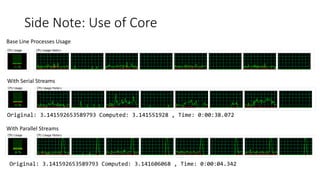
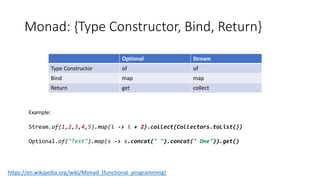
The document discusses Java 8 features such as monads, generics, and streams, showcasing examples of typed containers, optional handling, and stream operations. It provides practical use cases for encoding passwords and computing pi using random numbers and parallel streams. The content also includes exercises on writing methods employing monad patterns and encourages further study of related design patterns and concepts.





![Use Cases of Stream: Intro
There many Stream type constructors
• Directly from Stream class
Stream.of(T…t)
• From Collections
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.stream();
• Primitive Streams
• IntStream
• IntStream interator
IntStream.iterate(1, i -> i++).limit(100) [ for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) ]
• Random IntStream
ThreadLocalRandom.current().ints()
• LongStream (similar to intstream)
• Buffered Reader
• new BufferedReader(new FileReader("input.txt")).lines();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java8-monads-180531135418/85/Java-8-monads-7-320.jpg)