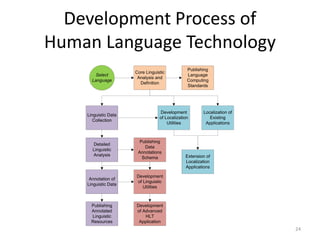
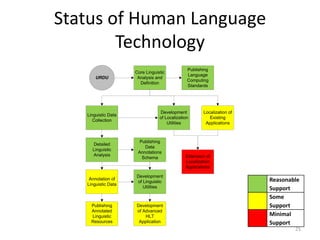
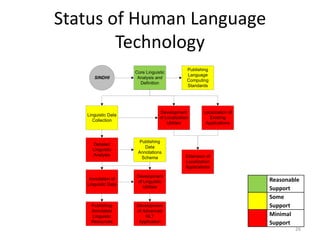
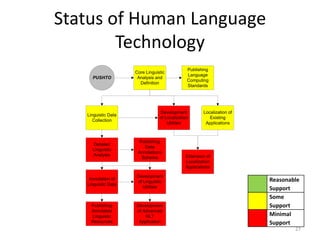
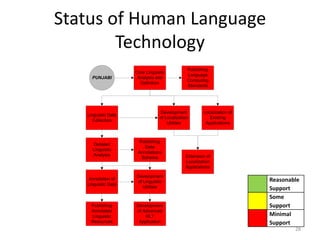
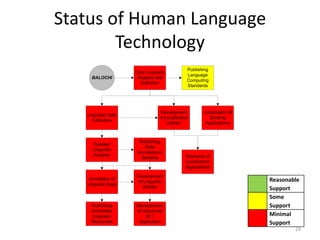
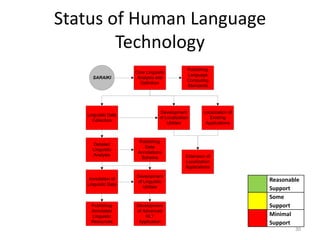
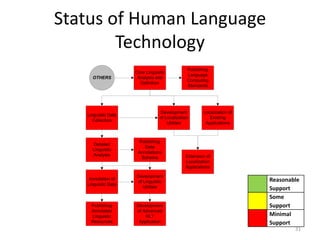
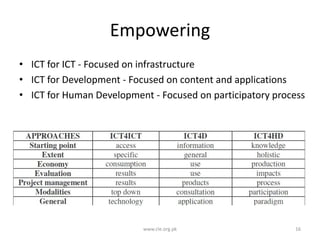
The document discusses the challenges and practices in providing computing support for the diverse languages of Pakistan, where a significant majority of the population lacks access to Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). It highlights the need for human language technology to bridge linguistic gaps, addressing issues of localization, software, and online content in languages such as Urdu, Punjabi, Sindhi, and others. The document emphasizes the socio-economic potential of ICT for human development by improving access to information and linguistic resources.








![[1]
One school did not participate, and one school website was disqualified as the team took significant external assistance.
LANGUAGE FOR CONTENT
DEVELOPMENT
Website Competition Category
Language of Website
Urdu
English
Total
School Website (by 10 School Teacher Teams)
9
1
10
Local Village Website (by 10 School Student
Teams)
8
0
8
Open Category (Individual Students)
38
0
38
Total
55
1
56
www.cle.org.pk
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/languagecomputingdig-it-131113055553-phpapp02/85/Computing-support-for-Pakistani-Languages-Challenges-Practices-by-Dr-Sarmad-Hussain-22-320.jpg)