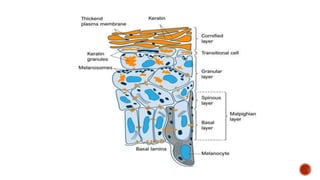
Keratin is a protein that forms hair, nails, and the outer layer of skin. It exists in two forms: alpha-keratin which is found in hair, nails, and horns of mammals, and beta-keratin which is found in feathers, claws, and scales of birds and reptiles. Keratinocytes are the main cell type in the outermost epidermal layer of skin, constituting 90% of epidermal cells. Keratinocytes form a protective barrier against environmental damage and migrate upwards through the epidermis as they differentiate. This process, known as cornification, results in the shedding of corneocytes from the skin surface approximately every 40-56 days.