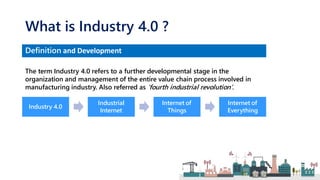
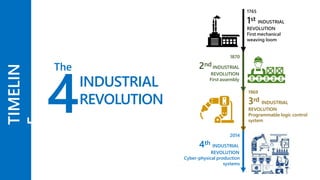
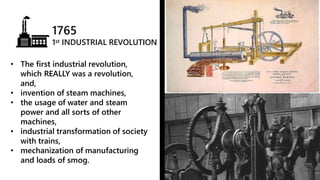
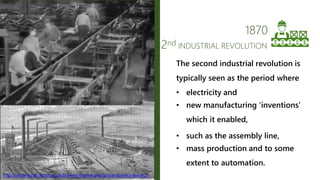
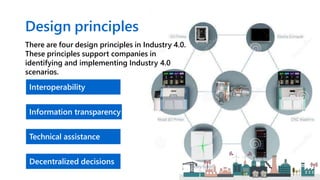
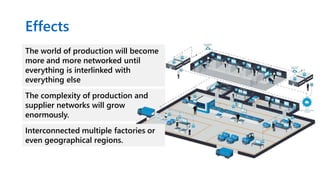
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution characterized by cyber-physical production systems. It builds on previous industrial revolutions driven by steam, electricity, and computers by introducing cyber-physical systems and the internet of things into manufacturing. Key technologies enabling Industry 4.0 include advanced robotics, artificial intelligence, the internet of things, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. While Industry 4.0 promises benefits like increased productivity and flexibility, it also faces challenges around skills, job disruption, security, and unclear economic benefits.