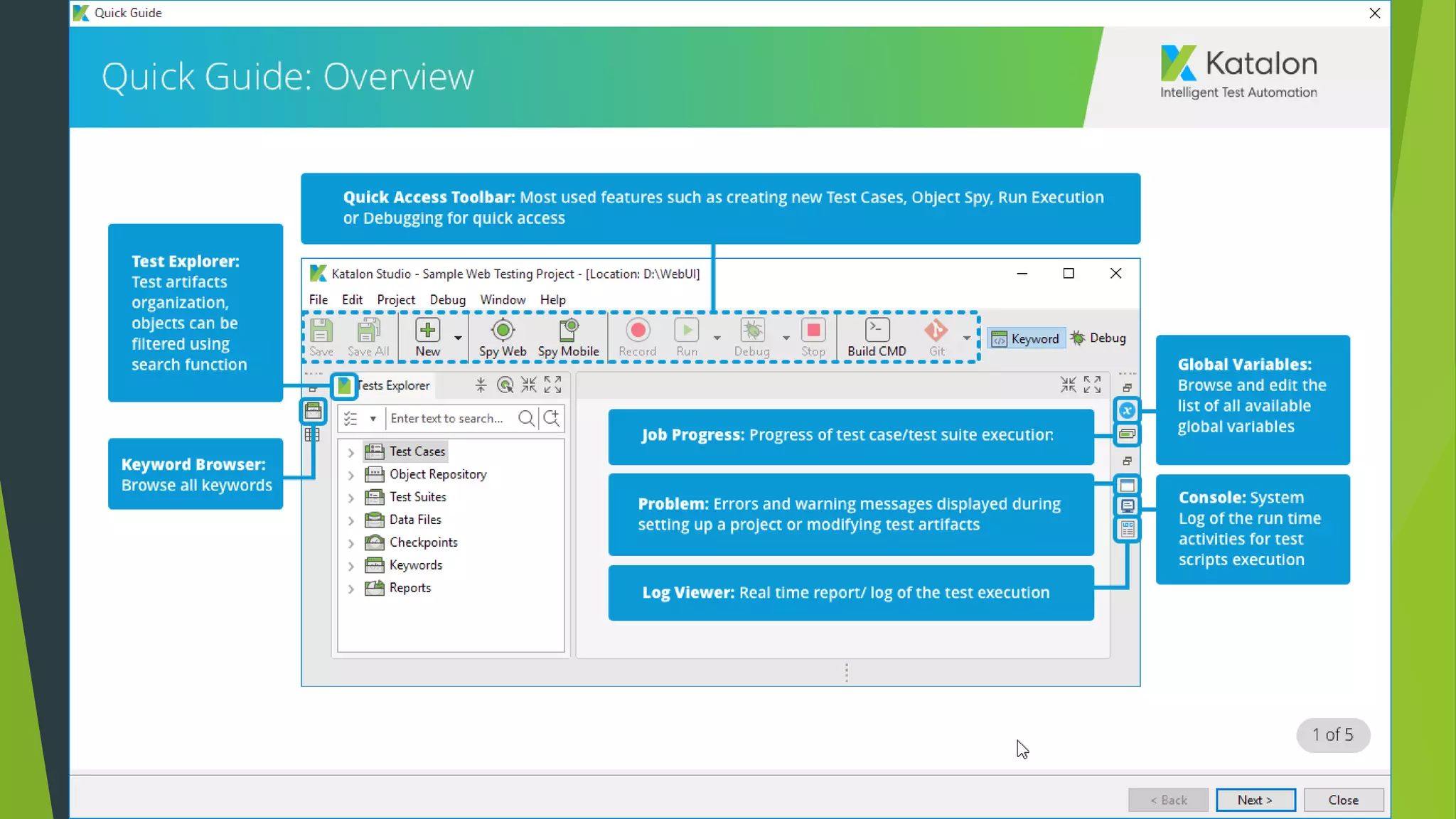
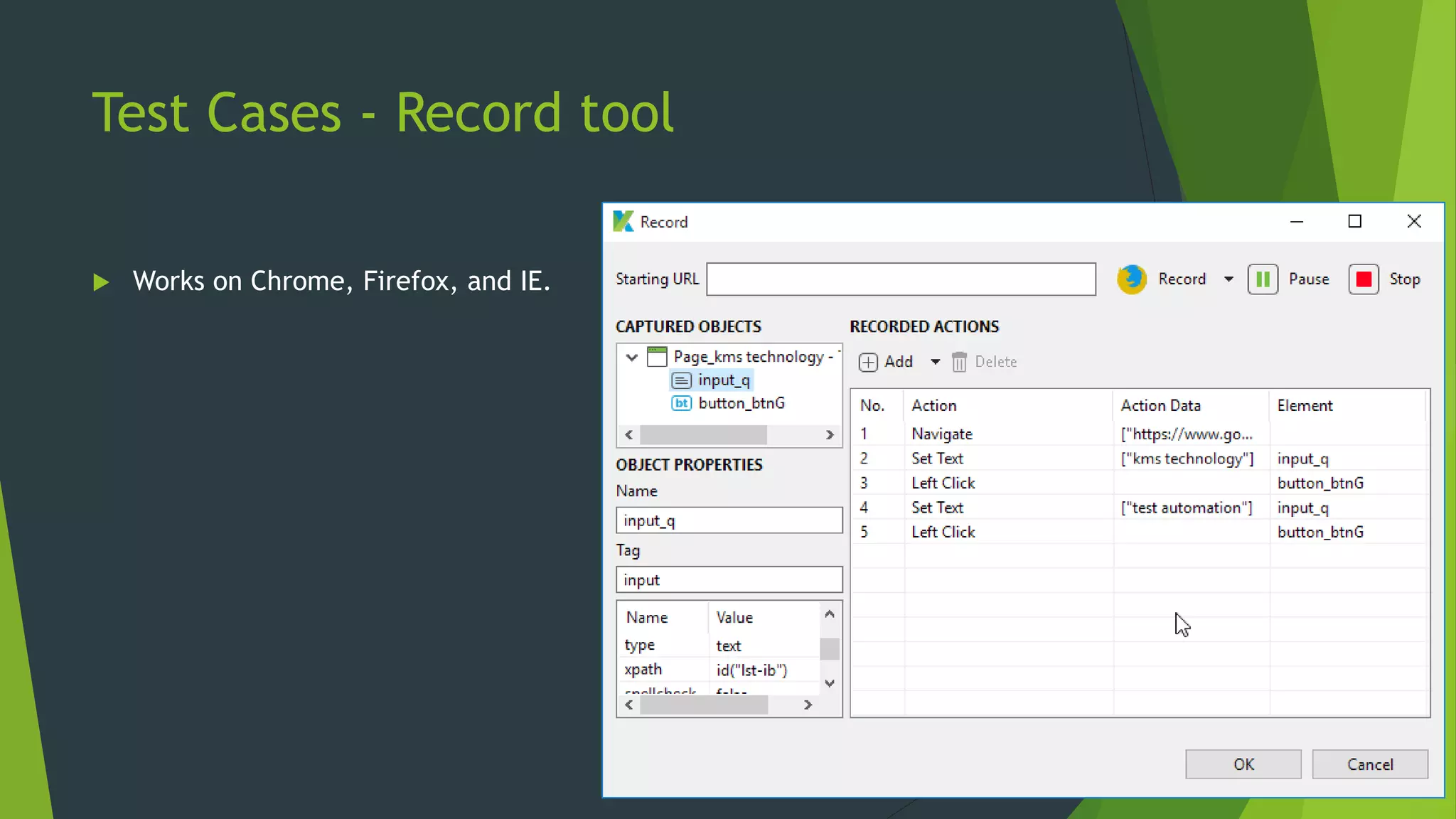
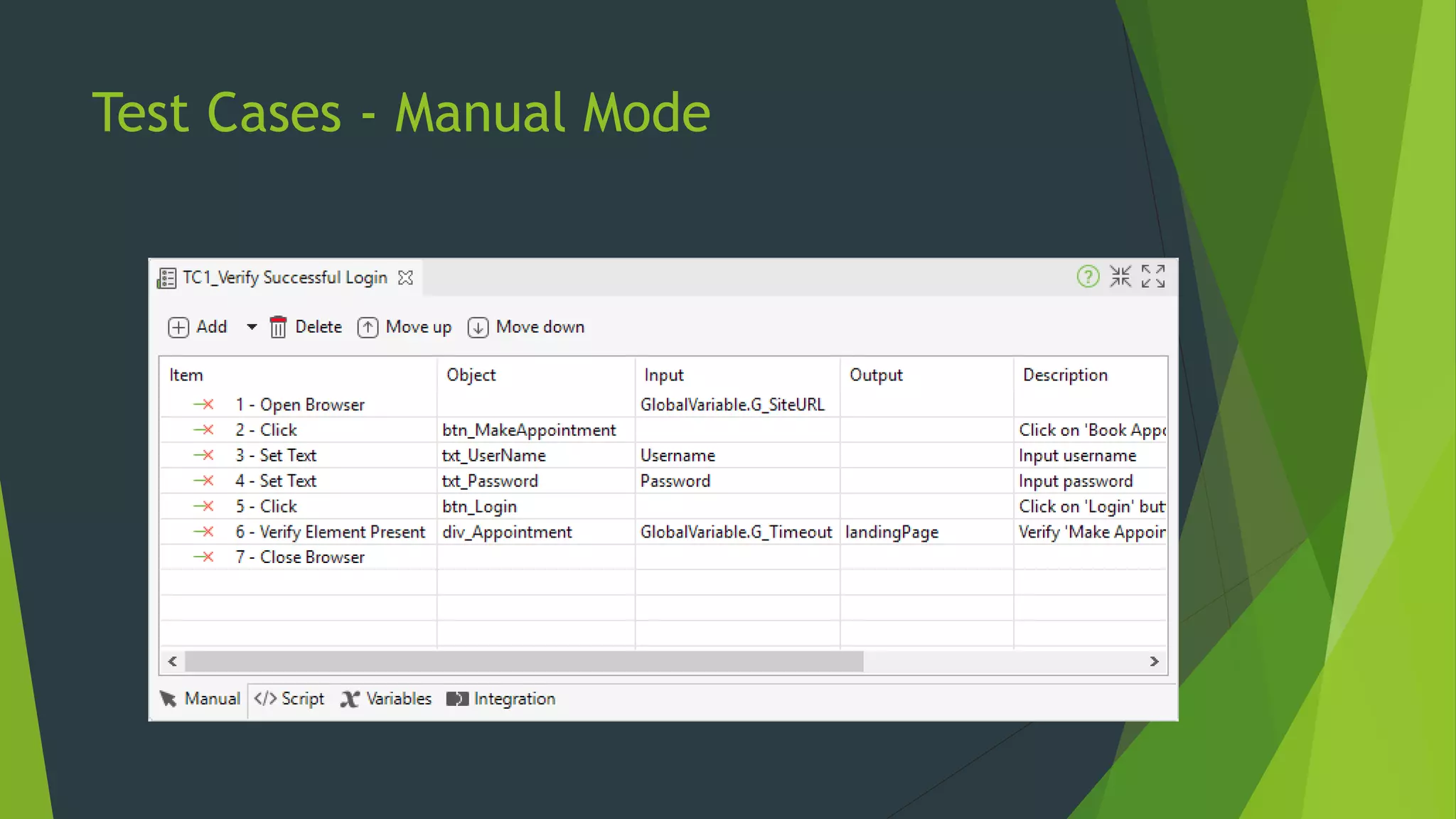
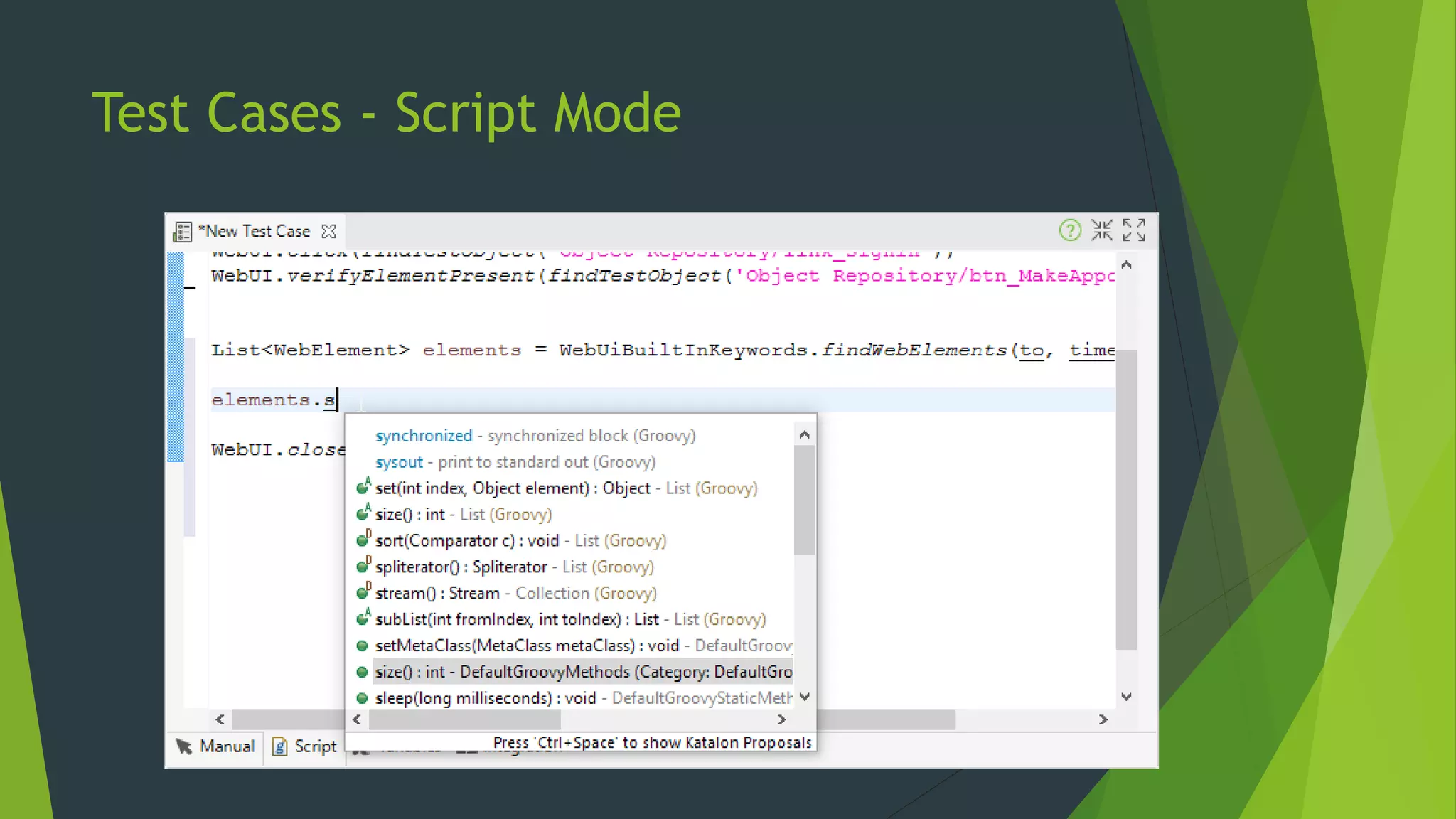
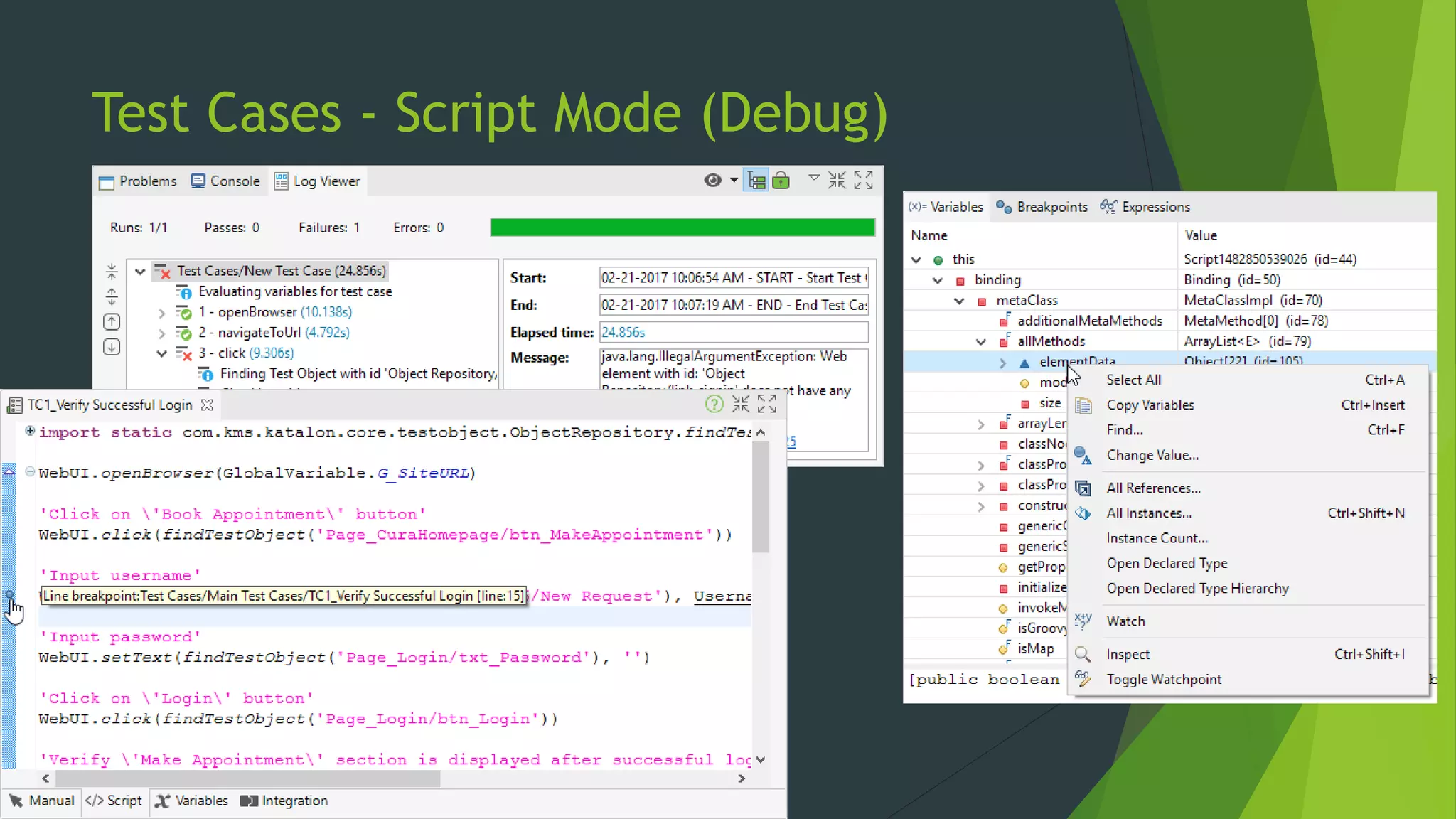
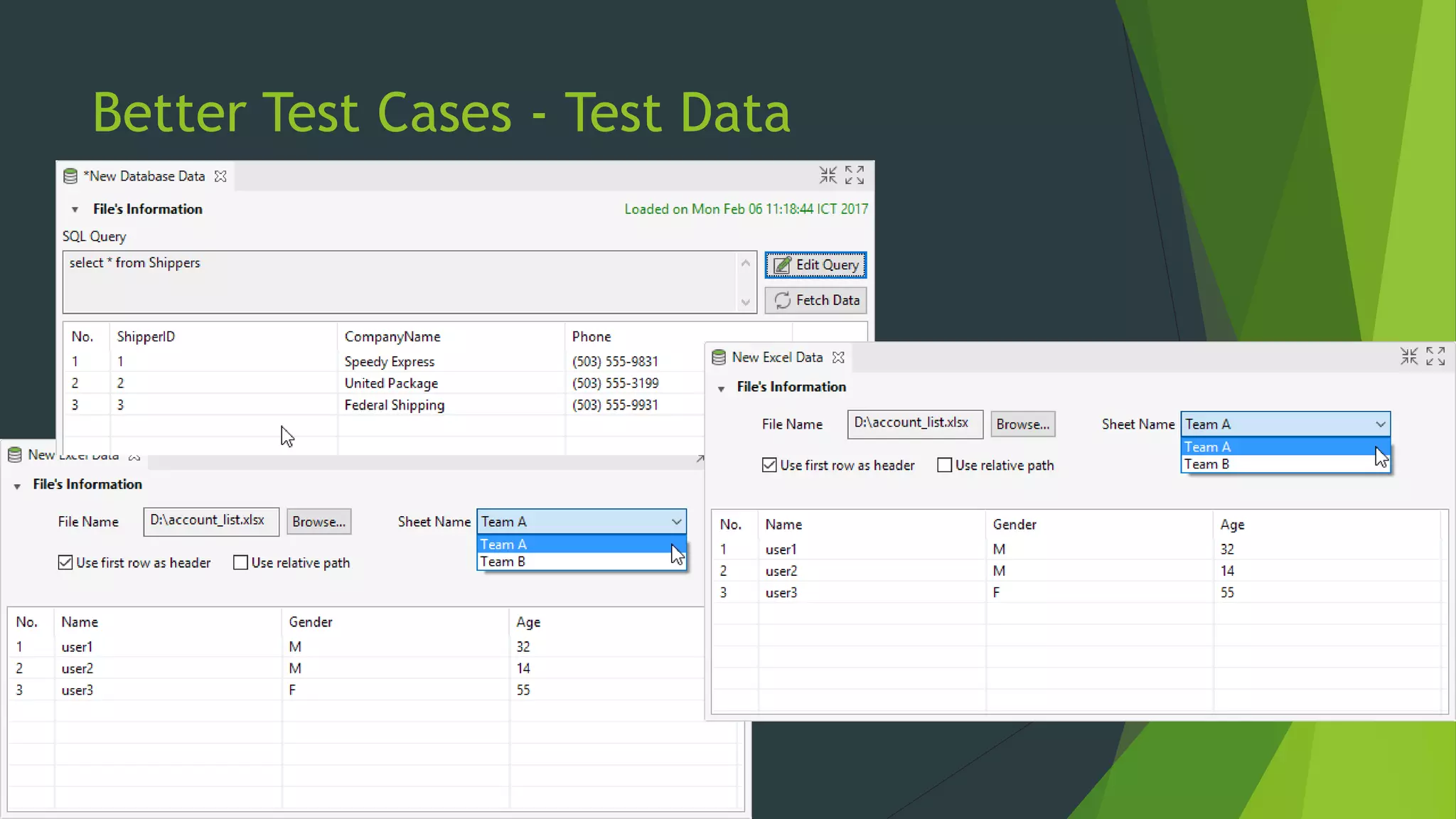
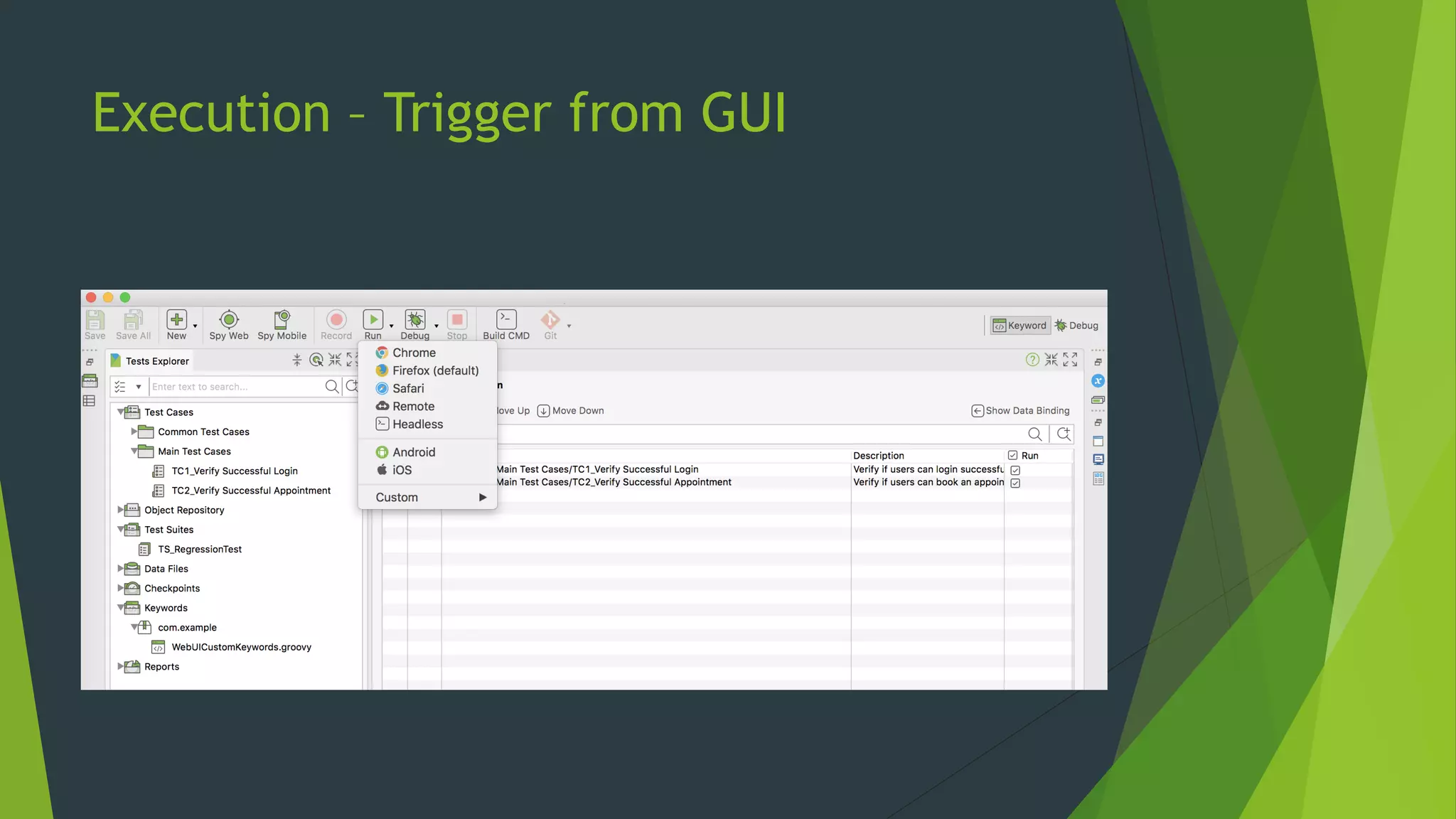
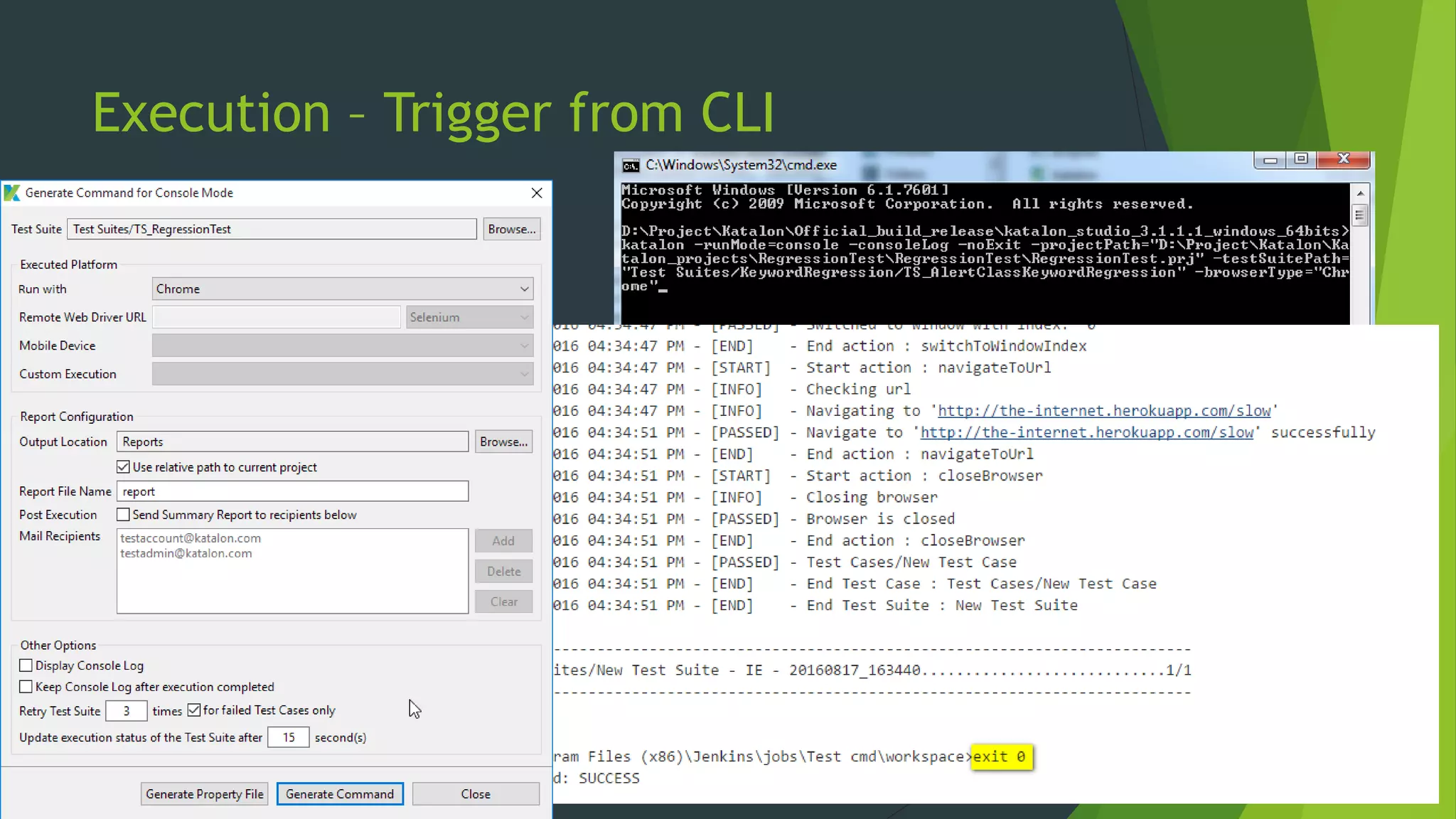
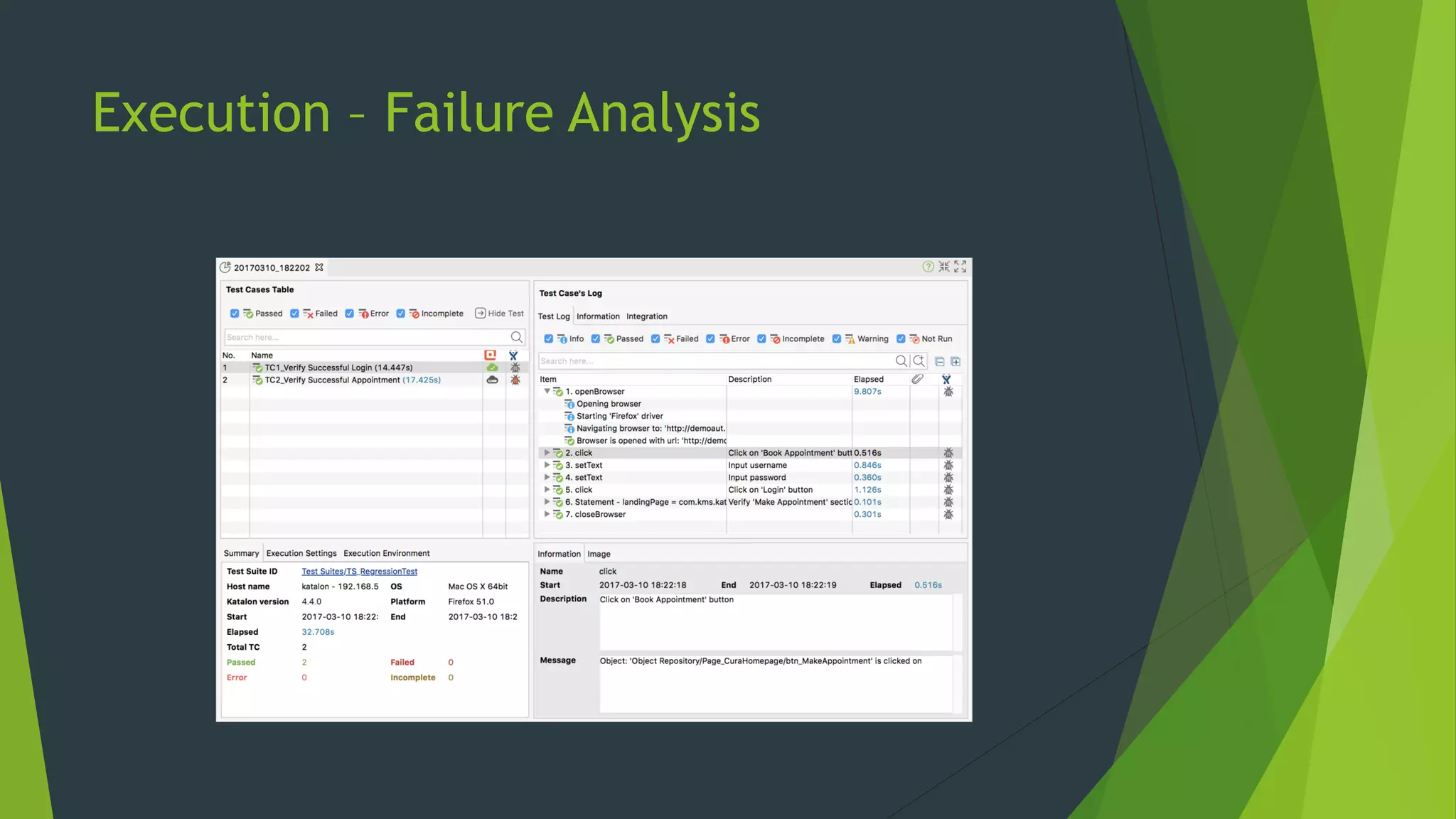
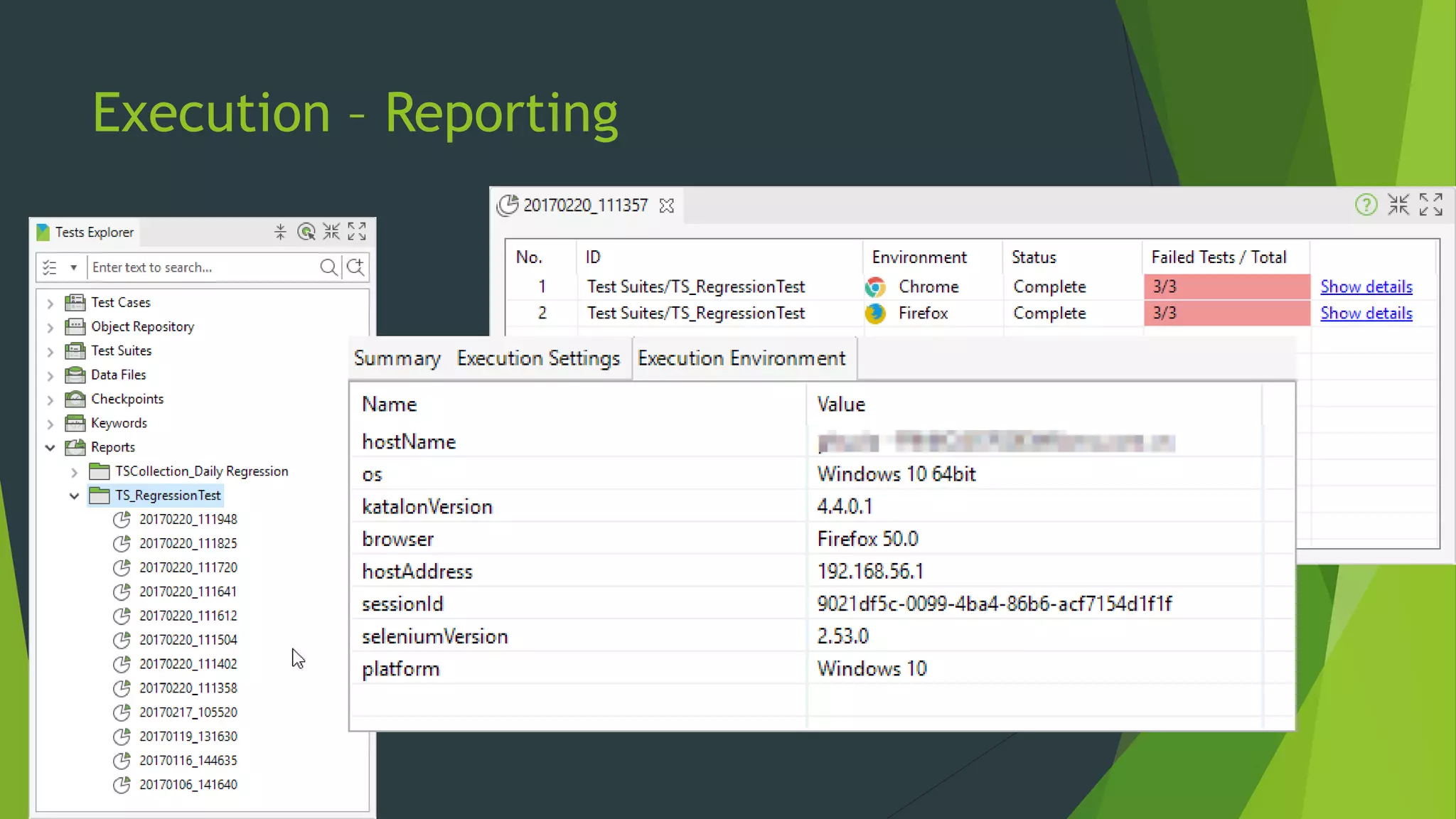
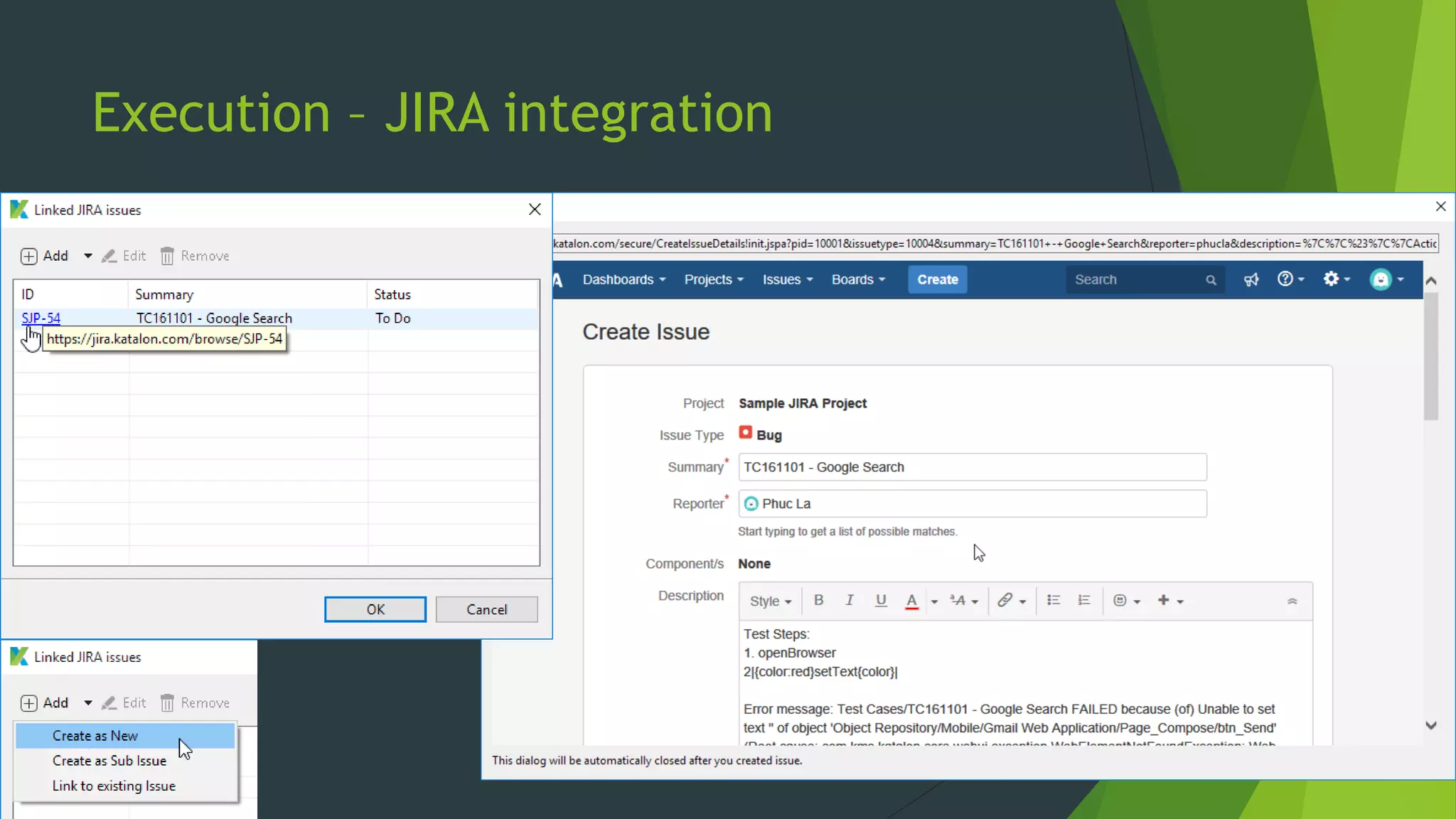
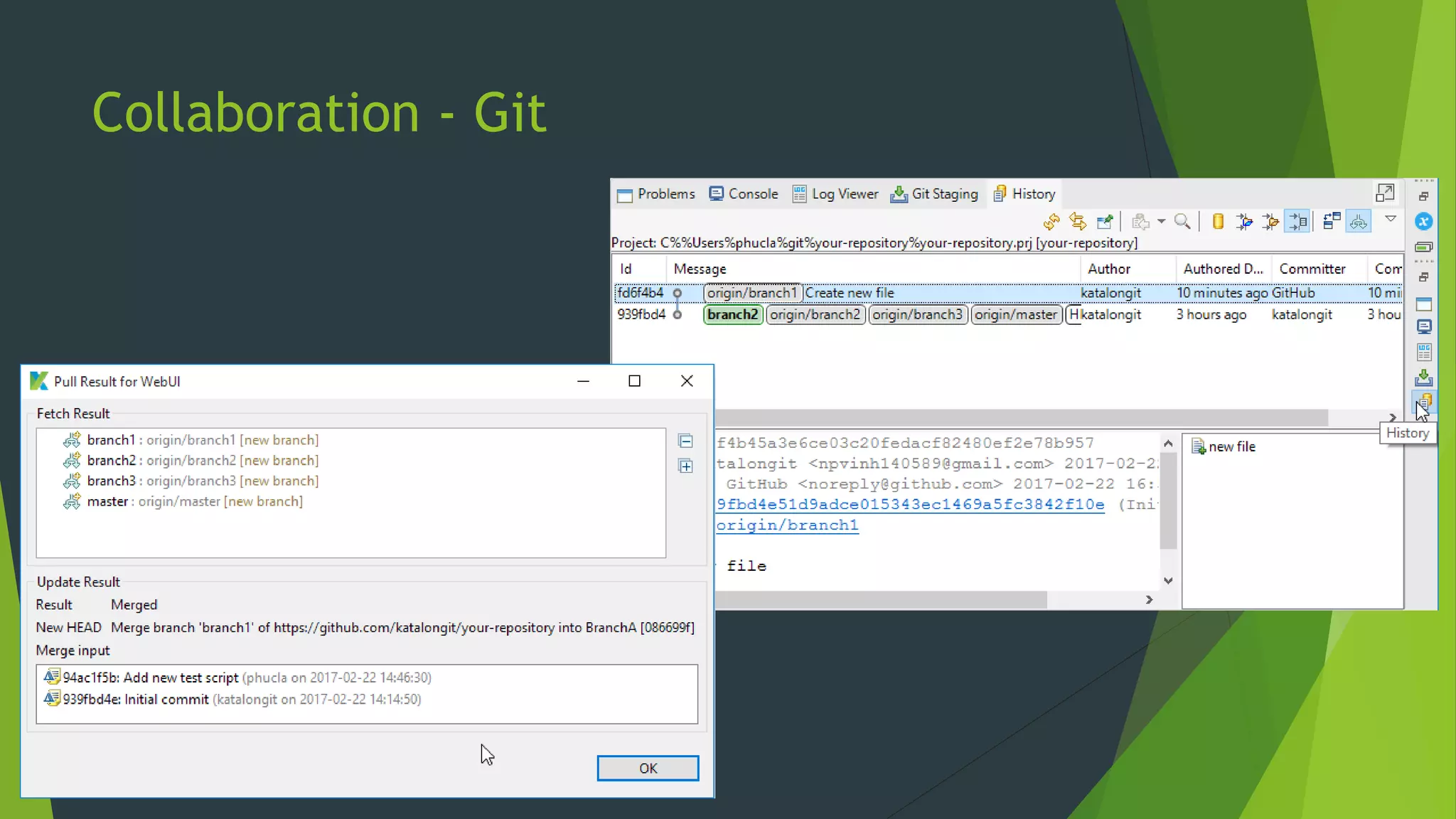
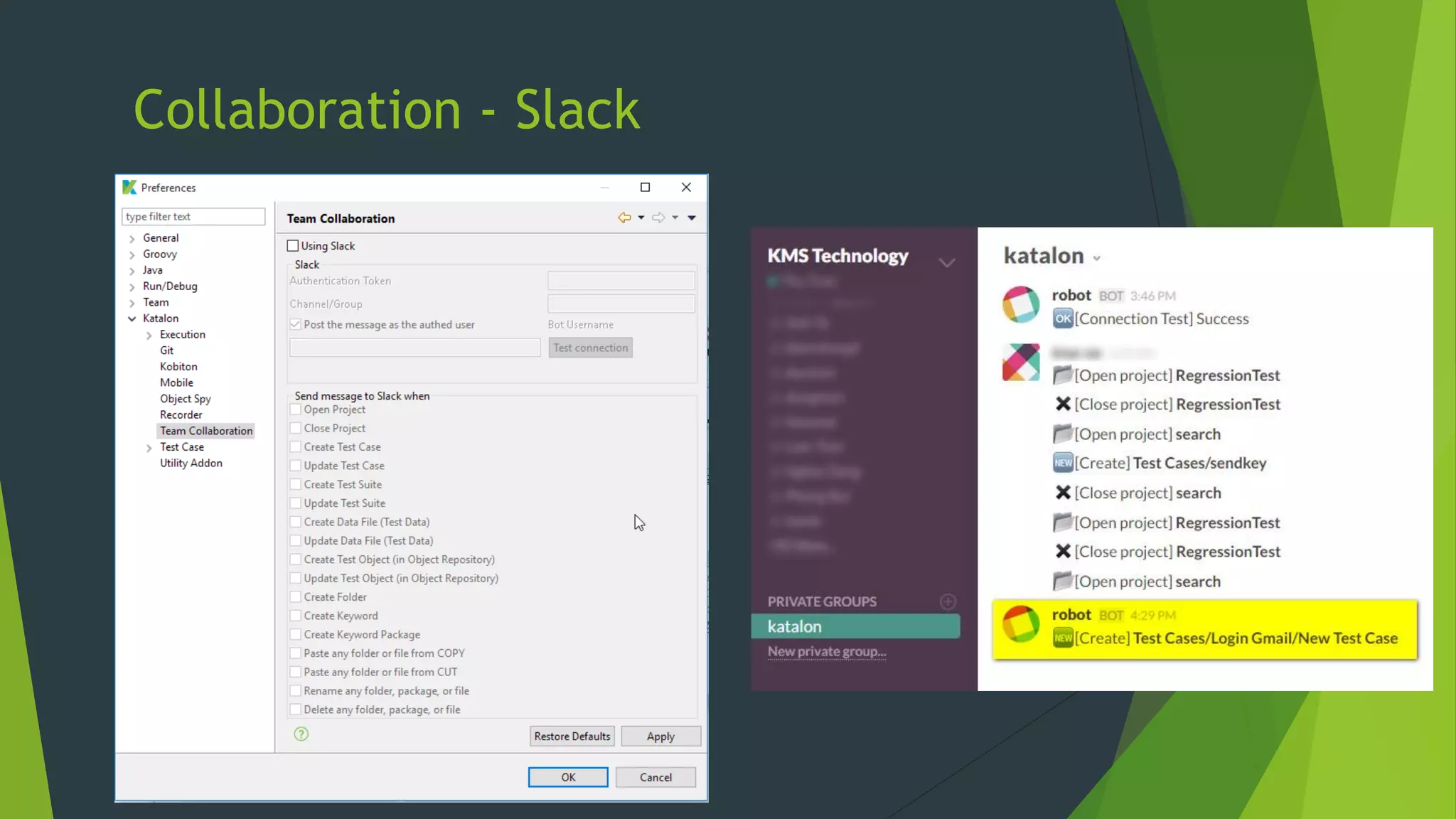
Katalon Studio is a free functional test automation IDE designed to enhance collaboration between testers and developers, addressing the complexities of modern web and mobile application testing. It allows for test case creation through recording, manual selection, or scripting in Groovy, all while integrating seamlessly with cloud services and offering powerful support for test management and execution. By bridging the gap between testers and developers, Katalon Studio aims to create efficient and effective functional test automation that meets the needs of both roles.