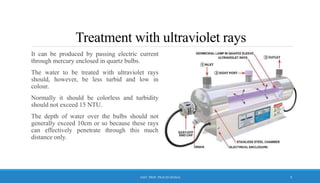
The document discusses the importance of water disinfection to eliminate harmful microorganisms and ensure microbial safety in drinking water. Various disinfection methods are highlighted, including physical (filtration, boiling), radiation (UV), and chemical methods (chlorination, ozonation). The text outlines the objectives, ideal properties of disinfectants, and the advantages and disadvantages of different treatment options.