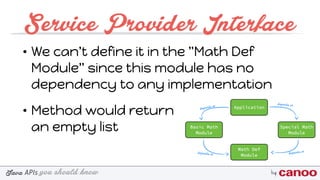
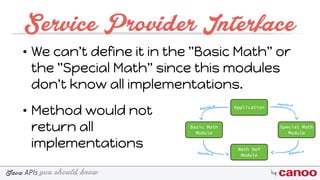
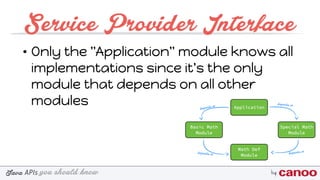
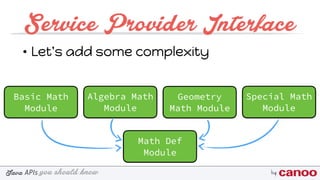
The document discusses various Java APIs and best practices for handling null values, particularly NullPointerExceptions (NPEs). It covers methods for preventing NPEs, using the Optional class in Java 8, and implementing a Service Provider Interface (SPI) for modular application design. Additionally, it explains the creation and utilization of custom annotations in Java programming.






















































![you should knowJava byAPIs
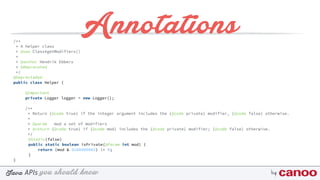
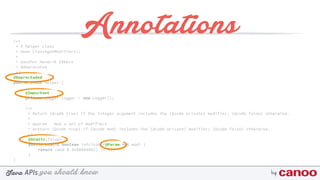
Annotations
• TYPE
• FIELD
• METHOD
• PARAMETER
• CONSTRUCTOR
• LOCAL_VARIABLE
• ANNOTATION_TYPE
• PACKAGE
• TYPE_PARAMETER
• TYPE_USE[ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaapisyoushouldknow-170419062346/85/Java-ap-is-you-should-know-76-320.jpg)

















