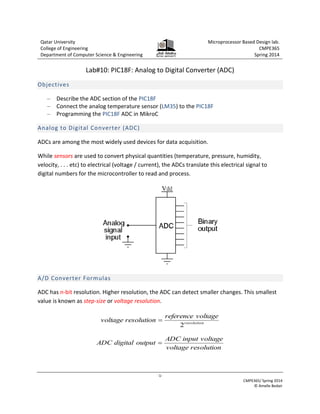
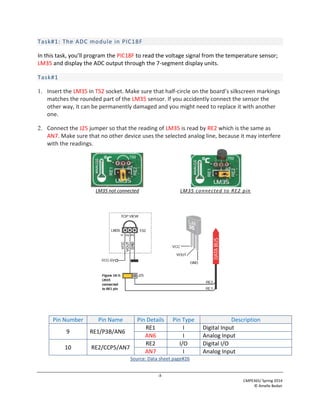
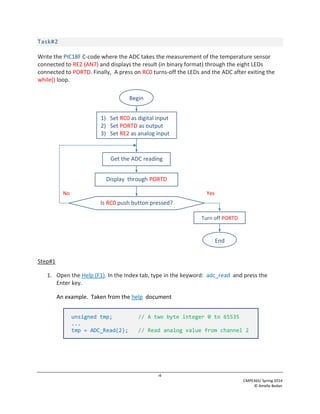
This document describes a lab experiment using an analog temperature sensor connected to a PIC18F microcontroller. The objectives are to describe the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) section of the PIC18F, connect an LM35 temperature sensor, and program the PIC18F to read the sensor values using its ADC. Students will write code to take an ADC reading from the temperature sensor on channel 7, display the 10-bit value on 8 LEDs, and turn off the LEDs when a button is pressed. The document provides background on ADCs and guidance on connecting the sensor and programming the ADC to read temperature values in Celsius.