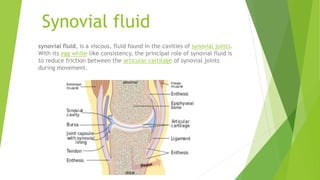
Synovial fluid is a viscous fluid found in cavities of synovial joints. Its role is to reduce friction between cartilage during movement. Synovial fluid may be collected via arthrocentesis, where a syringe is used to aspirate fluid from the joint capsule. Aspirated fluid is analyzed in a microbiology lab to diagnose infections like septic arthritis. Bacteria can enter joints through various routes and cause rapid cartilage damage and pain. Common bacteria that may be found in synovial fluid include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.