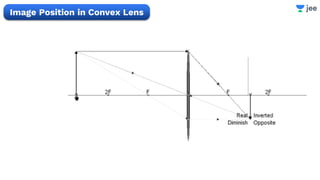
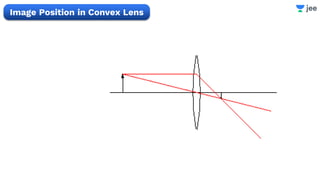
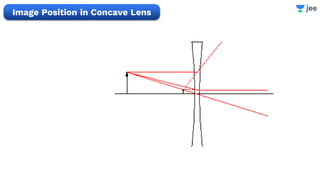
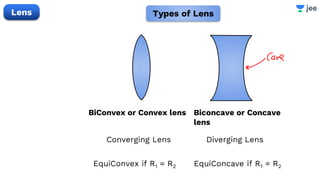
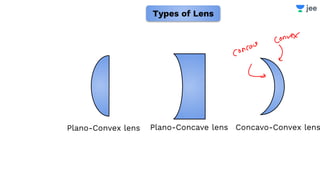
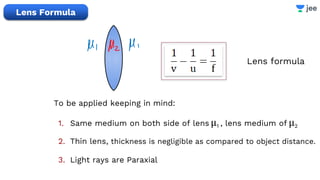
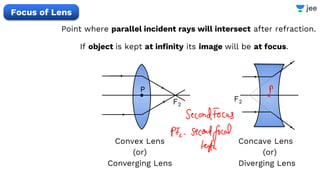
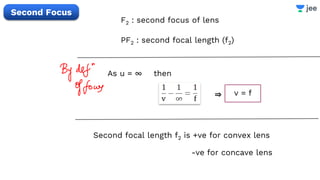
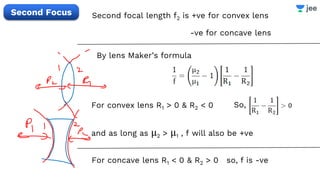
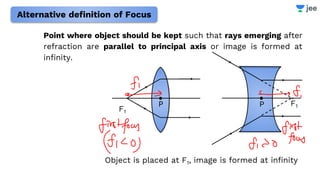
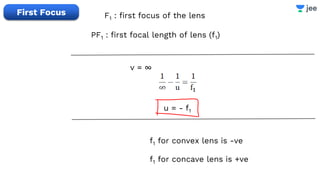
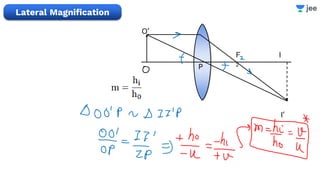
- The document discusses key concepts in ray optics and lens formula including different types of lenses, focal length, lens maker's formula, and image formation using lenses.
- It provides examples of problems calculating focal length, image position and size, and power of lenses using the lens formula and definitions of focal length.
- The document is a lecture on lens formula and ray optics by an experienced physics educator, providing an overview of core concepts and examples to help students learn.




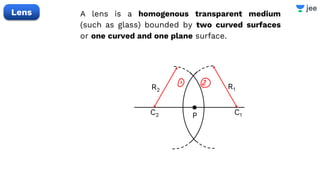
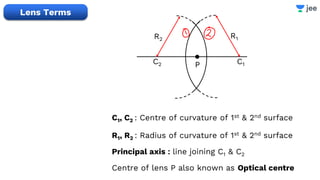
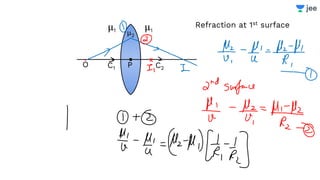
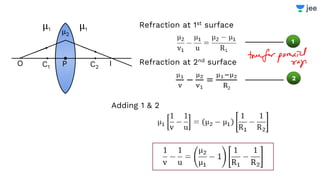
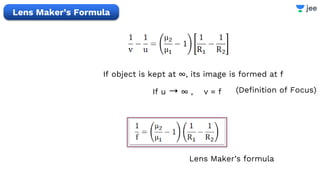
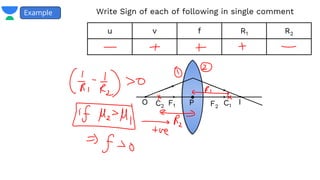
![Find the focal length of lens
Example
10 cm
10 cm
1.5
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-22-320.jpg)
![Find the focal length of lens
Example
1.5
10 cm
10 cm
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-23-320.jpg)
![Find the focal length of lens
Example
μ = 2
20 cm
μ = 1
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]
20 cm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-24-320.jpg)
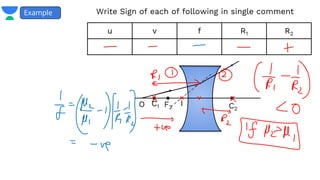
![Example
Concave lens of focal length 20 cm has object placed 12 cm
from it. Determine position of image.
A. 12.5 cm B. -9.5 cm D. 11 cm
C. -7.5 cm
MCQ type Question [ +4 , -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-31-320.jpg)
![Example
Convex lens of focal length 15 cm has object kept at 45 cm
from it. If height of Object is 15cm determine, position and
height of Image.
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-34-320.jpg)
![Example
A. 25 m/s B. 15 m/s D. 5 m/s
C. 45 m/s
f = 30 cm
20 cm
5 m/s
Find velocity of image of Object O shown
MCQ type Question [ +4 , -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-35-320.jpg)

![Find f
Example
60 cm 15 cm
1.5
A. 20 cm B. 18 cm D. 24 cm
C. 12 cm
MCQ type Question [ +4 , -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-40-320.jpg)
![Example
f = 15 cm
45 cm
O
A. 22.5, +2.5 B. 23.5, +1.5 D. 20.5, +1.5
C. 22.5, -2.5
Determine position & height of image when Object is
5cm high kept as shown:
MCQ type Question [ +4 , -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-41-320.jpg)
![Example
f = 12 cm
32 cm
Find position of object for which Image is formed 32 cm from
lens
A. 22.5 B. 17.5
D. 20
C. 19.2
MCQ type Question [ +4 , -1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-42-320.jpg)
![Example
Concave lens of focal length 20cm has object of height 2 cm
at 10 cm from it. Determine position and height of Image
formed?
Ans:
u = -10 cm,
h0 = 2 cm,
f = -20 cm,
v = -20/3 cm,
hi = +4/3cm
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-43-320.jpg)
![Example
Find the position where convex lens of focal length 9cm
must be placed so that the image of both Objects is
formed at same place
O1 O2
24 cm
9 cm
18 cm from O1
Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-44-320.jpg)
![Convex lens made of glass (1.5) of focal length 50 cm is
immersed in water μ = 4/3. What is its focal length in water?
Example Numerical Answer Type Question [ +4 , 0]
Ans: 100 cm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l1rayopticslenses15thsep-230420164015-af4920a1/85/L1-Ray-Optics-_-Lenses-15th-Sep-pdf-45-320.jpg)












