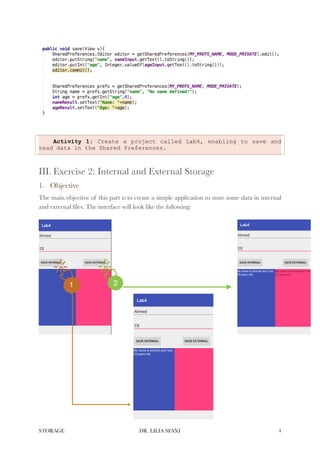
This document discusses different storage options in Android applications, including Shared Preferences, internal storage, external storage, and SQLite databases. It provides code examples for storing and retrieving data from Shared Preferences and reading and writing to internal and external files. The exercises guide the reader to create an Android application that uses Shared Preferences to save user preferences, and reads and writes to internal and external files to store application data.