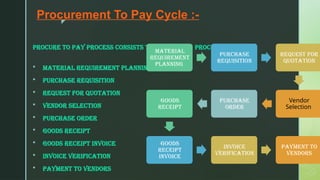
The document outlines the procurement to pay (P2P) cycle, which includes processes such as material requirement planning, purchase requisition, and invoice verification. It details each step's significance along with necessary documentation and tools used in the process, particularly focusing on vendor interactions and approvals. Best practices for procurement processes are also suggested for improving efficiency and preventing rejections.