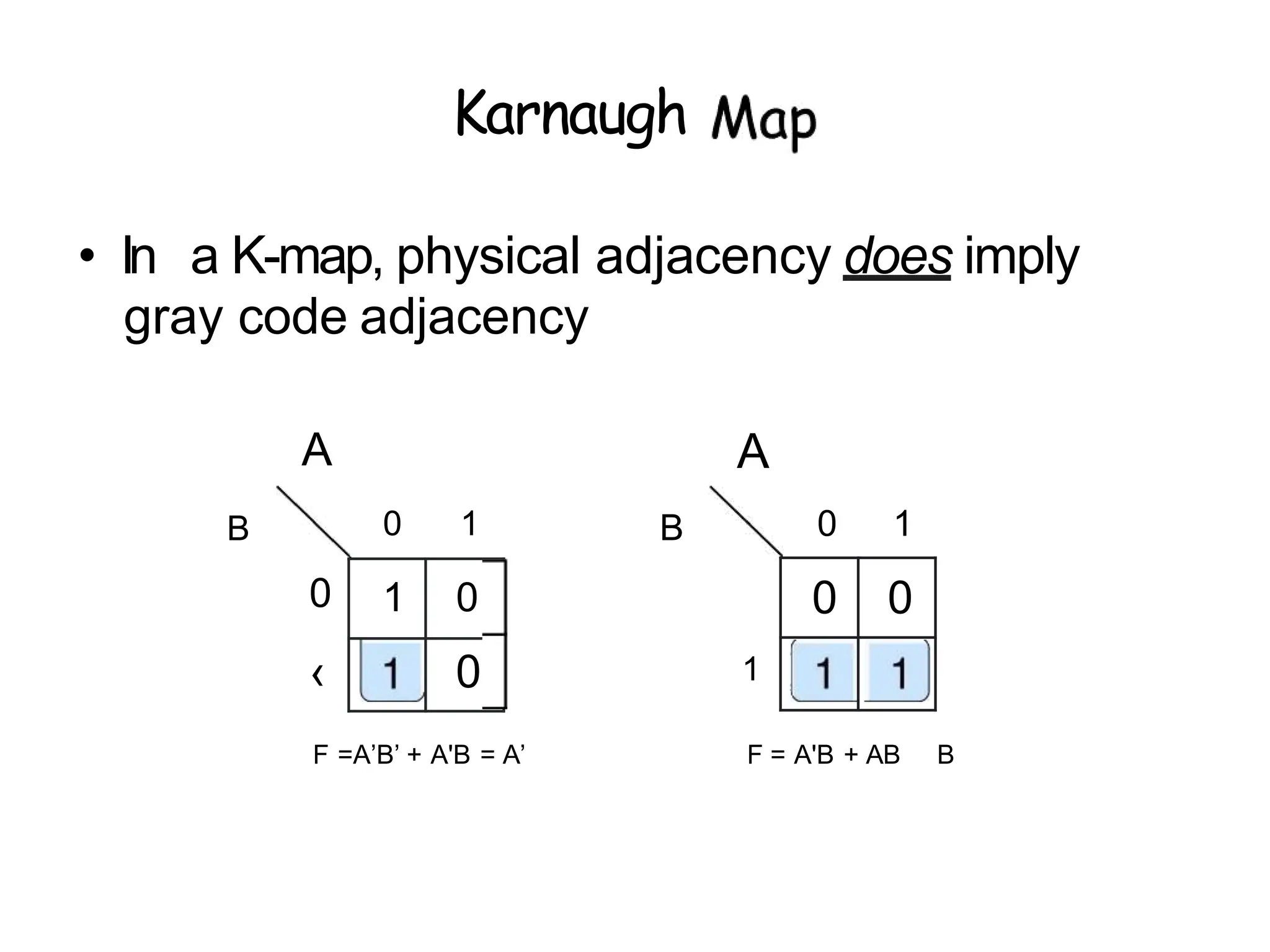
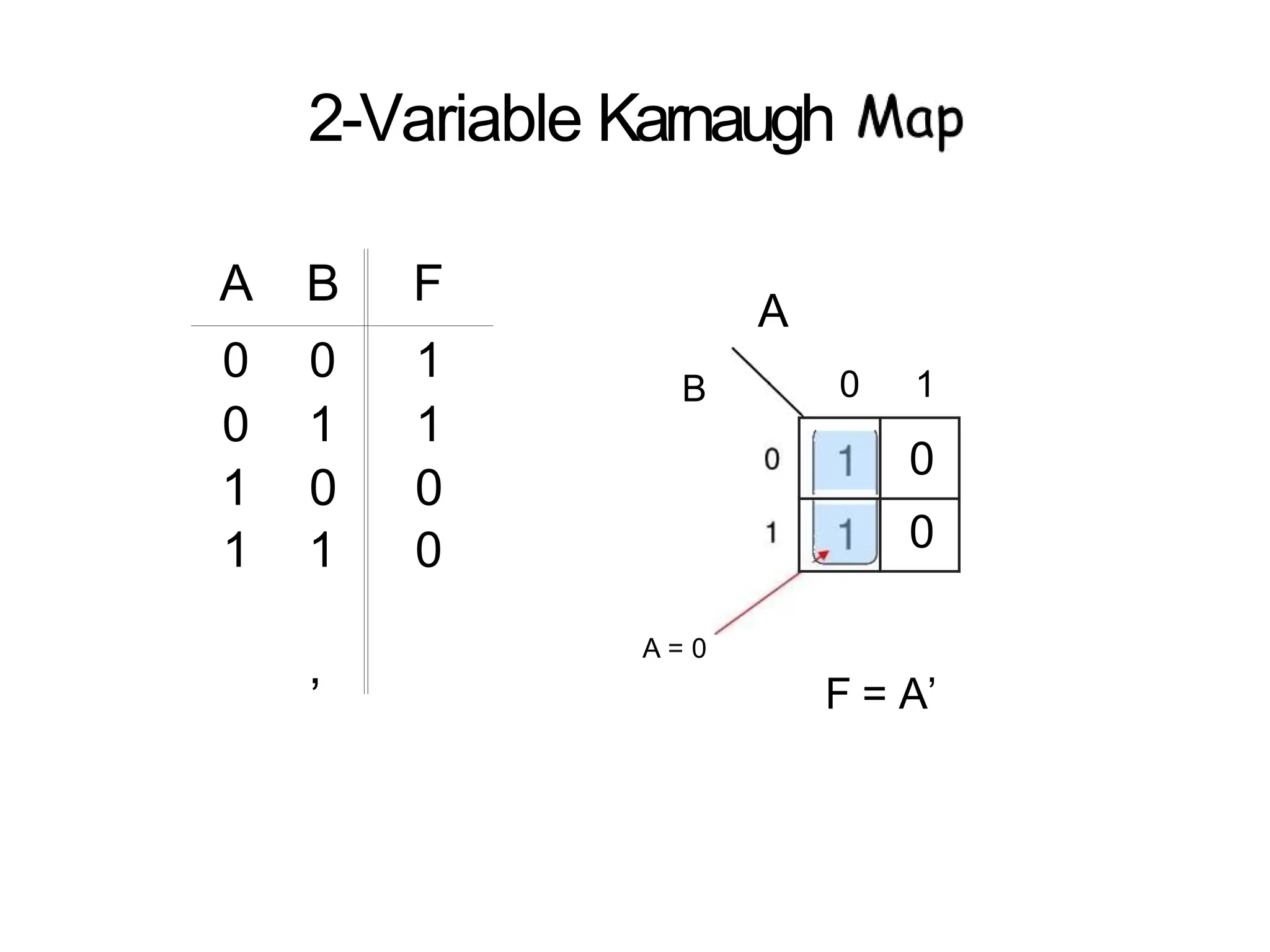
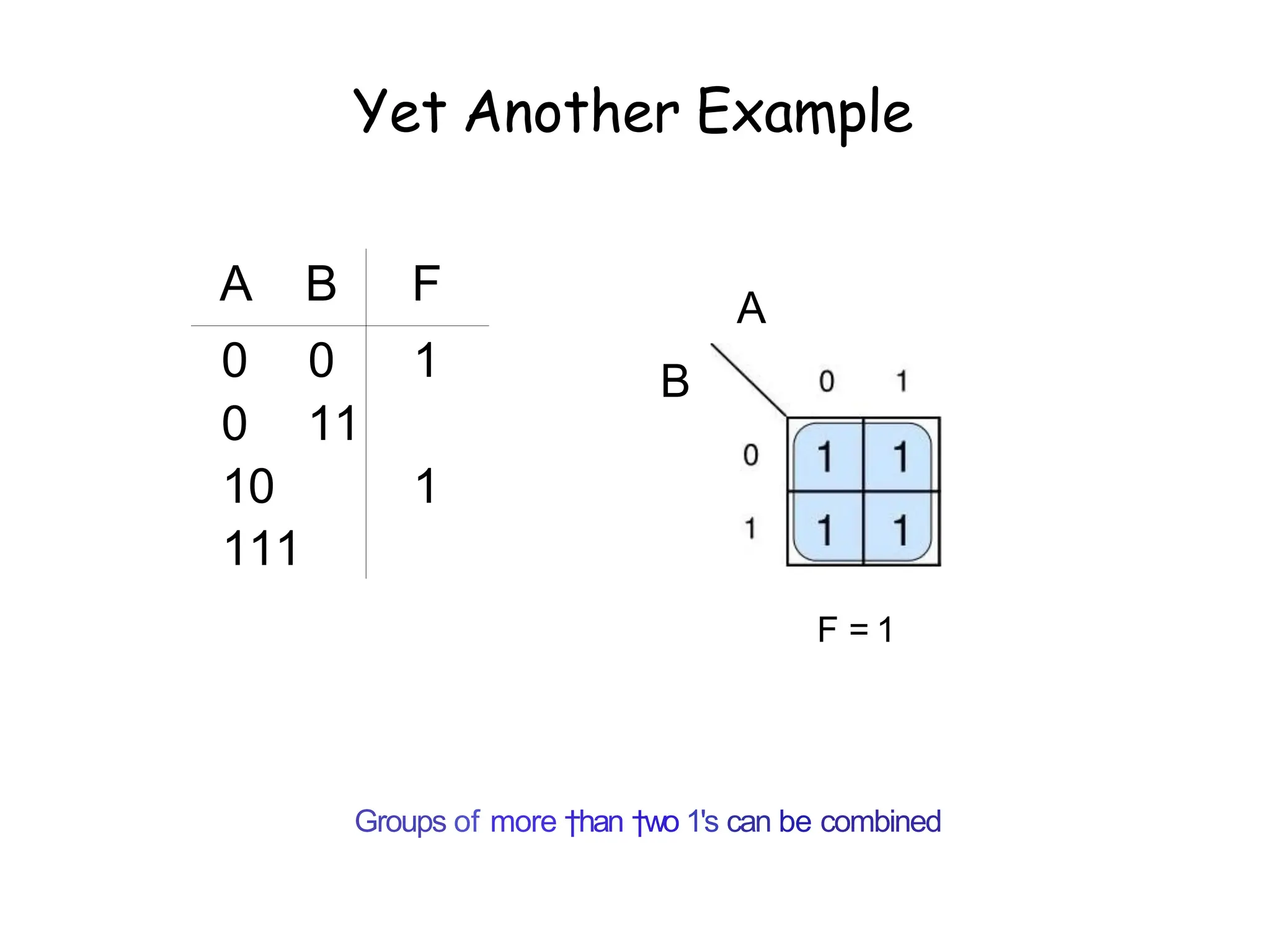
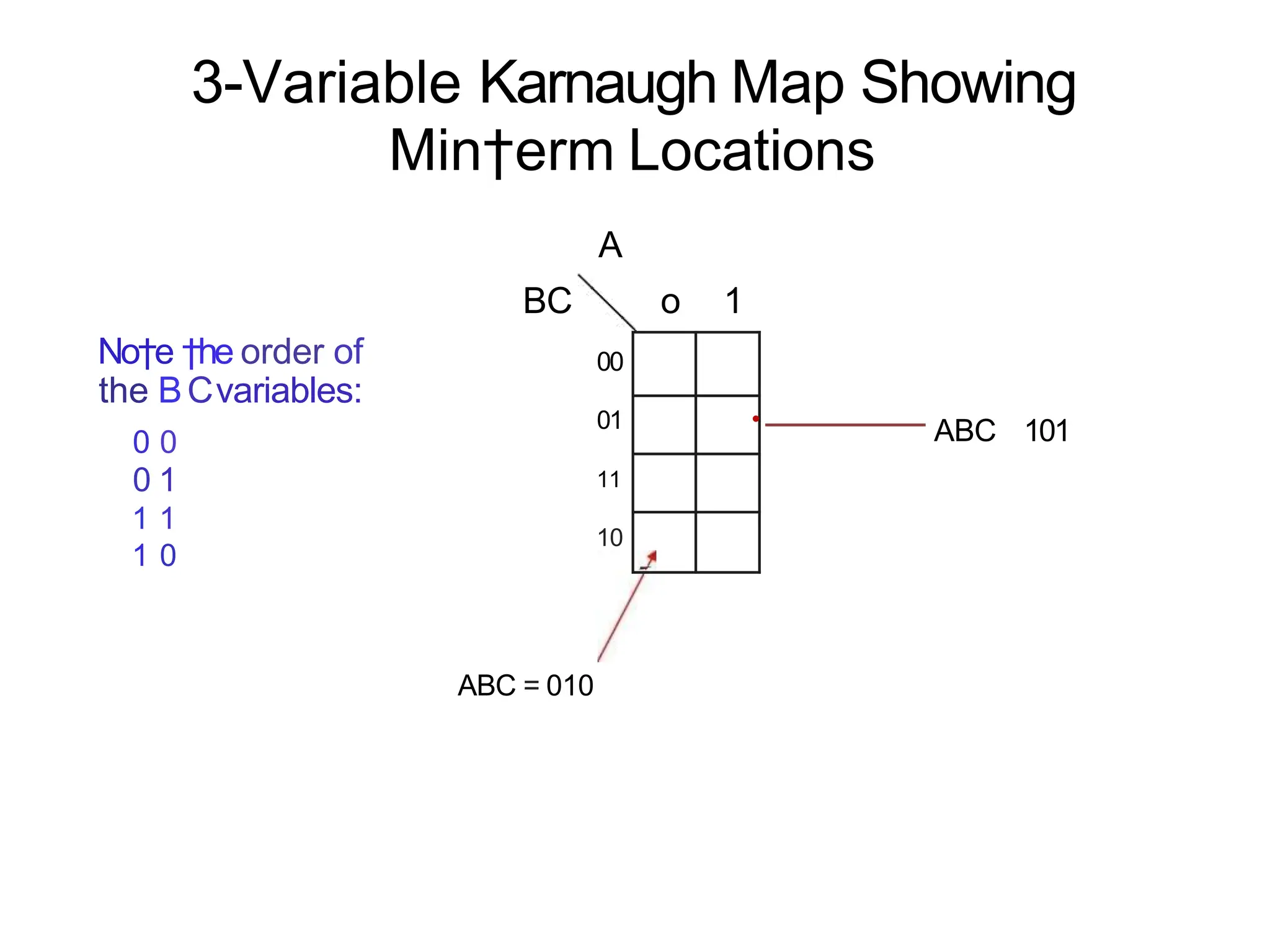
Karnaugh maps offer a systematic method for minimizing logic functions through graphical representation, simplifying the process compared to Boolean minimization. The document explains the adjacency in Gray code and how it applies to Karnaugh maps, emphasizing that physical adjacency in the map indicates Gray code adjacency. Various examples illustrate the application of Karnaugh maps for simplification of multi-variable logic functions.