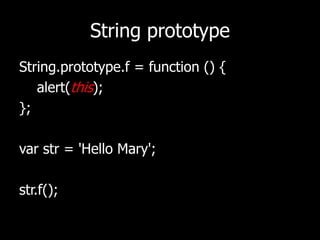
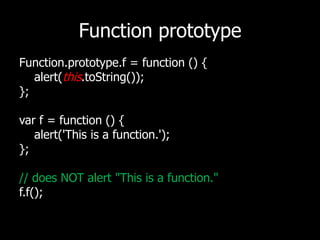
This document discusses JavaScript functions and related concepts. It defines functions, classes, and methods. It shows how functions can take arguments, be passed as callbacks, return other functions, and create closures. Classes can be defined using functions with the new keyword or by adding to prototypes. Built-in types like Number, String, and Array can be constructed or assigned directly. Functions are first-class objects that can be assigned and passed around.

![Define a functionfunction f(msg) {alert(msg);}// overridefunction f(msg1, msg2) {alert(msg1 + ' ' + msg2);}// arguments keywordfunction f() { for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i ++ ) { alert(arguments[i]);}}// callf();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-function-111013013116-phpapp02/85/Javascript-Function-2-320.jpg)

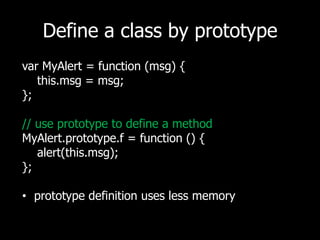
![Built-in typesNumbervarnum = new Number(2); or varnum= 2; Objectvarobj = new Object(); or varobj = {}; Arrayvararr = new Array(1, 2, 3); or vararr = [1, 2, 3];Stringvarstr = new String('Hello'); or varstr = 'Hello';Regular expressionvar regex = new RegExp('\s*'); or varregex = /\s*/;etc... - w3schools.com/js](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js-function-111013013116-phpapp02/85/Javascript-Function-5-320.jpg)