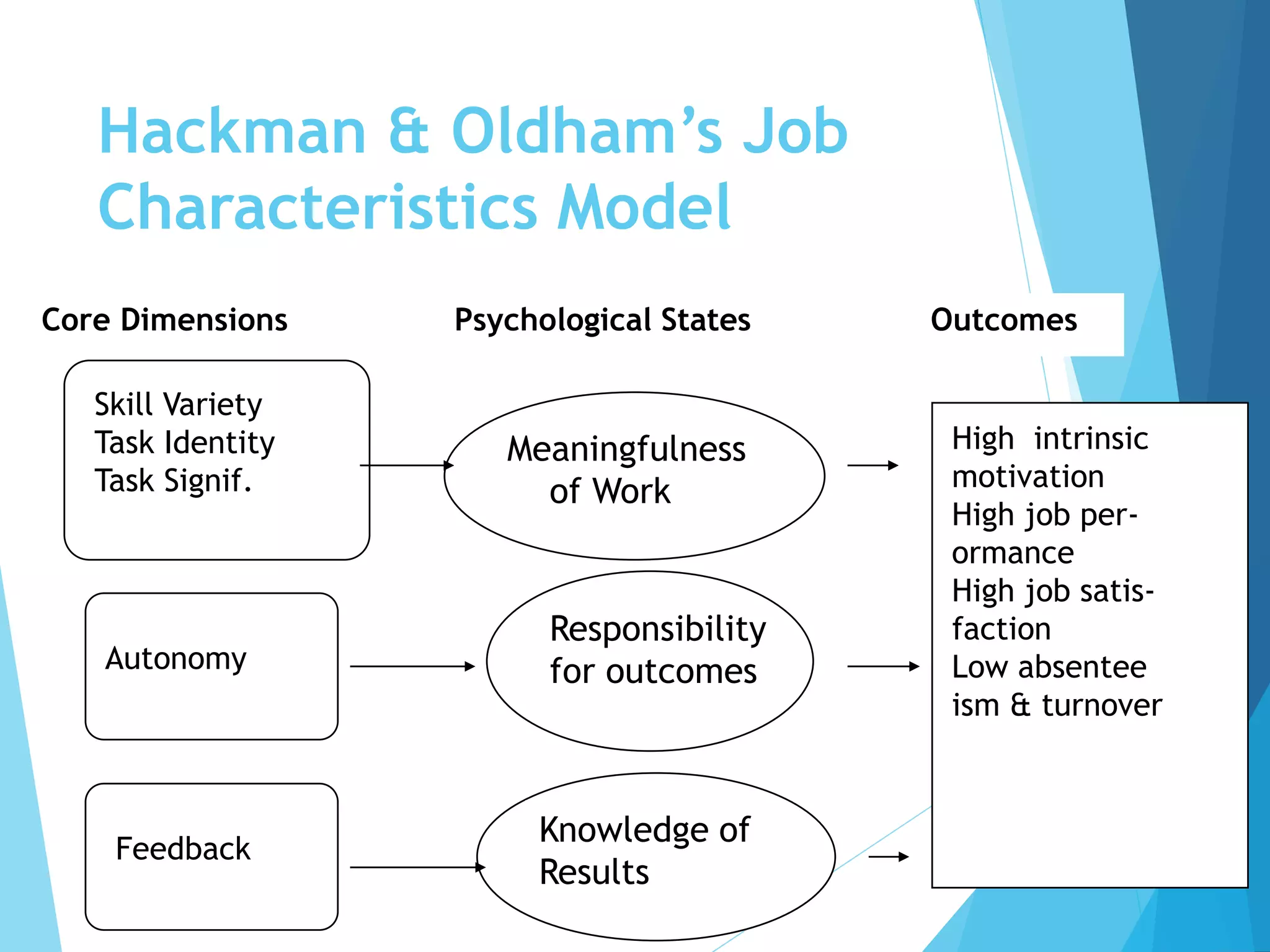
The document discusses job design and redesign. It defines job redesign as restructuring job elements like tasks and responsibilities to make jobs more motivating. A job redesign process typically involves clarifying current vs past roles, assessing employee skills, reallocating tasks, providing training, and revisiting changes. Reasons for redesign include enhancing work quality and satisfaction. Methods discussed include job enrichment, enlargement, rotation, teams, and work-life balance policies. The Job Characteristics Model links job design dimensions like autonomy and feedback to outcomes like motivation and satisfaction.