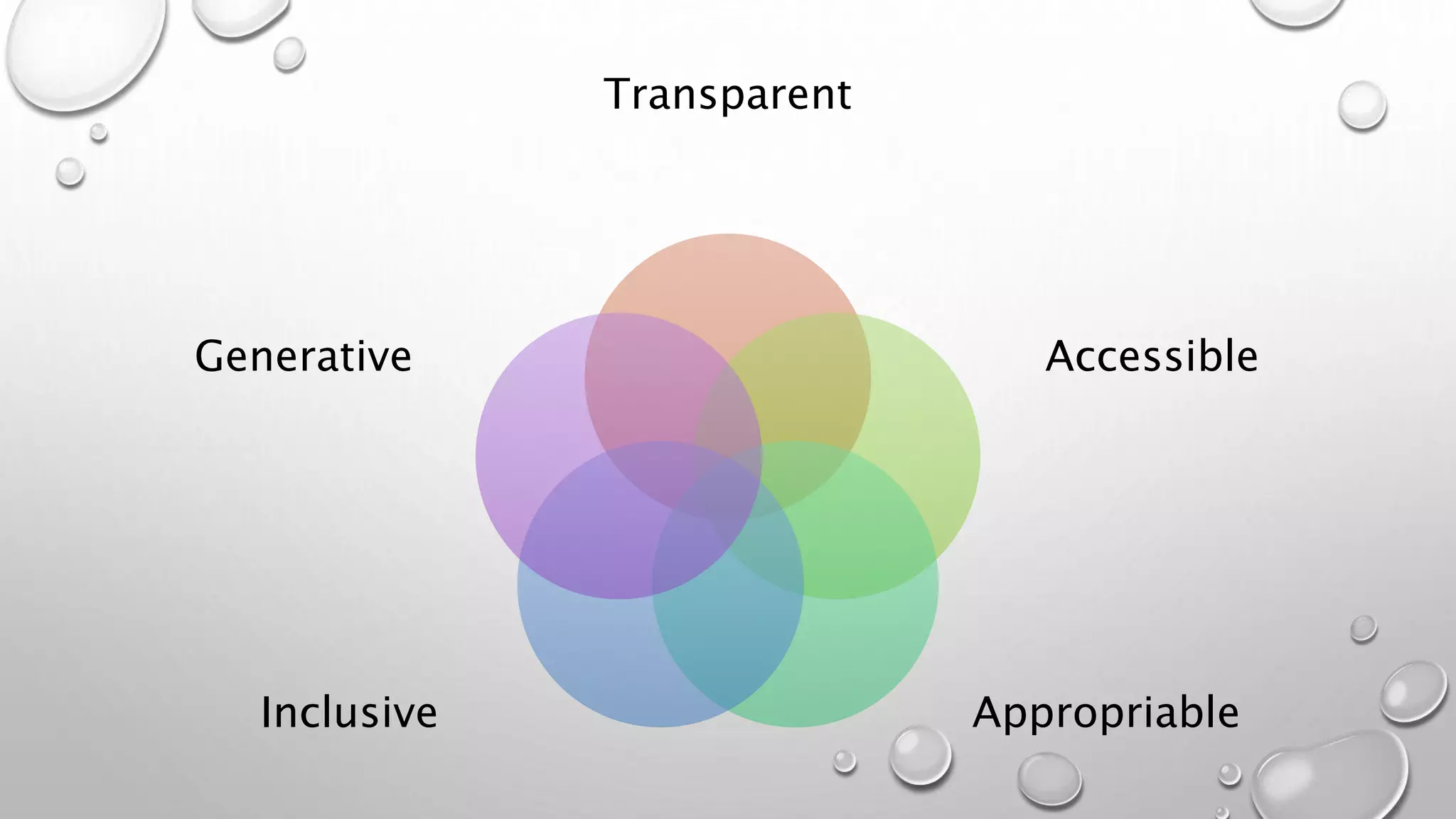
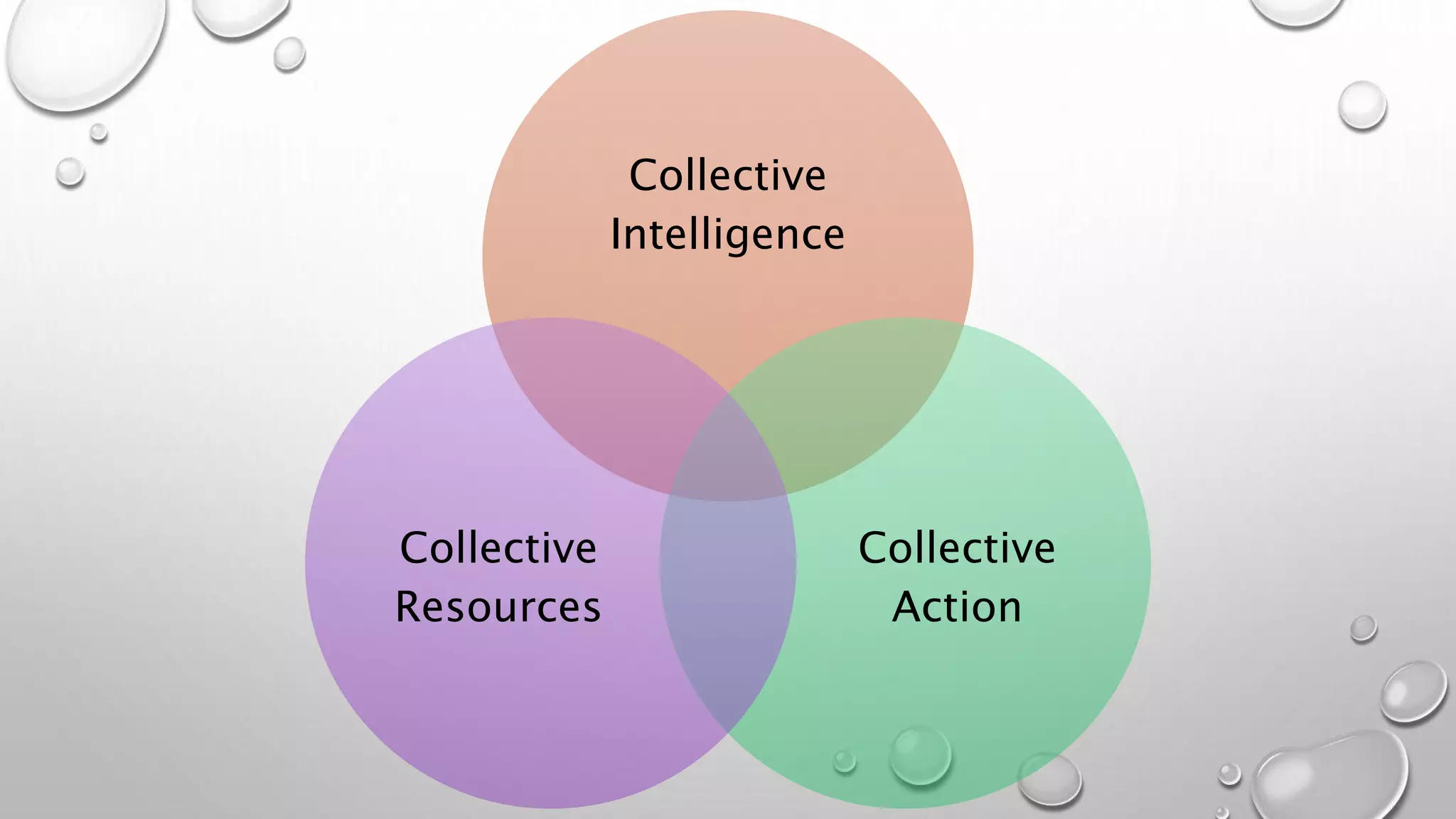
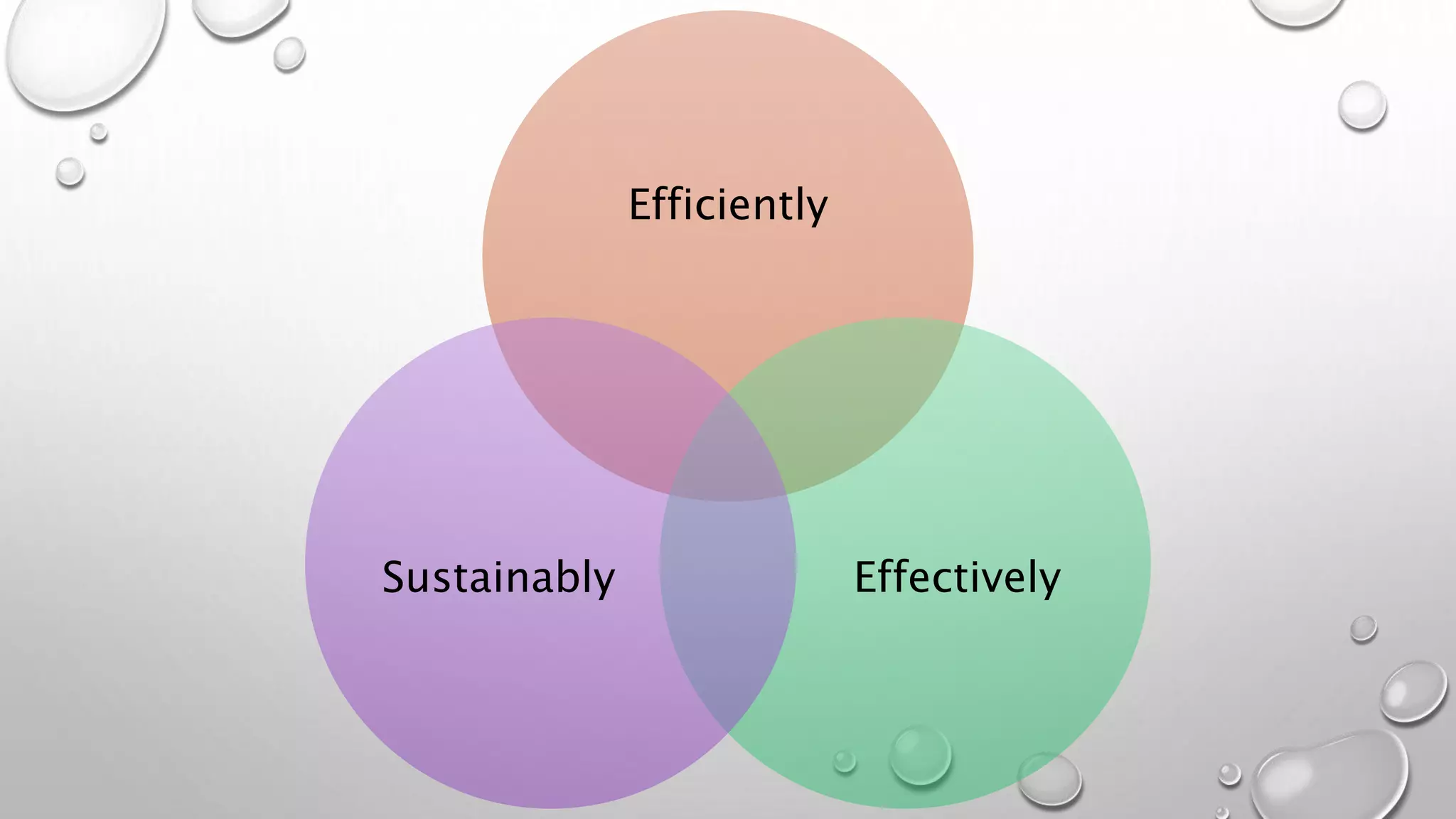
The document discusses the principles of open business models as influenced by open source software and innovation, emphasizing collaboration, co-creation, and sustainable business practices. It critiques traditional intellectual property rights for focusing on value capture rather than value creation and suggests a shift toward next-generation IP models that support community and ecosystem-based industries. The open business model canvas is introduced as a tool to analyze key partners, activities, resources, and customer relationships in creating value while promoting social good.