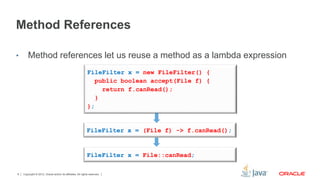
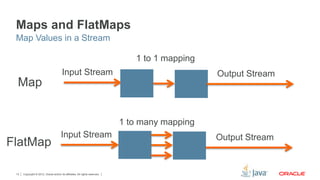
This document provides an overview of lambda expressions and Java streams. It defines lambda expressions as anonymous functions that can be used wherever anonymous inner classes are used. It also describes streams as sequences of elements that support sequential and parallel operations. Common stream operations like filter, map, and collect are discussed. Finally, it encourages readers to get started with the exercises by removing the ignore annotation from tests.



![Lambda Expressions
Lambda expression is an anonymous function
Think of it like a method
– But not associated with a class
Can be used wherever you would use an anonymous inner class
– Single abstract method type
Syntax
– ([optional-parameters]) -> body
Types can be inferred (parameters and return type)
Copyright © 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. 4 All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lambdas-hol-sritter-141002150723-phpapp02/85/Lambdas-And-Streams-Hands-On-Lab-JavaOne-2014-4-320.jpg)