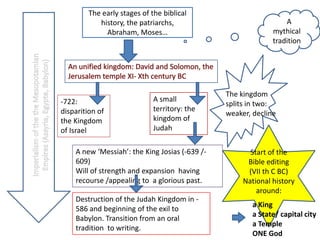
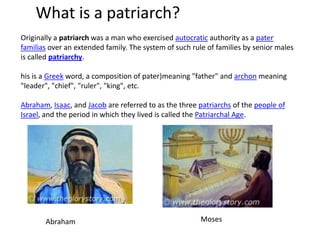
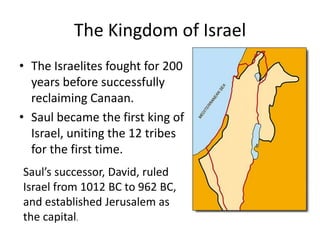
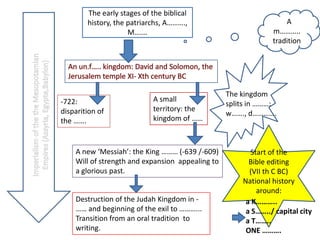
The early stages of Judaism began with the patriarchs Abraham, Moses, and the Israelites who settled in Canaan at God's command in 1900 BC. The kingdom of Israel was established but later split into the kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Both kingdoms were eventually conquered and the Israelites exiled, but maintained their religion. The editing of the Bible began as a way to preserve national identity and history during and after the exile. The diaspora and loss of the temple led to Judaism being centered around synagogues and rabbis rather than the land of Israel.