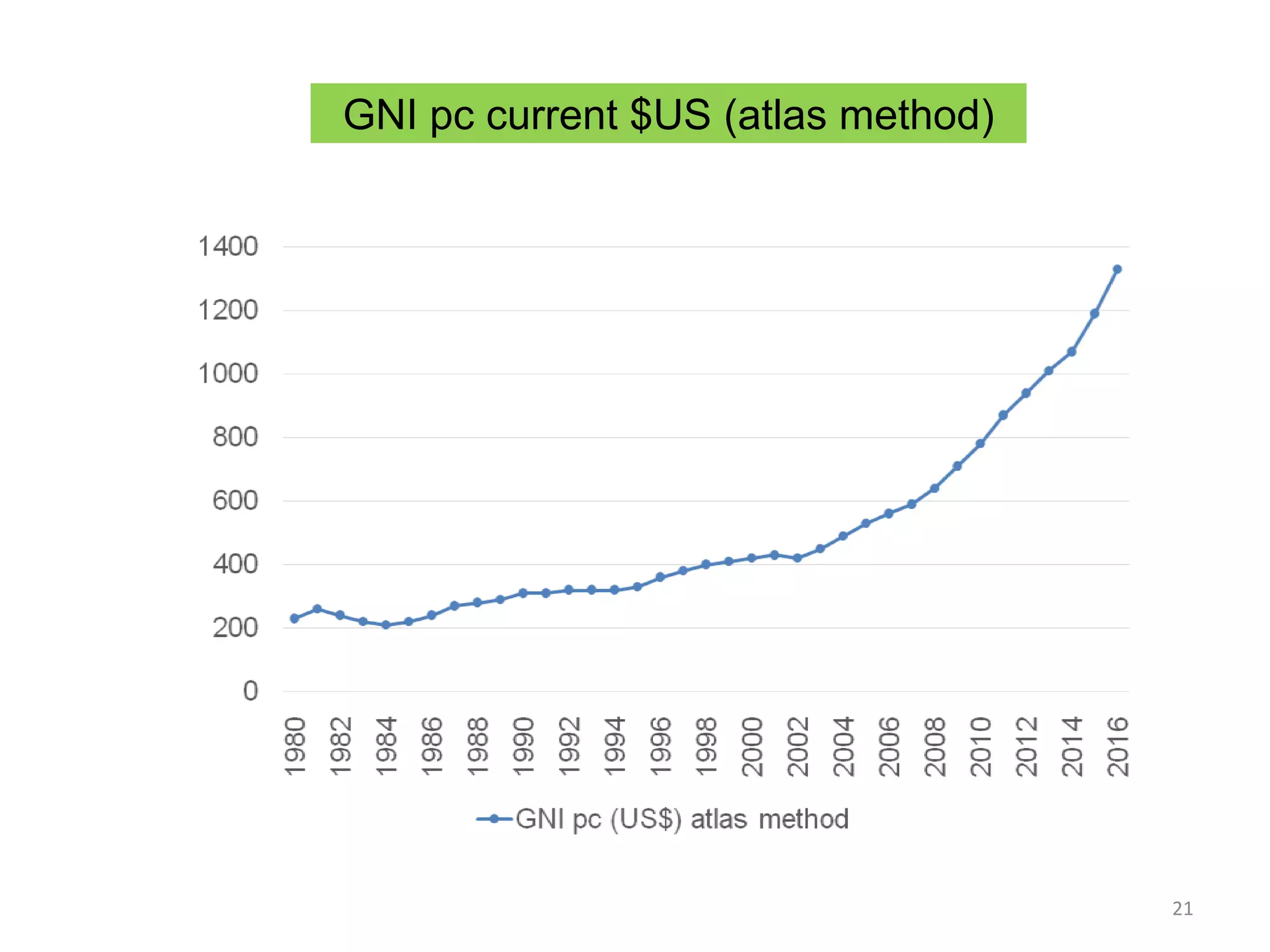
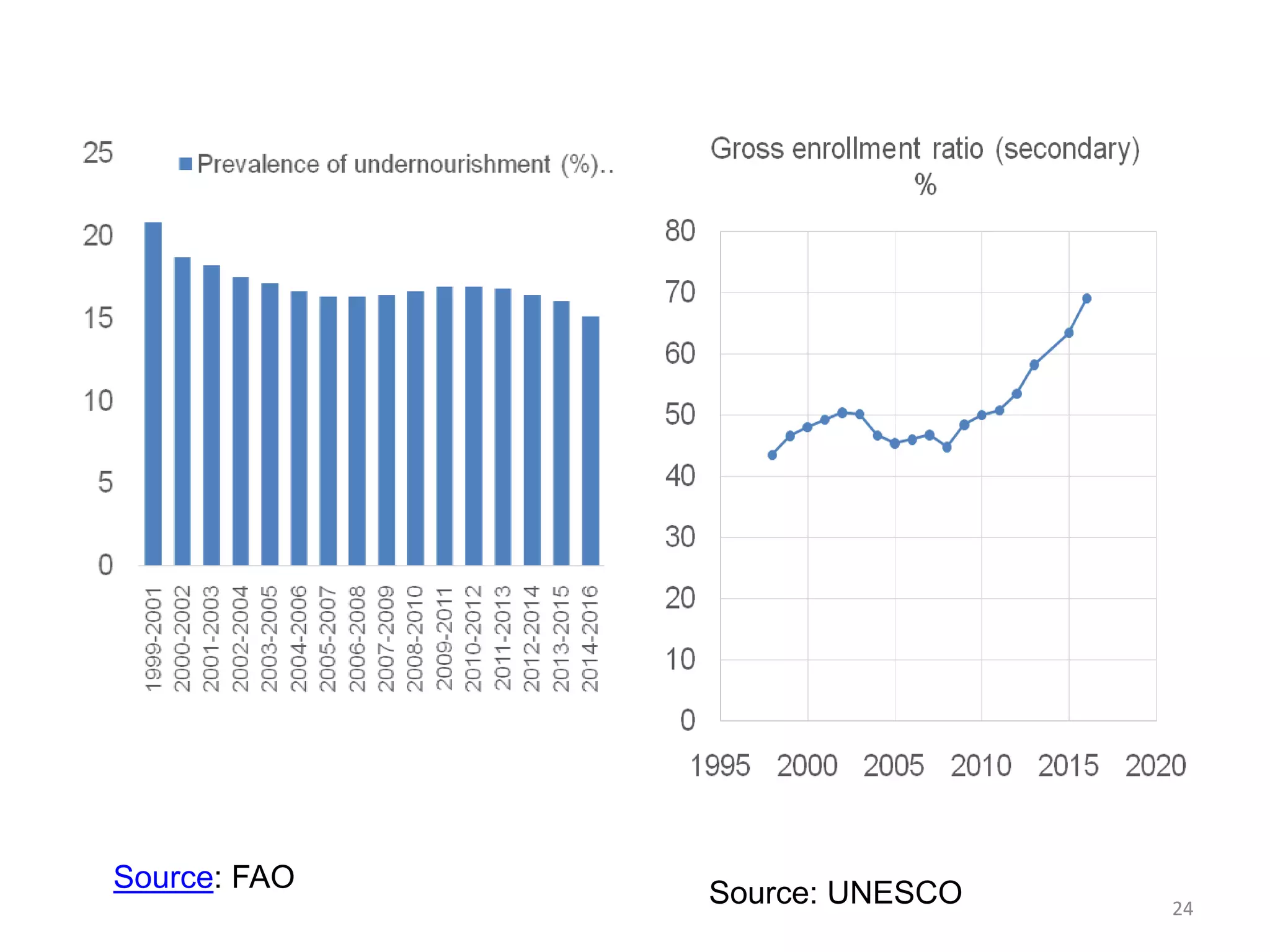
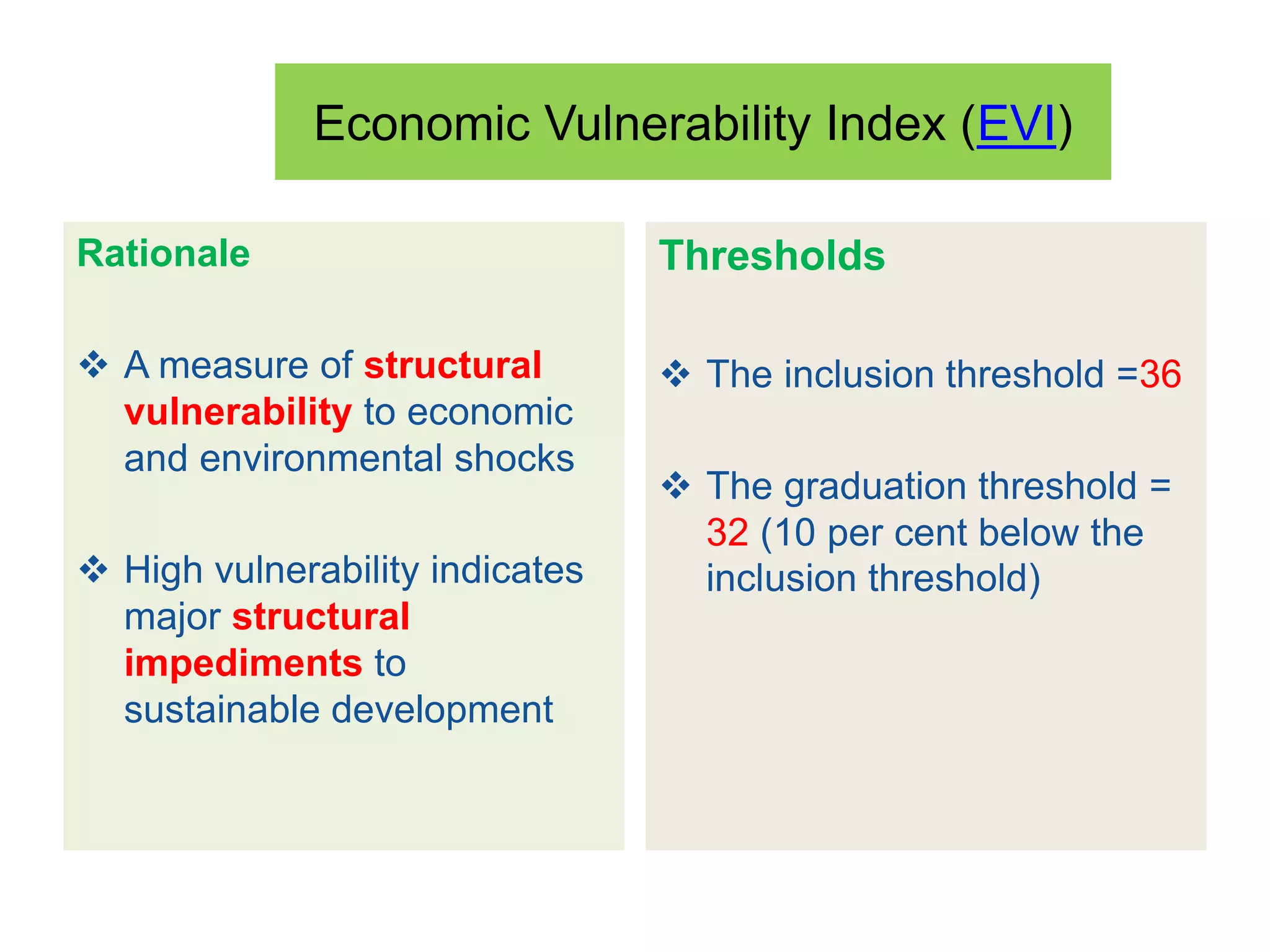
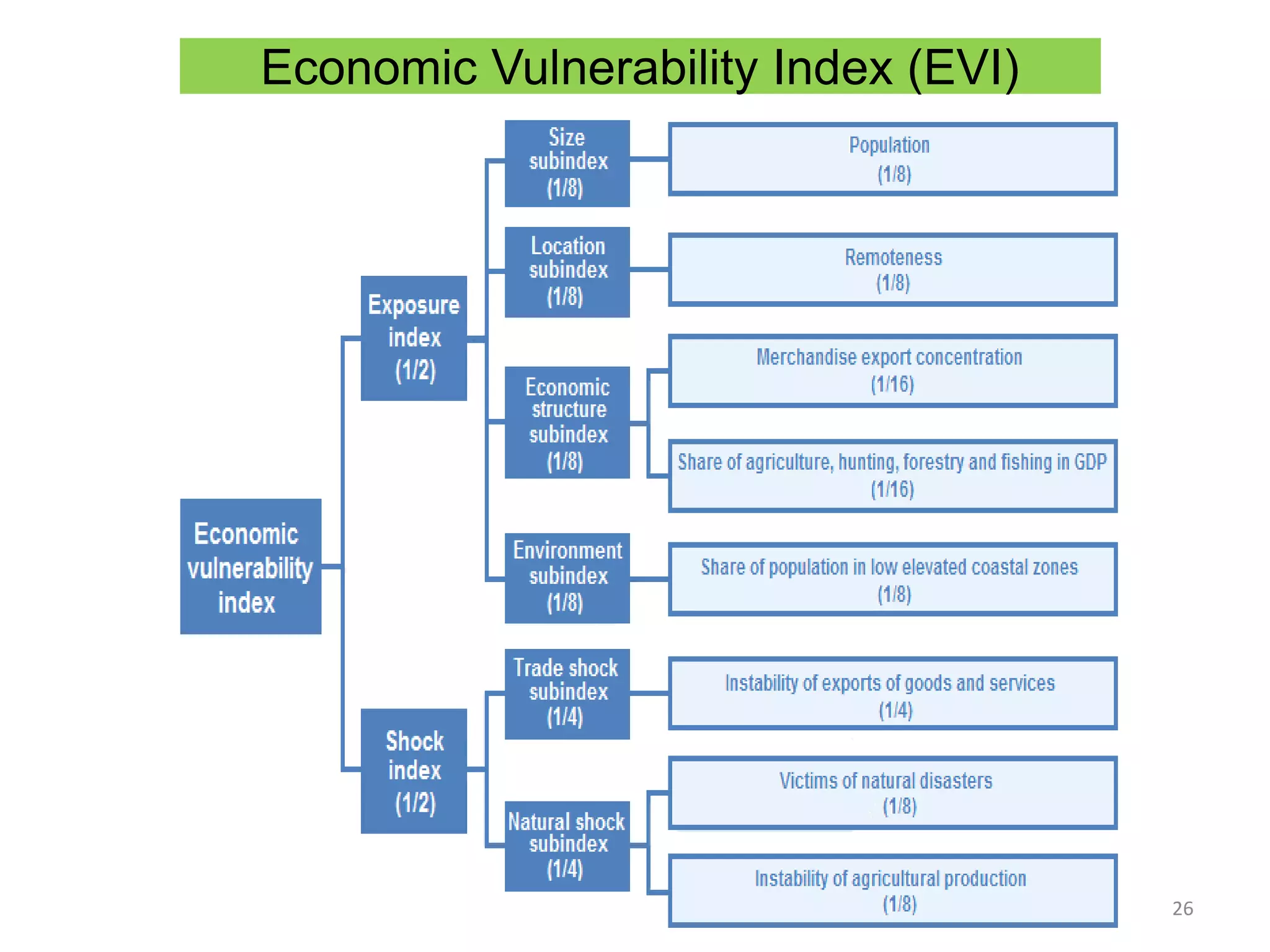
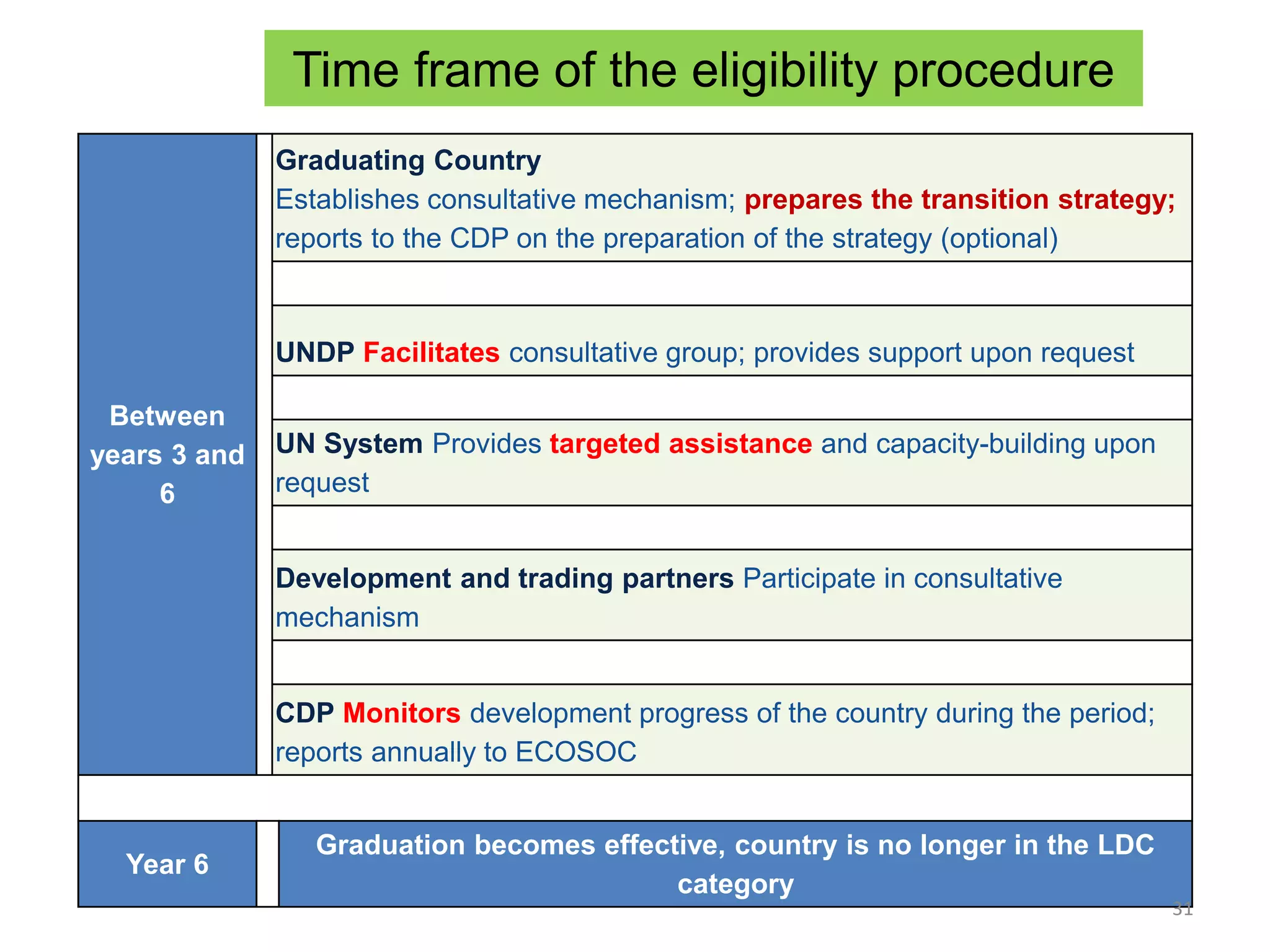
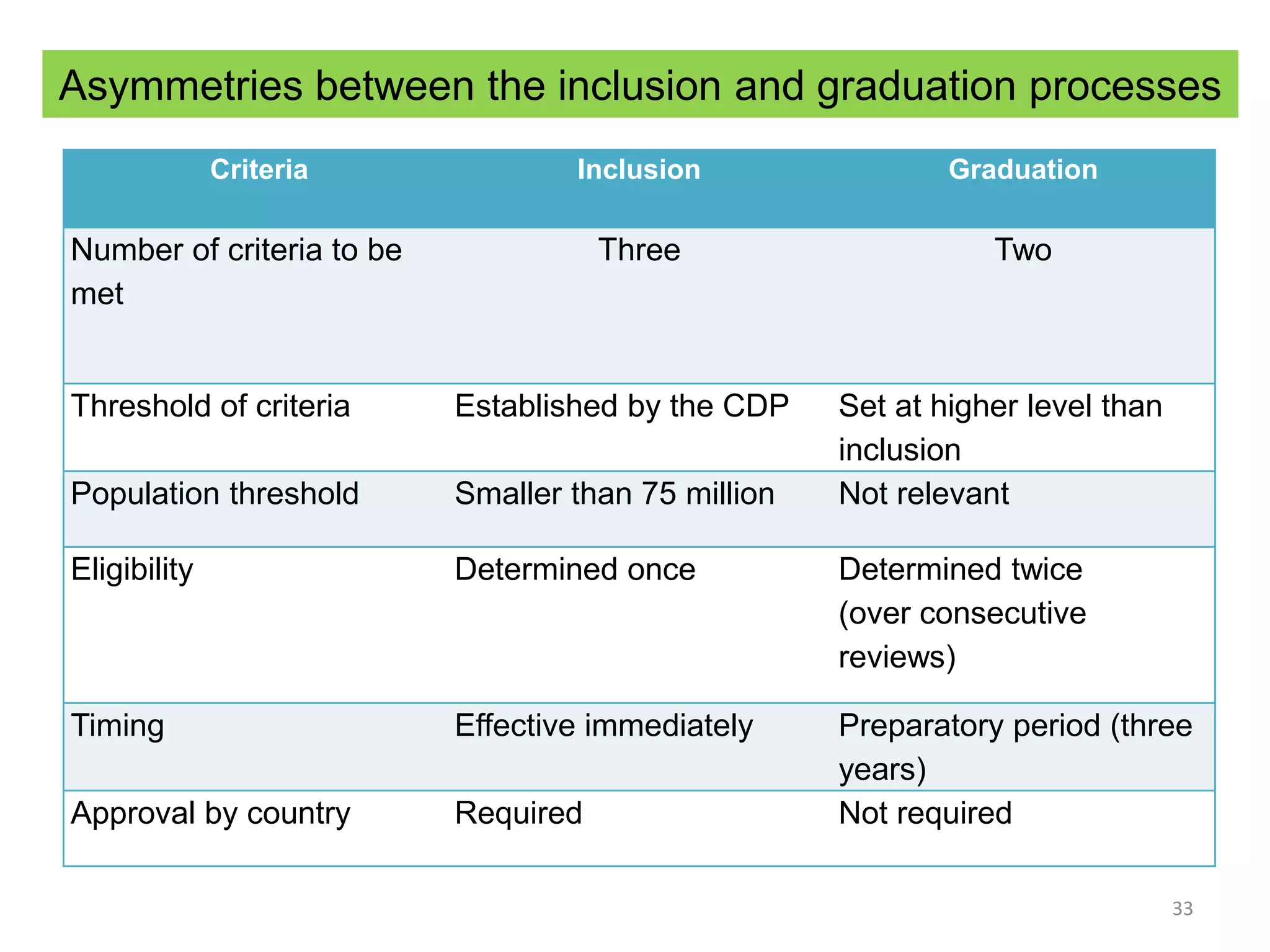
This document discusses Bangladesh potentially graduating from its status as a Least Developed Country (LDC). It provides background on the LDC category and criteria for inclusion and graduation. The criteria have evolved over time to include measures of income, human assets, and economic vulnerability. Bangladesh meets the graduation thresholds for income but still needs progress on the human assets and economic vulnerability indices. The document outlines Bangladesh's performance on the various criteria and the timeline and process for reviewing and potentially graduating countries from LDC status.