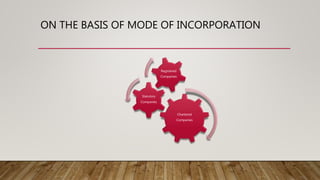
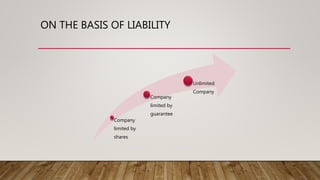
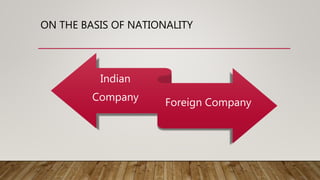
A joint stock company is a profit-driven, voluntary association of individuals with capital divided into transferable shares, characterized by legal independence and limited liability. It has various types based on nationality, membership, and liability, offering merits such as perpetual existence and large fund access while also facing demerits like complex formation and limited personal connection. In contrast, cooperatives are member-owned organizations focused on mutual benefit with features like equal voting rights and service motives, also presenting merits such as easy formation and democratic control.