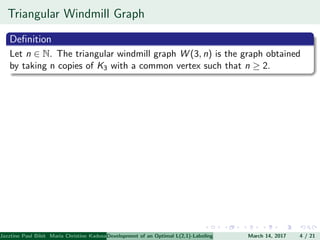
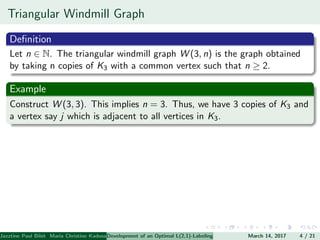
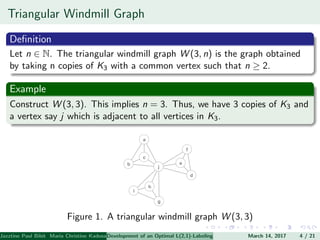
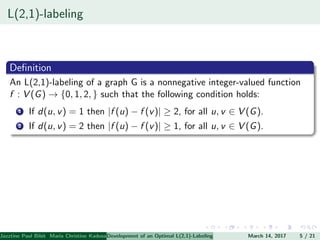
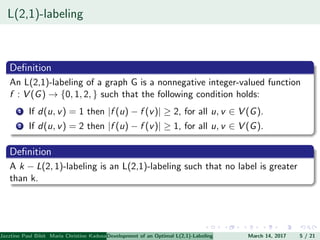
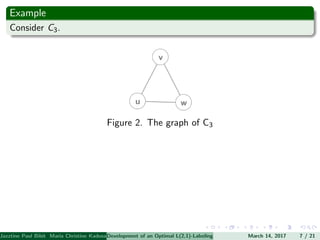
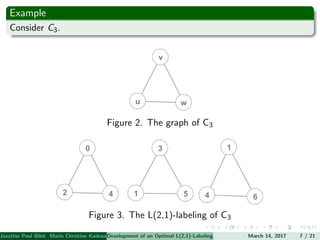
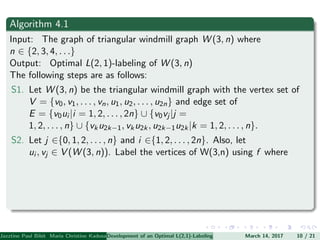
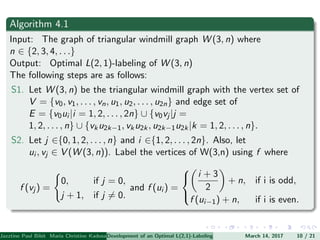
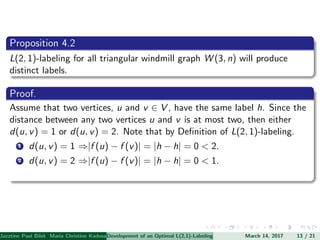
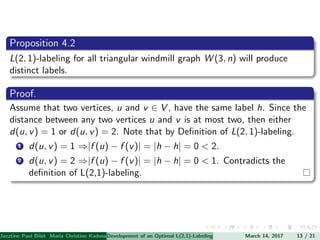
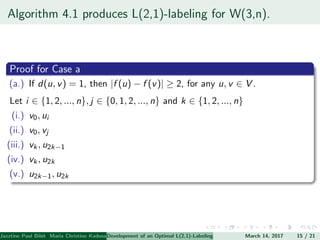
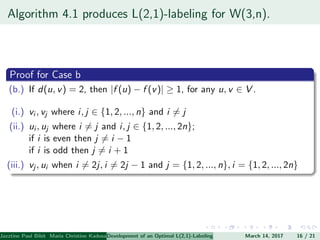
The document presents an algorithm to find an optimal L(2,1)-labeling for triangular windmill graphs. It begins with definitions of triangular windmill graphs, L(2,1)-labelings, and the Chang-Kuo algorithm. The Chang-Kuo algorithm is then applied to obtain an L(2,1)-labeling of a triangular windmill graph W(3,n) by iteratively finding and labeling maximal 2-stable sets. The maximum label used is the labeling number λ(G).
![Introduction
L(2,1)-labeling
1 Griggs and Yeh [7] ”Labeling Graphs with a Condition at Distance
Two”
2 Chang and Kuo [5] ”The L(2,1)-labeling Problem on Graphs”
3 Fiala, Klox and Kratochvil [6] ”Fixed Parameter Complexity of
L(2,1)-labelings”
4 Calamoneri and Vocca [4] ”Approximability of the L(h,k)-Labeling
Problem”
5 F. Roberts [10] ”Channel Assignment Problem”
Jazztine Paul Bibit Maria Christine Kadusale Marc Christian Satuito Ma. Jomelyn Ylen (Department of Mathematics PolytechnicDevelopment of an Optimal L(2,1)-Labeling Scheme for Triangular Windmill GraphMarch 14, 2017 2 / 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onl21-labeling-170327164252/85/L-2-1-labeling-2-320.jpg)