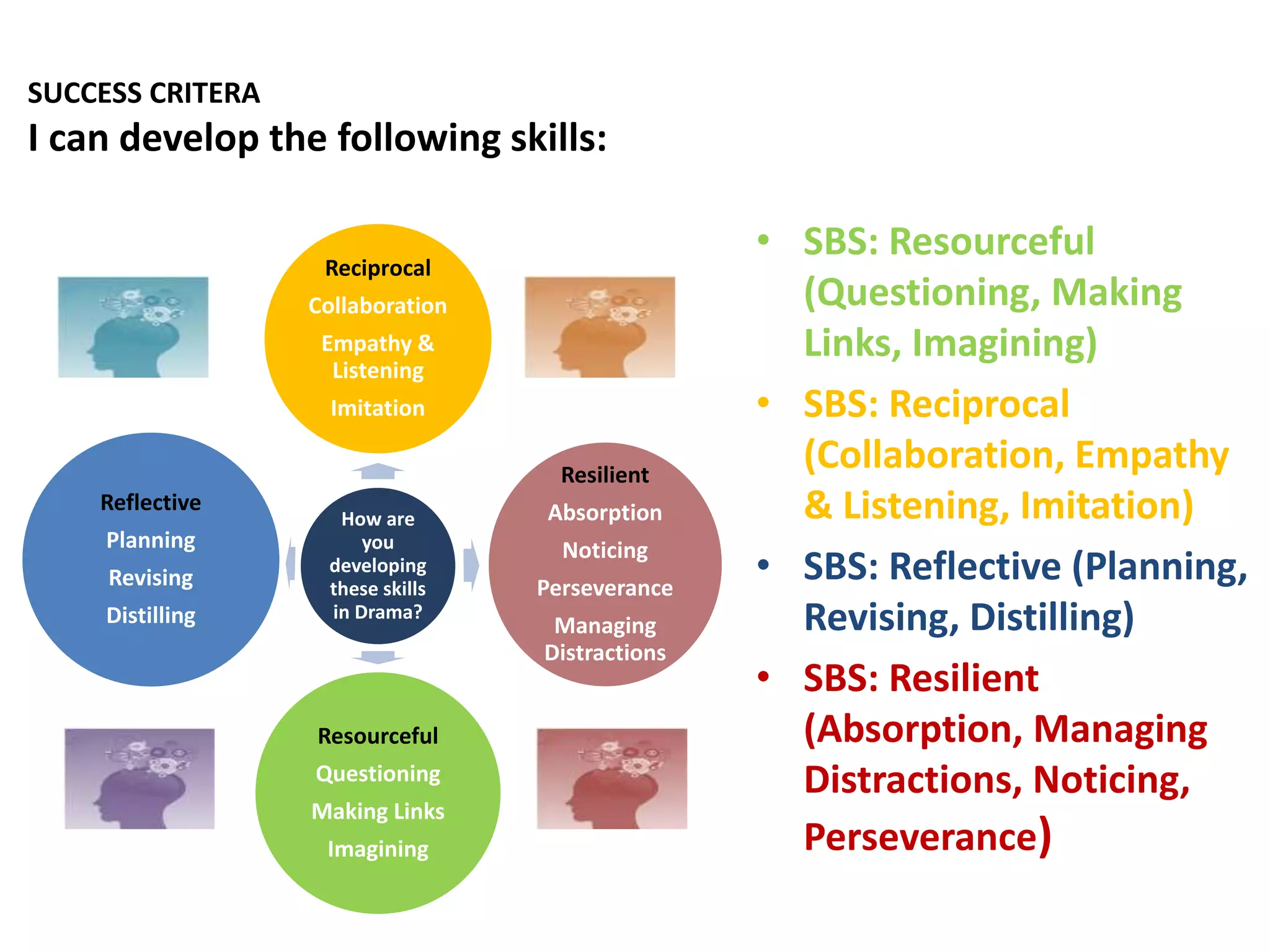
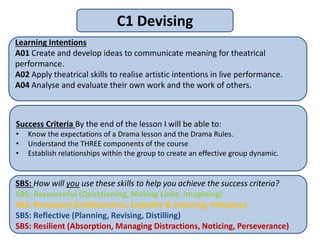
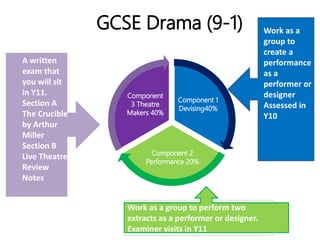
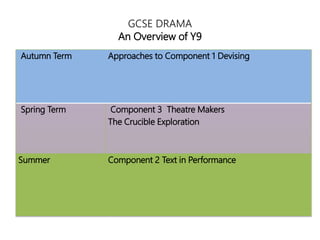
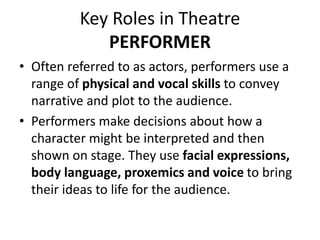
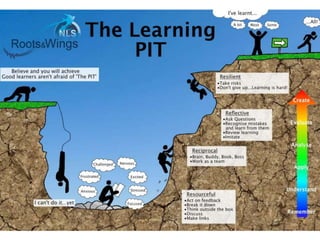
This document outlines the key components of a GCSE drama course, including the three assessment objectives. It provides an overview of what will be covered each academic year. It also defines devising and the collaborative skills needed for component 1. Reflective behaviour is identified as key to achieving high marks, including being self-aware, open to feedback, and motivated to improve.