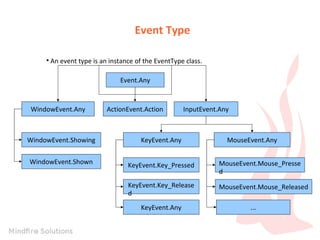
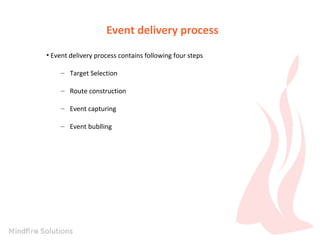
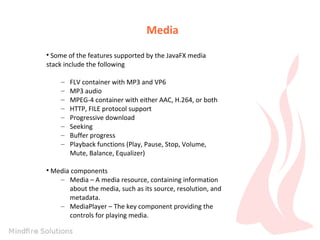
The document is an introduction to JavaFX by Prem Chand Mali, outlining his qualifications and skills in Java programming, web technologies, and event handling. It describes key concepts of JavaFX, including event handling, properties and bindings, webview capabilities, media playback support, and shape drawing. Additionally, it provides examples of event handling on shapes and the underlying event delivery process.