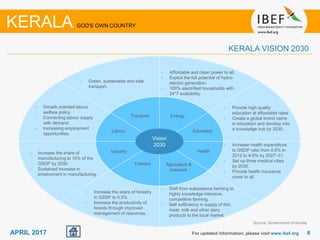
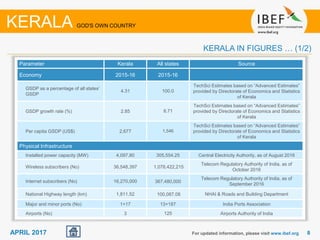
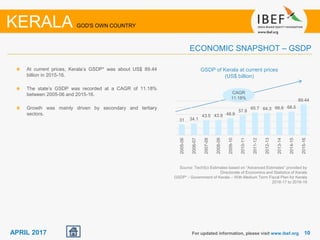
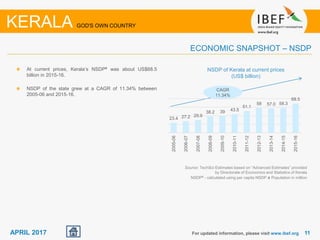
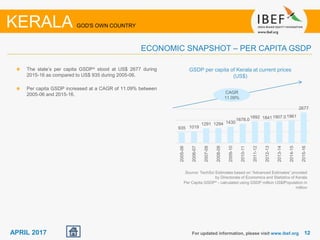
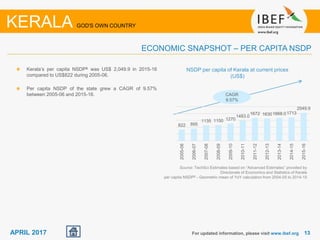
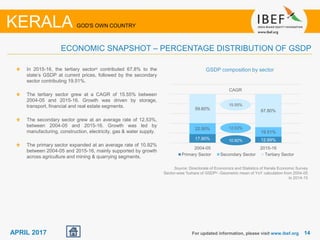
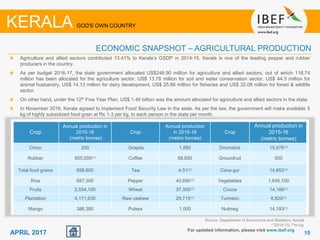
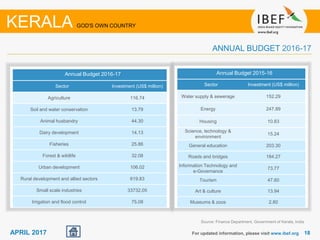
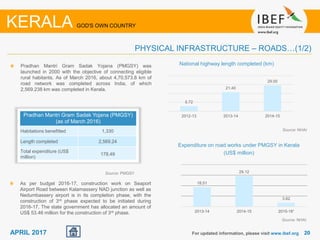
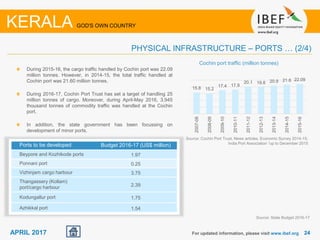
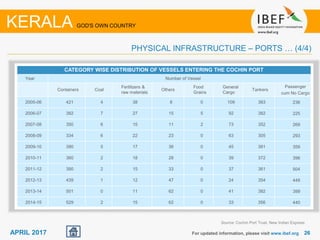
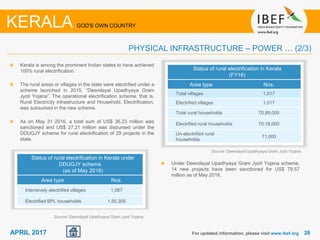
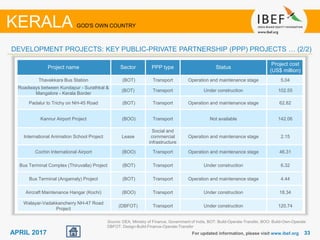
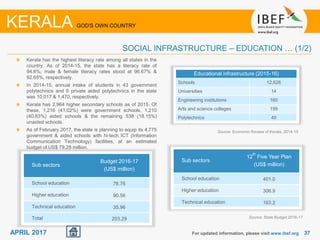
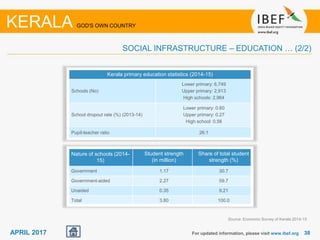
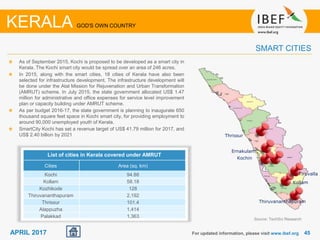
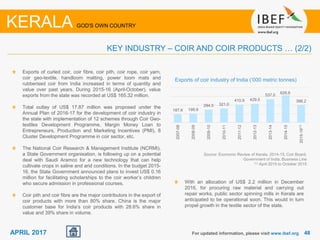
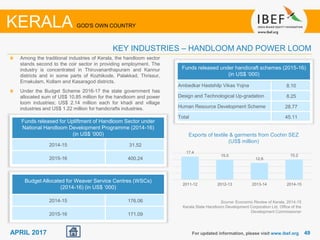
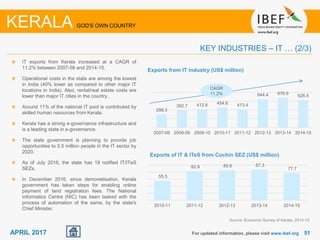
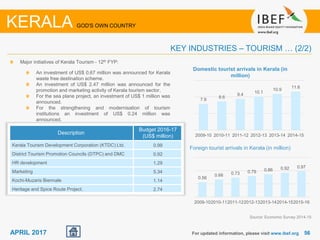
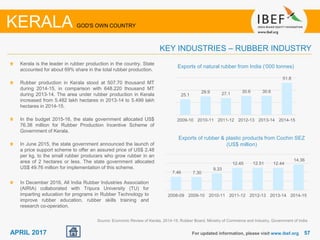
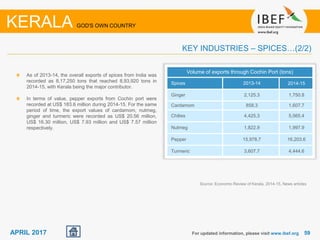
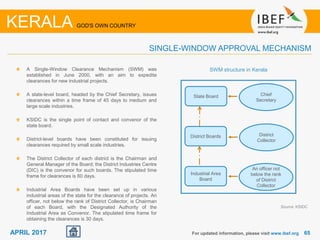
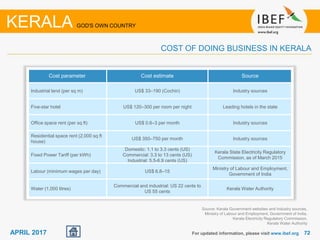
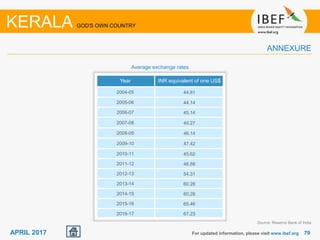
Kerala has a high literacy rate and sex ratio. It is known for its natural beauty and cultural diversity that attract many tourists. The state receives large foreign remittances and has a strong agricultural sector with crops like rubber, pepper, and coconut. Kerala aims to further develop its industries, infrastructure, education, and healthcare by 2030 as outlined in its vision plan. It has a well-educated population and ranks high on investment climate indexes.