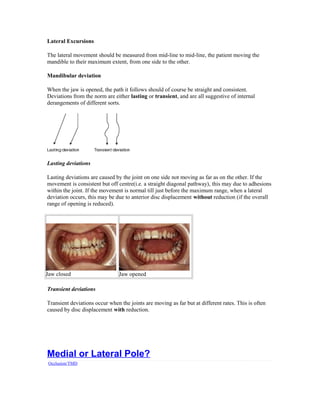
There are two types of joint sounds: clicks and crepitus. Clicks are single explosive noises that likely represent sudden distraction of wet surfaces, indicating disc displacement. Crepitus is a continuous grating noise caused by worn joint surfaces, common in degenerative joint disease. Determining if a click occurs during rotation or translation helps locate whether the disc is displaced medially or laterally. The temporomandibular joint rotates during the first half inch of opening and translates thereafter, so noises during rotation indicate medial disc displacement, while noises after translation begins indicate lateral displacement. Doppler auscultation allows differentiation between rotational and translational noises to accurately locate the site of disc displacement.